7.1 Physiological Factors Determining
the Component of Physical Fitness
Multiple Choice Questions
________ system provide energy during 5000 m race. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) ATP CP system
(b) Anaerobic system
(c) Aerobic system
(d) Endurance system
Slow twist fibres are of ________ colour. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Red
(b) White
(c) Black
(d) Blue
VO2 max is related to _________. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Muscular system
(b) Respiratory system
(c) Cardiovascular system
(d) Energy production system
Which is NOT a property of muscles? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Contractility
(b) Excitability
(c) Extensibility
(d) Durability
The amount of oxygen which can be absorbed and consumed by the working muscles from blood is called __________. (7.1) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) oxygen intake
(b) oxygen transport
(c) oxygen uptake
(d) energy reserve
Which one of these is a long term effect of exercise on cardiovascular system? (7.1) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Heart rate
(b) Body temperature
(c) Cardiac output
(d) BP
Physiological factor determining speed : (7.1) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Explosive strength
(b) Body weight
(c) Muscle composition
(d) Both (a) and (c)
The amount of oxygen which can be absorbed and consumed by the working muscles from the blood is called ________. (7.1) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) Oxygen uptake
(b) Oxygen intake
(c) Oxygen transport
(d) Vital capacity
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Suggest any two physiological factors determining ‘speed’ ? (7.1) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. • Muscle composition – fast twitch fibers
- Mobility of nervous system – reaction time
- Explosive strength
- Metabolic Reserve
- Bio-chemical Reserve
- Flexibility (Any two points)
What do you know about the term ‘cardiac output’ ? (7.3) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. • Cardiac output is the total volume of blood pumped by the heart in one minute.
• Cardiac output = Heart rate × Stroke volume (Any one)
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Point out physiological factor for strength. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The physiological factor for strength is the composition of muscle fibers in the skeletal muscles.
- The proportion of slow twitch fibers (Type I fibers) and fast twitch fibers (Type II fibers) in the muscles plays a dominant role in the development of strength.
- Different sports require different amounts of strength, and the mixture of slow twitch and fast twitch fibers needed varies accordingly.
Briefly describe the energy production system in our body. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The energy production system in our body consists of three main systems :
- The ATP-CP system provides energy for activities that last less than 10 seconds, such as jumps, throws, sprints, and weightlifting. It is a dynamic and intensive system.
- The anaerobic system provides energy for activities lasting less than two minutes, such as 200m and 400m races. It is used when the demand for energy is high but oxygen supply is limited.
- The aerobic system provides energy for long-duration activities like marathons, football, and hockey. It relies on oxygen and is used when the demand for energy is sustained over a longer period of time.
Explain different properties of muscles. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The different properties of muscles are :
- Contractility : Muscles have the ability to contract or shorten in length when stimulated by a nerve impulse.
- Excitability : Muscles are able to respond to stimuli, such as nerve impulses, by initiating a contraction.
- Extensibility : Muscles have the ability to stretch or lengthen without being damaged.
- Elasticity : Muscles have the ability to return to their original shape and length after being stretched or contracted.
Write a few points on cardiorespiratory factors determining fitness. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The cardiorespiratory factors that determine fitness include maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 Max), blood pressure, blood volume, oxygen diffusion and extraction, muscle and arterial blood flow, and the cardiovascular response to exercise.
- The demand for energy during exercise increases, and the respiratory and cardiovascular systems work to meet this demand by delivering oxygen in appropriate volumes.
- The intensity, duration, and type of activity also affect the demand for energy and the response of the cardiorespiratory system.
Write about Physiological Factors Determining Endurance? (7.1) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Physiological Factors Determining Endurance :
- Aerobic capacity : Activities for a certain length of time using energy derived from-oxygen intake- oxygen transport-oxygen uptake and energy resources.
- Lactic acid tolerance : Ability to tolerate higher concentration and removal of lactic acid.
- Muscle composition : Slow twitch and fast twitch muscle fibers determine the type of endurance activities.
