6.1 Fitness Test : SAI Khelo India Fitness Test in School
Fitness is the ability to perform physical activity, and encompasses a wide range of abilities.
- It is divided into specific fitness categories and components, which can be tested and trained individually.
- Khelo India Fitness Assessment App and School Dashboard on School Interface can help you do the Fitness Test Administration in your school more effectively.
Motor development : Motor development means the development of child’s bones, muscles and the ability to move around. They learn to sit, walk, stand and run. It is the study of changes in movement behaviour.
BATTERY OF TESTS : (Age Group 5-8 Years | Class 1 to 3 At Primary class 1-3)
- Children should acquire Fundamental Movement Skills (FMS) to build the building blocks for many physical activities, such as playing games, dance, and sport.
- Locomotor, Manipulative and Body Management abilities are key to success in most sports and physical activities.
- Abilities of children in class 1-3 which need to be measured and tracked are :
- Body Composition (BMI)
- Coordination (Plate Tapping)
- Balance (Flamingo Balance)
Which are important for controlling the body in various situations
(Age Group 9-18+ Years | Class 4 to 12 For Class 4 to 12)
It is important for students to have an overall physical fitness. The following Components are to be considered in Physical Health and Fitness Profile:
- Body Composition (BMI)
- Strength :
- Abdominal (Partial Curl-up)
- Muscular Endurance (Push Ups for Boys, Modified Push Ups for Girls)
- Flexibility (Sit and Reach Test)
- Cardiovascular Endurance (600 Meter Run/Walk)
- Speed (50 mt. Dash)
Items of Motor Fitness Test :
- 50 m standing start
- 600 yard run-walk
- Sit and reach test
- 4 × 10 m shuttle run
- Standing long/broad jump
- Pushups (Boys)/modified Pushups (Girls)
- Partial curl up.
How AAHPER youth fitness test is administered : Administered of AAHPER Motor Fitness Test. The test was administered on school students of 17 ages.
Pull up for boys : To measure arm and shoulder strength. This test measures the total number of repetitions performed without taking rest on a horizontal bar.
Flexed arm hang for girls : To measure arm and shoulder strength : The test is administered on a adjustable horizontal bar.
Sit-up : To measure abdominal strength and endurance. The total number of repetitions of sit-ups is noted in one minute only.
Shuttle run : To measure agility and speed. The subject starts race behind the other line. The best of two trials will be noted.
Standing long jump : To measure power. The best distance will be taken out of three trials.
50 m dash : To measure speed.
6.1.1 BODY MASS INDEX (BMI)
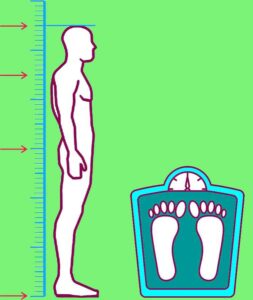
Purpose : Body Composition refers primarily to the distribution of muscle and fat in the body. Body size such as height, lengths and girths are also grouped under this component.
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Flat and Clean surface, Weighing Machine, Stadiometer/Measuring Tape pasted on a wall
Procedure : Measuring Height Accurately
- Take a height measurement on flooring that is not carpeted and against a flat surface such as a wall with no moulding.
- Remove shoes, bulky clothing, and hair ornaments, and unbraid hair that interferes with the measurement.
- Have the participant stand with feet flat, together, and back against the wall.
- Make sure legs are straight, arms are at sides, and shoulders are level.
- Take the measurement while the participant stands with head, shoulders, buttocks, and heels touching the flat surface (wall).Use a flat headpiece to form a right angle with the wall and lower the headpiece until it firmly touches the crown of the head.
- Lightly mark where the bottom of the headpiece meets the wall and use a metal tape to measure from the base on the floor to the marked measurement on the wall to get the height measurement.
- Accurately record the height to the nearest 0.1 centimeter.
Procedure : Measuring Weight Accurately
- Participants should use a digital scale instead of carpet.