- Movement economy : Saving energy through efficient movements is always an advantage in the endurance activities. (Any three points)
Explain in detail any three factors that affect physical fitness. (7.1) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Three factors that affect physical fitness in detail are :
Skeletal Muscle Composition :
- The proportion of these fibers in the muscles is determined by genetics, hormones, and exercise habits.
- The composition of muscle fibers plays a dominant role in the development of strength, endurance, and speed performance
Cardiovascular System :
- The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
- Regular cardiovascular exercise improves the efficiency of the cardiovascular system, leading to better endurance and overall physical fitness.
Metabolic System :
- The metabolic system is responsible for producing energy and regulating the intake and output of energy in the body.
- Regular exercise can improve the efficiency of the metabolic system, leading to better endurance and overall physical fitness.
What are the changes that take place in cardiovascular system by doing regular exercise? (7.1) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. Some of the changes that take place in the cardiovascular system by doing regular exercise include :
- Increased Heart Rate : Exercise makes the body work harder, which increases the demand for oxygen.
- Increased Blood Circulation : As the heart rate increases, blood circulation also increases.
- Increased Stroke Volume : Stroke volume refers to the volume of blood pumped during one heartbeat.
- Increased Cardiac Output : Cardiac output is the amount of blood pumped out by each ventricle of the heart in one minute.
- Increased Size and Strength of the Heart : Continuous aerobic exercise helps to increase the size and strength of the heart.
- Decreased Resting Heart Rate : Due to the improved efficiency of the heart, it is required to pump less blood to meet the needs of the body.
- Normal Blood Pressure : Regular exercise can lead to a substantial reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- Increased Capillary Network : Regular exercise leads to an increase in the capillary network.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Explain physiological factors determining fitness. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The physiological factors that determine fitness include skeletal muscles, cardiovascular system, metabolic system, respiratory system, nervous system, endocrine system, immune system, and neuroendocrine system.
- These systems work together during exercise, but their responses are independent.
- Each system plays a role in different components of fitness such as strength, endurance, speed, and flexibility.
- The composition of muscle fibers, the presence of oxidative enzymes and capillaries, and the ability to produce energy are some of the factors that determine fitness.
Define flexibility and explain methods to develop flexibility. (7.1) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. Flexibility refers to the ability of muscles and tendons to lengthen without getting damaged. It is an important component of physical fitness and is necessary for activities like stretching or yoga.
There are several methods to develop flexibility :
-
Stretching exercises : Performing static stretches where you hold a stretch for a certain period of time can help improve flexibility. Examples include hamstring stretches, quadriceps stretches, and shoulder stretches.
-
Dynamic stretching : This involves moving your body through a full range of motion to improve flexibility. Examples include arm circles, leg swings, and walking lunges.
-
Yoga : Practicing yoga poses and sequences can greatly improve flexibility. Yoga focuses on stretching and strengthening the muscles and tendons.
-
Pilates : Pilates exercises also help improve flexibility by targeting specific muscle groups and promoting lengthening and stretching.
-
Foam rolling : Using a foam roller to apply pressure to different muscle groups can help release tension and improve flexibility.
-
Regular physical activity : Engaging in activities like swimming, cycling, or dancing can also help improve flexibility over time.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Explain the physiological factors determining speed. (7.1) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. The physiological factors that determine speed are primarily related to the skeletal muscles and the cardiovascular system.
- In terms of skeletal muscles, the composition of muscle fibers plays a significant role in speed performance.
- Slow twitch fibers are more oxidative and have a higher concentration of capillaries, myoglobin, and mitochondrial enzymes.
- These characteristics promote aerobic activity and resistance against fatigue.
- On the other hand, fast twitch fibers have a higher capacity for anaerobic activity and produce quick bursts of energy.
- The proportion of slow twitch and fast twitch fibers in the muscles is influenced by genetics, hormones, and exercise habits.
- In sports that require speed, such as sprinting or power-based activities, a higher percentage of fast twitch fibers is needed.
- This allows for quick force production and rapid muscle contractions, leading to faster movement.
- Additionally, the cardiovascular system plays a crucial role in speed performance.
- The cardiovascular system controls circulation, transports oxygen and energy to the muscles, and removes waste products from the muscles.