- Have the participant stand with both feet in the center of the scale to remove shoes and heavy clothing.
- Record the weight to the nearest decimal fraction.
Scoring : Body Mass Index (BMI) is a test performed to measure body weight and height. It is calculated from body Weight (W) and height (H),
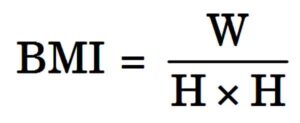
[Where, W = body weight in kilograms and, H = height in meters]
Height recorded in cm and mm is recorded in kilogram (kg) and grams (gms).
The weight is recorded to the nearest decimal fraction and the height is accurately recorded at 0.1 centimeter.
6.1.2 PLATE TAPPING TEST
Purpose : Tests speed and coordination of limb movement.
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Table (adjustable height), 2 yellow discs (20 cm diameter), rectangle (30 x 20 cm), and stopwatch.
Procedure :
- The table height should be adjusted so that the subject is standing comfortably in front of the discs.
- The two yellow discs are placed 60 cm apart and the rectangle is placed equidistant between them.
- The subject moves the preferred hand back and forth between the discs over the hand in the middle as quickly as possible.
- This action is repeated for 25 full cycles (50 taps).
Scoring : The time taken to complete 25 cycles is recorded

6.1.3 FLAMINGO BALANCE TEST
Static balance (Flamingo Balance Test) :
What does it measure : Ability to balance successfully on a single leg. This single leg balance test assesses the strength of the leg, pelvic and trunk muscle as well as static balance.
Infrastructure/Equipment required : No slippery even surface, stopwatch, can be done by just standing on a beam.
How to perform : Stand on the beam. Keep balance by holding the instructor’s hand (if required to start).
While balancing on the preferred leg, the free leg is flexed at the knee and the foot of this leg held close to the buttocks.
Start the watch as the instructor lets go of the participant/subject.
Pause the stopwatch each time the subject loses balance (either by falling off the beam or letting go of the foot being held).
Resume over, again timing until they lose balance. Count the number of falls in 60 seconds of balancing.
If there are more than 15 falls in the first 30 seconds, the test is terminated.
Administrative suggestion : Participants should be encouraged to focus eyes on stationary objects straight ahead.
Suggested physical activities to improve balance (Flamingo Test) : To improve balance, you should practice one foot balance, walking on toes and heel toe walking, walking on straight lines, skipping, hopping, vrikshasana, walking on beam etc.
Scoring : The total number of falls or loss of balance in 60 seconds of balancing is recorded.
If there are more than 15 falls in the first 30 seconds, the test is terminated.
6.1.4 AGE GROUP : 9-18+ YEARS | CLASS 4 TO 12
For Class 4 to 12, it is important for students to have an overall physical fitness. The following Components are to be considered in Physical Health and Fitness Profile :
- Body Composition (BMI)
- Strength
- (a) Abdominal (Partial Curl-up)
- (b) Muscular Endurance (Push Ups for Boys, Modified Push Ups for Girls)
- Flexibility (Sit and Reach Test)
- Cardiovascular Endurance (600 Meter Run/Walk)
- Speed (50 mt. Dash)
6.1.5 TEST TO MEASURE AGILITY
Test to measure agility : 4 × 10 m shuttle run.
Procedure : Two lines are drawn parallel to each other with a distance of 10 mts. in between. The subject is required to stand behind one line and two blocks are kept behind the line on the other end.
On the signal ‘Ready’ ‘Go’ subjects should run to pick up one block, run back to the starting line and place the block at the line. He should again run back to pick up the second block and bring it also to the starting line. Two successful trials are given.
Scoring : The best time of the 2 trials to the nearest 10th of a second is the score of the subject.
6.1.6 ABDOMINAL (PARTIAL CURL-UP)
Purpose : The curl up test measures abdominal muscular strength and endurance of the abdominals and hip flexors, important in back support and core stability
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Flat clean cushioned surface with two parallel strips (6 inches apart), Stopwatch, Recording sheets andpen.
Procedure :
- The subject lies on a cushioned, flat surface with knees flexed and hands straight on the sides, parallel to the ground.
- The subject raises the trunk in a smooth motion, keeping the arms in position, curling up the desired amount (at least 6 inches above/along the ground).
- The trunk is lowered back to the floor so that the shoulder blades or upper back touch the floor.
Scoring : Record the maximum number of Curl ups in a certain time period (30 seconds).
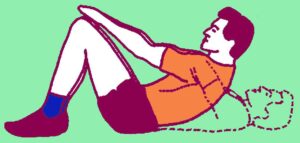
6.1.7 PUSH UPS (BOYS)/MODIFIED PUSH UPS (GIRLS)
Purpose : Upper body strength endurance, and trunk stability.
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Flat clean cushioned surface/Gym mat
Procedure :
- A standard push up begins with the hands and toes touching the floor, the body and legs in a straight line, feet slightly apart, and the arms at shoulder width apart.
- Keeping the back and knees straight, the subject lowers the body to a predetermined point, or until there is a 90-degree angle at the elbows, then returns back to the starting position with the arms extended.
- The test continues until exhaustion, or until they can do no more in rhythm or have reached the target number of push-ups.
- For Girls, push-up technique is with the knees resting on the ground.
Scoring : Record the number of correctly completed pushups.
6.1.8 SIT AND REACH
Method of sit and reach test : The subject is advised to sit on the edge of the chair. One foot is kept at the floor while the other leg is extended with knee straight. The subject must keep the back straight and head up. The subject has to touch the toe with fingertips. If the fingertips do not touch than the distance in between fingertips and is measured and the score will be negative.
Purpose : This test measures the flexibility of the lower back and hamstring muscles, which is important because tightness in this area is linked to lumbar lordosis, forward pelvic tilt and lower back pain.
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Sit and Reach box with the following dimensions: 12” x 12” (sides) 12” x 10” (front and back) 12” x 21” (top). Inscribe the top panel with centimeter/mm gradations. It is crucial that the vertical plane against which the subject’s feet will be placed is exactly at the 23 cm mark. Flat clean cushioned surface/Gym Mats
Procedure :
- This test involves sitting on the floor with legs stretched out straight ahead.
- The soles of the feet are placed flat against the Sit and Reach box.
- Both knees should be locked and pressed flat to the floor – the tester may assist by holding them down.
- With the palms facing downwards, and hands on top of each other, the subject reaches forward along the measuring line as far as possible.
- After some practice reaches, the subject reaches out and holds that position for at one-two seconds while the distance is recorded.
Scoring : The score is recorded (difference between initial position and final position), in cm and mm, as the distance reached by the hand.
6.1.9 600 MTR RUN/WALK
Purpose : Cardiovascular Fitness/Cardiovascular Endurance
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Stopwatch, whistle, marker cone, lime powder, measuring tape, 200 or 400 mts with 1.22 mt (minimum 1 mt) width preferably on a flat and even playground with a marking of starting and finish line.
Procedure :
- Participants are instructed to run 600 mts. at the fastest possible pace.
- The participants begin on signal, “ready, start”.
- As they cross the finish line, the elapsed time should be announced to the participants.
- Walking is permitted but the objective is to cover the distance in the shortest possible time.
Scoring : Time taken for completion (Run or Walk) in min and sec.
6.1.10 50 MTR DASH (STANDING START)
Purpose : Determines acceleration and speed
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Measuring tape or marked track, stopwatch, cone markers, flat and clear surface of at least 60 metres.
Procedure :
- A thorough warm up should be given, including practice starts and accelerations.
- Start from a stationary position with one foot in front of the other and the front foot on or behind the starting line.
- The tester should provide hints for maximizing speed and encourage running hard through the finish line.
Scoring : Time taken for completion
Important Terms : ———————————————————–
General Instructions before Exercise/Testing
Clothes : Students should wear comfortable, loose fitting sportswear during the test.