- The stroke volume, which is the volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart during each systolic cardiac contraction, is an important parameter for speed.
- A higher stroke volume means that more oxygen and nutrients can be delivered to the muscles, allowing for increased energy production and better performance in speed-related activities.
What are the important functions of our skeletal system ? (7.1) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. The skeletal system has several important functions :
-
Support : The skeletal system provides structural support for the body, giving it shape and stability.
-
Protection : The bones of the skeletal system protect vital organs such as the brain, heart, and lungs. For example, the skull protects the brain, and the ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
-
Movement : The skeletal system works together with the muscular system to allow movement. Muscles attach to bones via tendons, and when the muscles contract, they pull on the bones, causing movement.
-
Blood Cell Production : The bone marrow, found inside certain bones, is responsible for the production of red and white blood cells and platelets.
-
Mineral Storage : The bones of the skeletal system store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, which are important for various bodily functions.
-
Endocrine Regulation : The bones also play a role in the regulation of hormones, such as osteocalcin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels and metabolism.
Explain any four physiological factors determining strength. What are the effects of regular exercise on the muscular system ? (7.1) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Four physiological factors determining strength are :
(1) Muscle size : More the muscle mass, more forceful contraction. Males tend to be stronger because of higher Muscle mass and larger size. Muscle size and strength can be improved by strength training.
(2) Body weight : Individuals who are heavier are generally stronger than individual who are lighter. There is positive correlation between body weight and strength. As in case of weightlifting it is seen that heavier weight lifters lift heavier weight. Therefore, body weight determines strength.
(3) Muscle composition : Each muscle consist of two types of muscle fibers, fast twitch fibers (white fibers) and slow twitch fibers (Red fibers). The fast twitch fibers are capable to contract faster and therefore produce more force, whereas slow twitch fibers are capable of contracting for a longer duration.
Therefore the muscles with more of fast twitch fibers can produce more strength. The percentage of slow and fast fibers is genetically determined and thus determines the strength of a person.
(4) Nerve impulse intensity : A muscle is composed of many motor units. The force of muscle depends on the number of contracting motor units. Whenever a stronger nerve impulse from central nervous system excites more motor units, the muscle will contract more strongly thus producing more force or strength.
Effect of regular exercise :
- Hypertrophy of muscle/change in shape and size of muscle
- Better posture
- Delayed fatigue
- Better reaction time
- Swifter muscle movement
- Better muscle tone
- Formation of more capillaries
- Control extra fat
- Change in connective tissue
- Non-functioning fibers become active
- Lactic acid tolerance (Explain any two relevant point)
What are the physiological factors that help a physical education teacher/coach in selection of a sports activity for a student ? (7.1) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The physiological factors that a physical education teacher/coach considers when selecting a sports activity for a student include :
-
Strength : The teacher/coach will assess the student’s strength levels to determine if they have the necessary muscle power and ability to work against resistance required for the sport.
-
Endurance : The teacher/coach will evaluate the student’s endurance capacity to determine if they can sustain physical activity for a prolonged period of time without fatigue.
-
Speed : The teacher/coach will consider the student’s speed capabilities to determine if they have the necessary quickness and agility required for the sport.
-
Flexibility : The teacher/coach will assess the student’s flexibility to determine if they have the necessary muscle and tendon lengthening ability required for the sport.
-
Cardiovascular fitness : The teacher/coach will evaluate the student’s cardiovascular fitness to determine if their heart and lungs can efficiently supply oxygen and energy to the muscles during physical activity.
-
Age and physiological changes : The teacher/coach will take into account the student’s age and any physiological changes that may occur due to growth and development, as these factors can affect the student’s physical capabilities and limitations.