Food : Students should take food at least three hours before testing. Plenty of fluids should be taken 24 hours before testing. Alcohol and caffeine should be avoided 24 hours before testing.
Rest : Students should take proper rest and sleep on the night of testing. Any strenuous exercise should be avoided on the day of tests.
Warming up and cooling down : Students should do proper warm up and cooling down exercises before and after the testing respectively.
Equipment : Equipment should be calibrated, organized, sterilized and tested before the test.
Administration : Temperature should not be too hot, cold, or humid. All stationary item should be ready before the test.
———————————————————–————————–
6.2 Measurement of Cardio-Vascular Fitness
Rockport 1 mile walk Test : Rockport 1 mile test is a test for measuring cardio-respiratory fitness. The objective of this test is to check/observe the development of the individual’s VO2 max. i.e., maximum volume of oxygen.
Purpose : The purpose of this test is to measure cardio-vascular fitness or VO2 max (maximum volume of oxygen). The objective of the test is to walk as fast as possible for 1 mile.
Equipment required : Stop watch, weighing scale and track.
Procedure : The test is organised on a track/open area marked for this purpose.
- Body weight of the subject is recorded.
- Then the subject is made to walk a distance of 1 mile.
- Time is recorded when the subject crosses the finish line.
- Immediately after finishing the walk, the pulse rate of the subject is recorded for
10 seconds. - VO2 max score can be calculated using the formula.
Calculation : Using this data cardiovascular endurance is calculated.


1. What is the formula for computation of the Fitness Index ? (6.2) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans.

2. How many times is the reading taken for calculating a long term fitness index? (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 4
Ans. (b) 3
3. What will be the fitness index score of a girl if the test duration was 300 sec and the pulse count (1 min – 1.5 min) was 80. (6.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 73.2
(b) 62.8
(c) 68.1
(d) 85.3
Ans. (c) 68.1
Given that,
test duration in seconds = 300
pulse count (1 min – 1.5 min) = 80
Give formula :

Harvard Step Test : Harvard Step Test was developed by Brouha in 1943. It measures the cardiovascular fitness or aerobic fitness by checking the recovery pulse rate. In this test an athlete stands in front of a box or bench which is 16 inches (female) to 20 inches (male) in height and steps up and down for 5 minutes at a rate of 30 steps/minute. The pulse rate is counted 1-1½ minutes, 2-2½ minutes and 3-3½ minutes immediately after the test is administrated.
The fitness Index score is calculated by a simple formula :
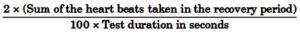
Cardiovascular fitness is the ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscle tissues and the ability of the muscles to use oxygen to produce energy for movements. Harvard Step Test is a cardiovascular fitness test. It is also called aerobic fitness test.
Administrative procedure of Harvard Step Test :
Purpose : To measure the general capacity of the heart and circulatory system for measurement of cardiovascular efficiency.
Time Allotment : 5 minutes
Facilities and Equipment : A stop watch, A bench or box 20 for male or 16 for female, partners, stethoscope, metronome, score sheet.
Procedure : The athlete stands in front of the bench or box. On the command ‘Go’ the athlete steps up and down on the bench or box at a rate of 30 steps per minute (one second up one second down) for 5 minutes (150 steps). Stopwatch is also started simultaneously at the start of the stepping. After that the athlete sits down immediately after completion of the test i.e., after 5 minutes. The total number of heartbeats are counted between 1 to 1.5 minutes after completion of the last step. The heartbeats are counted for 30 seconds period. Again the heartbeats are noted for 30 seconds after the finishing of the test. After that third time the heartbeats are noted after 3 minutes of completion of the test for 30 seconds period. The same foot must start the step up each time, and an erect posture must be assumed on the bench.
Administration Procedure : (1) A tester gives a demonstration of the stepping-up style to be followed by the subjects during the test.
(2) After the command ‘Go’ the stop watch is started and athlete steps-up and down for five minute at the rate of 30 steps per minute.
(3) The stop watch is stopped after 5 minutes and athlete is asked to stop.