What are the different types of body movements ? Explain. (7.1) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. ……………………………………
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. CARDIORESPIRATORY FACTOR : The Cardiorespiratory system is combination of respiratory and cardiovascular systems which jointly work to transport oxygen to the cells and support metabolism by delivering nutrients, which provide energy to neuromuscular system and neuroendocrine system. During exercise, the demand for energy increases and to meet the demand, oxygen is required in appropriate volume to achieve the same. Demand of energy depends on intensity, duration, and type of activity. To match the same, the respiratory system — pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, and internal respiration work together. The cardiovascular response to exercise is directly proportional to the demands of the skeletal muscles for Oxygen. Maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 Max), Blood pressure, blood volume, oxygen diffusion and extraction, muscle and arterial blood flow etc. simultaneously increase as per activity.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Flexibility : It is the ability of muscle and tendons to lengthen without getting damaged. Activities of stretching or yoga require a good deal of flexibility. Physiological factors like elasticity and extendibility of muscles, type of joint, homothermic temperature are key determinants of flexibility. Muscles, tendons, and ligaments are key components that affect flexibility. Muscles groups like agonists, antagonists, neutralizers, and stabilizers should be understood for training purpose. Agonists are the muscles which contract to perform a certain action. Antagonists are muscles which oppose the prime movers as they relax and lengthen progressively to allow agonists to move. Synergists are muscles that work together in a close cooperation as they either contract or relax to modify the action of the agonist. Synergists include Conjoint, Neutralizer and Stabilizer muscles.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Endurance : Endurance is the ability of the body to work for a longer period without getting fatigued. Endurance also varies from brisk walk to running to marathon. While in each activity intensity and duration varies, but one thing is common in all these activities: that is long duration and low fatigue activity. Activities like cycling, swimming or long duration activities come under endurance component. Slow twitch fibre percentage must be higher in comparison with fast twitch fibres to give better performance in endurance. Aerobic system provides energy in endurance training. Maximal oxygen consumption (Vo2), ventilation capacity plays dominating role in endurance training.
What ______
Ans. –
4. Strength : Strength is the ability of the body to work against resistance and has varied sub-types such as Maximum Strength, Explosive Strength, Strength, Endurance etc. Each has different types of exercise, intensity and duration so physiological factors vary. Different sports require different amount of strength and according to that, mixture of the slow twitch fibre and fast twitch fibre is needed. Generally in all the strength related sports where sudden burst of energy is required, high percentage of fast twitch fibre is required. In games like weightlifting, jumps, sprint or power, agility and strength dominating sports where force production is high, fatigue is quick, and fast twitch fibre percentage must be high in muscles.
What ______
Ans. –
7.2 Effect of Exercise on Muscular System
Multiple Choice Questions
Which is not a long term effects of exercise on muscular system? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Hypertrophy of muscle
(b) Increased metabolism
(c) Increased myoglobin
(d) Increased blood supply
Which is not a short term effects of exercise on muscular system? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Accumulation of lactate
(b) Micro-tears in muscle fibers
(c) Increase muscle temperature
(d) Increase in lactate acid tolerance
Physical activity helps to increase _______. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) size of muscle
(b) size of bone
(c) size of brain
(d) size of liver
Increase in glycogen stored in muscle is an effect of _________. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Aerobic training
(b) Anaerobic training
(c) Cross training
(d) Multi training
Overstretching of ligament cause : (7.2) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Strain
(b) Sprain
(c) Contusion
(d) Bruises
Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)
Explain the term hypertrophy of muscles. (7.2) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Hypertrophy of muscles refers to the increase in size or thickness of muscle fibers, resulting in an overall increase in muscle size. It is a long-term effect of scientific and systematic exercise.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Explain long term effects of exercise on muscular system. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The long term effects of exercise on the muscular system include :
- Hypertrophy of muscle : Regular exercise leads to an increase in the thickness of muscle fibers, resulting in an increase in muscle size.
- Increased strength of ligaments and tendons : Exercise helps to strengthen bones, ligaments, and tendons, which helps prevent injury and promotes performance.
- Increase in size and number of mitochondria : Aerobic exercises lead to an increase in the size and number of mitochondria, which take in more oxygen and produce more ATP and energy.
- Increase in myoglobin storage : Long term aerobic exercise increases the storage of myoglobin, which transports oxygen to mitochondria.
- Increase in glycogen storage : Regular exercise helps the body increase the storage of glycogen, which provides continuous energy for 90 to 120 minutes.
- Increase in oxidation/metabolism : Endurance exercise training increases the capacity of skeletal muscle fat oxidation by increasing mitochondrial density.
- Increase in lactate acid tolerance : Regular exercise helps the muscles tolerate pain and soreness due to the accumulation of lactic acid.
Explain short term effects of exercise on muscular system. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The short term effects of exercise on the muscular system include increased blood supply, increased muscle temperature, increased muscle flexibility, accumulation of lactate, micro tears in muscle fibers, increase in glycogen storage, increase in oxidation/metabolism, increase in lactate acid tolerance, and increase in myoglobin storage
List any four changes happening in the muscular system due to exercising. (7.2) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. Four changes that occur in the muscular system as a result of exercising are :
- Increased blood supply : During exercise, the concentration of blood increases in the muscles, providing more oxygen and nutrients to support muscle activity.
- Increased muscle temperature : Exercise generates heat energy, which increases the temperature of the muscles and the body.
- Increased muscle flexibility : The increase in blood flow and rise in temperature during exercise also increase the elasticity of muscles, leading to improved flexibility.
- Accumulation of lactate : If the blood supply does not provide enough oxygen to the muscles during exercise, it can result in the accumulation of lactate acid, causing muscle pain and soreness.
List down any four effects of exercise on the muscular system. (7.2) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Four effects of exercise on the muscular system are :
- Hypertrophy of muscle : Regular exercise leads to an increase in the thickness of muscle fibers, resulting in an increase in muscle size.
- Increase in strength of ligaments and tendons : Exercise helps to strengthen the connective tissues surrounding the muscles, which helps prevent injury and improves performance.
- Increase in size and number of mitochondria : Aerobic exercises increase the size and number of mitochondria in muscle cells, which improves the muscles’ ability to produce energy.
- Increase in myoglobin storage : Long-term aerobic exercise increases the storage of myoglobin, a protein that transports oxygen to the muscles, allowing for more oxygen and energy to be available during exercise.
Explain any three effects of exercise on the muscular system. (7.2) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Three effects of exercise on the muscular system are :
- Hypertrophy of Muscle : Regular exercise leads to an increase in the size and thickness of muscle fibers, resulting in muscle hypertrophy. Hypertrophy of muscles improves strength, power, and overall muscle function.
- Increase in Strength of Ligaments and Tendons : Regular exercise helps to strengthen the ligaments and tendons that connect muscles to bones. This increased strength helps to prevent injuries and improves overall stability and performance.
- Increase in Oxidation/Metabolism : Endurance exercises, such as running or cycling, increase the capacity of skeletal muscles to oxidize fat and produce energy. Regular exercise leads to an increase in the number and size of mitochondria, which are responsible for energy production in cells.
What are the effects of exercise on muscular system ? (7.2)
Ans. The effects of exercise on the muscular system include :
- Increased blood supply
- Increased muscle temperature
- Increased muscle flexibility
- Accumulation of lactate
- Micro tears in muscle fibers
- Increase in glycogen storage
- Increase in oxidation/metabolism
- Increase in lactate acid tolerance
- Increase in myoglobin storage
- Increase in size and number of mitochondria
- Hypertrophy of muscles
- Increase in strength of ligaments and tendons
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Short Term Effect of Exercises on Muscular system :
Increased blood supply : During exercise, in order to match demand of fuel to muscle, the supply or concentration of blood increases in the whole body or, in the particular muscle group where activity is largely impacted.
Increased muscle temperature : During exercises muscles demand energy, which comes from contracting muscles. During the process, a lot of heat energy is generated which increases the temperature of muscles, and/or the body.
Increased muscle flexibility : Due to increase in blood flow and rise in temperature, elasticity of muscles increases. Stretching and mobility exercises also play a dominant role in increasing muscular flexibility.
Accumulation of Lactate : Muscles requires oxygen. If blood supply does not provide appropriate volume of oxygen to muscles, it leads to accumulation of lactate acid in muscles which result in pain, and soreness in muscles.
Micro-tears in Muscle Fibres : During exercises muscle tissue is placed under stress which results in micro-tears in muscle fibres. The body responds by repairing the muscle fibres and making them larger. When a muscle gets bigger, this process is called hypertrophy.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Long term effects of Exercise on Muscular system :
Hypertrophy of Muscle : Scientifc and systematic exercise leads to increase in thickness of muscle fibres that results in increase in muscle size also known as muscle hypertrophy.