(4) The heart-rate is measured between 1 to 1.5 minutes, after finishing the exercise.
(5) The same is repeated after 2 to 2.5 minutes and 3 to 3.5 minutes.
The pulse of all the 3 half minute counts are recorded together and computed in the fitness index.
Calculation of the Score : The athlete’s fitness index score is calculated with the help of following formula :
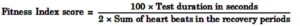
6.3 Computing Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
The Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories burned by the body while performing basic life sustaining functions, essential for maintaining body function and resting condition.
Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy a person requires to maintain their internal organs, even when they do not work.
Unit of BMR is calculated in Kcal.
There are factors that may affect BMR like Muscle Mass, age, state of mind, Gender, Genetics, Body composition etc. Environment changes like change in heat and cold may change the requirement of the body.
Purpose : determine Basal Metabolic Rate
Equipment : Stadiometer, Weight machine, Pen and paper
Procedure : method to measure height and weight is given at BMI
Formula used : The mifflin-St Jeor BMR Equation
Male calculation = (10 * weight(kg.)) + (6.25 * height(cm)) – (5 * age) + 5
Female calculation = (10 * body weight(kg.)) + (6.25 * height(cm)) – (5 * age) – 161

Name the tests used to calculate cardiovascular fitness. Write the formula for short term and long term fitness index and calculate long term fitness index if duration of exercise is 300 sec and sum of heart rate is 230. (6.2) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Rockport Walk Test (One Mile Test) The formula used to calculate VO2 max is :
132.853 – (0.0769 × weight) – (0.3877 × age) + (6.315 × gender) – (3.2649 × time) – (0.1565 × Heart Rate)
Ans. 65.2
6.4 Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test
The senior citizen’s fitness test (SFT) was developed by Rikli and Jones to evaluate functional ability and monitor physical fitness status of older people aged between 60 to 94 years. It should not be practiced by those with any medical conditions like chest pain, dizziness, high blood pressure, heart problems etc, and is economical and easy to administer.
Senior Citizen Fitness Test – Test items of Rikli and Jones :
(1) Chair Stand Test for Lower Body Strength
(2) Arm Curl Test for Upper Body Strength
(3) Chair Sit and Reach Test for Lower Body Flexibility
(4) Back Stretch Test for Upper Body Flexibility
(5) Eight Foot Up and GoTest for Agility
(6) Six Minute Walk Test for Aerobic Endurance
(7) Minutes Step Test
Importance of Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test :
Fitness in Older Adults : Functional fitness test assesses the physiologic capacity of old person to perform normal everyday activities safely and independently without undue fatigue. Importance of assessing the functional fitness of older adults include the following :
Identification of at-risk participants : Early identification of physical decline and appropriate interventions could help to prevent functional impairments, such as in walking and stair climbing, that often result in falls and physical frailty.
Programme planning and evaluation : To plan safe and effective exercise or physical activity programmes for older adults, it is important to know as much as possible about the client’s health and fitness status, current physical activity level, activities likes and dislikes, and personal goals.
Goal setting and motivation of participants : Assessing the functional fitness levels of participants is a precursor to helping them set worthwhile short-term and long-term personal goals.
6.4.1 30 SECOND CHAIR STAND TEST
Purpose : To determine lower body strength.
Objective : To complete maximum stands in 30 seconds.
Equipment : Straight back chair without arms and stopwatch.
Procedure :
- The chair should be placed against the wall or somewhere where it can be stabilized.
- Individuals should sit on the chair with back straight, arms crossed and feet firmly on floor, shoulder width apart.
- The person will completely stand up upon hearing the word “Go,” then return to their starting posture. This will count as one stand. The person should be motivated to perform as many stands as possible in 30 seconds.
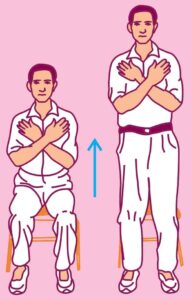
Scoring : Maximum number of complete stands will be counted as score. If the individual is in half way of the stand and time is over, then it will be counted as a full stand.
Risk zone : Less than 8 unassisted stands for men and women.
6.4.2 ARM CURL TEST
Purpose : To determine upper body strength.
Objective : To complete maximum arm curls in 30 seconds.
Equipment : Straight back chair without arms; Dumbbell for men–8 pounds (3.6kgs) and women–5 pounds (2.3kgs) and stopwatch.
Procedure :
- The chair should be placed against the wall or somewhere where it gets stabilized.
- The individual sits on the chair with back straight, feet on floor, holing dumbbell with dominant hand using handshake grip.
- On the command “Go” the individual flexes the elbow or curls the arm with full range of motion then returns back to its initial position.
- In the down position dumbbell will return to handshake grip.
- The individual can perform as many arm curls as possible in 30 seconds.
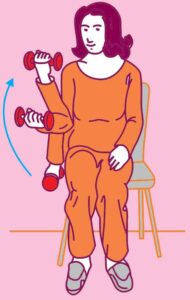
Scoring : Maximum number of correct arm curls in 30 second will be counted.
Risk zone : Less than 11 curls using correct form for men and women.
6.4.3 CHAIR SIT AND REACH TEST
Purpose : To determine lower body flexibility.
Objective : To stretch the lower body as far as possible.
Equipment : Straight back chair without arms; 18 inches ruler.
Procedure :
- he chair should be placed against the wall or where it is stabilized.
- Participant sits on a chair with one foot flat on the ground and the other leg extended forward, knee straight, heel uncorrected, and ankle bent at 90°.
- Participant attempts to touch toe of their foot by bending and sliding hands towards the toes.
- Participant must hold a certain position for 2 seconds to clock score.

Scoring : Measurement will be taken between extended long finger and tip of the toe and minimum to .5 inches will be recorded as score. If fingers cross the toe, then + will be indicated before the score and if the participant is unable to touch the toe, then – sign will be indicated.
Risk zone : Men : Minus (–) 4 inches or more. Women : Minus (–) 2 inches or more.
6.4.4 BACK STRETCH
Purpose : To determine upper body flexibility
Objective : To touch or overlap the finger of the both hands behind the back.
Equipment : 18 inches ruler
Procedure : In standing position participant will place one hand over the shoulder and one hand middle of the back and try to touch or overlap each other.

Scoring : Measurement will be taken by measuring the distance between the tips of the middle fingers. If the fingertips touch, then the score is zero. If they do not touch, measure the distance between the finger tips (a negative score), if they overlap, measure by how much (a positive score).
Risk zone : Men : Minus (–) 4 inches or more. Women : Minus (–) 2 inches or more.
6.4.5 FOOT UP AND GO
Eight foot up and go test for agility :
Purpose : This test helps to evaluate speed, agility and dynamic balance
Equipment required : A chair about 44 inch high, a stop watch, cone, marker, measuring tape, and an area without any hindrance.
Procedure : Place the chair next to a wall (for safety) and the marker 8 feet away in front of the chair. Clear the path between the chair and the marker. The subject starts fully seated, hands resting on the knees and feet flat on the ground. On the command, ‘Go’ stop watch is started and the subject stands and walks (no running) as quickly as possible (and safely) to and around the cone, returning to the chair to sit down. Timing stops as they sit down. Two trials are given to each participant.
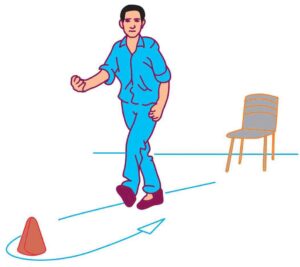
Scoring : Two attempts will be made and the best score will be taken for record. Fastest time taken between command “Go” and return to the chair will be recorded.
Risk zone : More than 9 seconds.
6.4.6 MINUTE WALK TEST
Purpose : To determine aerobic endurance.
(This test helps in early identification of participants at risk. The individuals health and fitness level can be known better with the help of this test or to check aerobic fitness/aerobic endurance of a person.)