Increase in Strength of Ligaments and Tendons : regular exercise helps to strengthen bones, ligaments, and tendons. This helps prevent injury and promotes performance.
Increase in Size and Number of Mitochondria : Aerobic exercises leads to increase in size and numbers of mitochondria, and which take in more oxygen and produce more ATP and energy.
Increase in Myoglobin Storage : Long term effect of aerobic exercise is to increase the storage of myoglobin which transports oxygen to mitochondria. Large amount of myoglobin means large amount of oxygen and large amount of energy.
Increase in Glycogen Storage : Glycogen is generally stored in muscles and liver. Regular exercise helps the body to increase the storage of glycogen which may give continuous energy for 90 to 120 minutes.
Increase in Oxidation/Metabolism : Endurance exercise training increases the capacity of skeletal muscle fat oxidation by increasing mitochondrial density. Long term exercises demand a lot of energy, and to meet this demand, metabolism increases due to oxidation of fat. This leads to increase in provision of energy.
Increase in Lactate Acid Tolerance : Regular exercises help to tolerate pain and sourness in muscles due to accumulation of lactate acid.
What ______
Ans. –
7.3 Effect of Exercise on Cardiorespiratory System
Multiple Choice Questions
The resting cardiac output is approximately (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 10.0 lt.
(b) 1.0 lt.
(c) 5.0 lt.
(b) 15.0 lt
The volume of blood pumped during one beat (contraction) is called, (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Blood flow
(b) Stroke volume
(c) Veins and arteries
(d) Capillaries
Cardiac hypertrophy is (CBSE TBQ)
(a) plateauing of heart rate due to maximal exercise intensity.
(b) enlargement of heart due to chronic endurance training.
(c) lowering of heart rate due to physical training.
(d) increase in ventricular volume because of exercise.
The amount of breath per minute increases during exercise to : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 20 breath per minute
(b) 40 breath per minute
(c) 30 breath per minute
(d) 10 breath per minute
The amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute is called ___________. (7.3) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
(a) Stroke volume
(b) Cardiac output
(c) Heart rate
(d) Cardiac arrest
What is cardiac output ? (7.3) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Blood pumped in one minute
(b) Blood pumped in one beat
(c) Blood pumped in one stroke
(d) None of the above
______________ bone comes out of socket in hip dislocation. (7.3) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Femur
(b) Humerus
(c) Tibia
(d) Fibula
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
What type of injuries are laceration and incision? Explain. (7.3) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Laceration and incision are soft tissue injuries. Soft tissue include all muscles, ligament, tendons, skin etc.
Or
Aim of sports medicine :
- To Educate about sport injuries
- To Provide knowledge about causes of injuries.
- To Provide knowledge about treatment and rehabilitation of sports injuries
- To Provide knowledge about preventive measures of sports injuries
(Or any two relevant points)
Explain the meaning of cardiac output. (7.3) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. It is the amount/volume of blood pumped out by the heart in one minute.
What is hypertrophy of muscles ? (7.3) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Increase in number of muscle fibres and size of muscle components resulting into enlargement of skeletal muscles.
What do you mean by ‘Cardiac Output’ ? (7.3) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Cardiac output is the volume of the blood pumped by the heart, measured in liters per minute. It is a product of stroke volume and heart rate.
What is ‘Stroke Volume’? (7.3) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Amount of blood pumped by left ventricle in per beat.
- At rest period — 50 to 70 ml/beat
- During exercise – 110 to 130 ml/beat
Or
Amount of blood ejected by heart in one stroke.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What is Stroke Volume? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Stroke volume refers to the volume of blood that is pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart during each contraction (systole) of the heart.
- Stroke volume is influenced by factors such as the strength of the heart muscle, the size of the ventricles, and the amount of blood returning to the heart.
What is Residual Volume? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Residual volume refers to the volume of air that remains in the lungs after forceful expiration.
- It is the amount of air that cannot be expelled from the lungs, even with maximum effort.