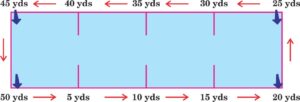
Equipments : A stop watch and measuring tape.
Procedure : The subject is asked to walk for six minute around the 50 yards dimensional area. The cones are placed at regular intervals to indicate distance covered. The maximum distance covered in six minutes. Measure the distance covered in six minutes to the nearest metre.
Objective : To walk maximum distance in 6 minutes.
Walking course in a rectangular area of 50 yards or 45.72 mts.

The person has to walk maximum distance as quickly as possible for six minutes. He/she may stop at any time if desires so.
The total distance covered in six minute is recorded to the nearest yards/meters.
Scoring : Maximum distance covered in 6 minutes will be recorded as score.
6.4.7 MINUTES STEP TEST
Purpose : To determine aerobic endurance.
Objective : To count maximum number of steps in 2 minutes. This test is performed as an alternative to the 6- minute walk test for people who use orthopaedic devices when walking, as well as in the case of people who have difficulty balancing.
Equipment : tape for marking the wall; stopwatch; wall.
Procedure : The participant up straight next to the wall while a mark is placed on the wall at the level corresponding to midway between the patella (knee cap) and illiac crest (top of the hip bone). The participant then marches in place for two minutes, lifting the knees to the height of the mark on the wall. Resting is allowed, and holding onto the wall or a stable chair is allowed. Stop after two minutes of stepping.

Scoring : The total number of times the right knee reaches the tape level in two minutes is recorded.
6.5 Johnson : Metheny Test of Motor Education
Objective : The Johnson-Metheny Test is a revised version of the Johnson Educability Test, designed in 1932 to measure neuromuscular skill capacity. In 1938, Methney eliminated six items.
The test battery consist of four motor stunts are given below :
- Front Roll
- Back Roll
- Jumping Half-Turns
- Jumping Full-Turns
Four stunts are to be performed by the boys and three stunts for girls.
Test Area : Mat area length is 15 feet and 2 feet wide, divided into ten sections for 18” each. Width of transverse line is ¾” and 3” alternatively, centre of lines 18” apart, and ¾” wide line marked lengthwise in the middle.
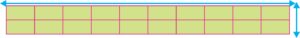
Procedure :
- Front Roll : Ignoring the long middle dividing line, the subject is asked to start outside the marked area and perform two front rolls, one up to 7.5’ i.e. 3” wide centre line and the second in the other half of 7.5’. The subject is to perform the rolls without touching the limits or over reaching the zones mentioned above.
- Scoring : Each correct roll gets 5 points, hence maximum of 10 points. Two points are deducted for over-reaching side line, right or left for each roll; one point is deducted for over reaching the end limit on each roll and full five points are deducted when the subject fails to perform a true front roll
- Back Roll : The test is similar to front roll both in performing and scoring. The subject is to start outside the marked chart area and is to ‘perform two back rolls in the 2 feet lane area, one up to first half and the second back roll in the second half.
- Jumping Half Turns : The subject is asked to start with feet on first 3” line, jump with both feet to second 3” wide line, executing a half turn either right or left; jump to third 3” line executing half turn in opposite direction to first half-turn and then to 4th and 5th 3” wide lines executing half turns, right or left alternatively.
- Scoring : Perfect execution of four jumps is worth ten points. Only 2 points are deducted for each wrong jump when the subject either does not land with both feet on the 3” line or turns the wrong way or both.
- Jumping Full Turns : The subject is asked to start with the feet outside the marked area at about the centre of the lane. He/She is required to jump with feet together to second rectangular space, executing a full turn with the body either right or left; continue jumping to alternate rectangular spaces across the marked mat executing full turns, rotating body in the same direction, landing on both feet every time.
- Scoring : Perfect execution of five jumps is worth ten points. Two points are deducted, if the subject fails to keep balance on landing on both feet; turns too far or oversteps the squares.