What are the effects of exercise on the heart? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The effects of exercise on the heart’s stroke volume and residual volume are as follows :
- Stroke Volume : During exercise, the stroke volume of the heart increases.
- With regular exercise, the heart becomes stronger and more efficient, allowing it to pump out a larger volume of blood with each beat.
- This increased stroke volume helps to deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during exercise, improving overall performance.
- Residual Volume : Residual volume refers to the amount of air that remains in the lungs after a maximal exhalation.
- Exercise does not have a direct effect on the residual volume of the heart.
- Residual volume is primarily influenced by factors such as lung capacity and respiratory muscle strength, rather than exercise.
Write briefly about the effect of training on
(a) Blood flow (b) Blood volume (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. (a) Blood flow :
- The effect of training on blood flow is that it increases.
- During exercise, the demand for oxygen and nutrients in the muscles increases, and the body responds by increasing blood circulation.
- Regular exercise also leads to an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output, which further enhances blood flow throughout the body.
(b) Blood volume :
- The effect of training on blood volume is an increase.
- Regular exercise and training can lead to an increase in blood volume.
- With an increase in blood volume, there is an improved oxygen-carrying capacity, allowing for better endurance and performance during physical activity.
How does cardiac output respond to training? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The response of cardiac output to training is an increase.
- Regular exercise and training can lead to an increase in the size and strength of the heart, which allows it to pump more blood with each contraction.
- This increase in stroke volume, combined with an increase in heart rate, results in an overall increase in cardiac output.
What is pulmonary diffusion? How does it respond to training? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Pulmonary diffusion refers to the capacity of the lungs to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood.
- Regular sub-maximal exercise training can improve pulmonary diffusion.
- As a result of training, the size of the alveoli (tiny air sacs in the lungs) increases, which increases the surface area available for gas exchange.
- This allows for a more efficient exchange of gases, leading to improved oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide removal during exercise.
Briefly explain the effects of exercise on respiratory system. (7.3) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Effects of exercise on respiratory system :
- Strengthens will power to push beyond the capacity of regular training
- Decreases rate of respiration during exercise and at rest
- Strengthens muscles of diaphragm and chest
- Increase in tidal capacity
- Activates unused alveoli since more oxygen is required for endurance activities
- Avoid second wind
- Efficient gaseous exchange
- Increase in residual air volume
- Increase in size of lungs and chest
- Increase in vital air capacity
- Increase in endurance
- Exhale and inhale in fast pace prevents accumulation of waste in lungs and prevents lungs diseases (Any three Points explained)
Elucidate any two effects of exercise on the cardio-respiratory system. (7.3) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Two effects of exercise on the cardio-respiratory system are :
-
Increased Heart Rate : During exercise, the body requires more oxygen to meet the increased demand of the muscles. This increased heart rate helps to circulate oxygen-rich blood to the muscles and remove waste products like carbon dioxide.
- Increased Cardiac Output : Cardiac output refers to the amount of blood pumped out by the heart in one minute. During exercise, the increased heart rate, combined with an increase in stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped with each heartbeat), leads to an increase in cardiac output.
What are the long term effects of exercise on cardio-vascular system ? (7.3) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The long term effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system include :
-
Increased Size and Strength of Heart : Continuous aerobic exercises help to increase the strength and size of the heart, which improves its performance.
-
Decrease in Resting Heart Rate : Due to the improved efficiency of the heart, it is required to pump less blood to meet the needs of the body.
-
Normal Blood Pressure : Regular exercise can lead to a substantial reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure, helping to keep blood pressure within a normal range.
-
Increase in Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output : With the increased size and strength of the heart, it can pump blood more efficiently, resulting in an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output.
-
Increase in Capillary Network : To meet the demand for oxygen, the capillary network increases. This allows for greater oxygen transport to the muscles, improving their ability to perform intense exercise.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Write briefly about the effect of training on :
(a) Lung volume (b) Heart rate (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. (a) Lung volume :
- The effects of training on lung volume include an increase in the capacity and volume of the lungs.
- Continuous exercises done for a long duration help to increase the vital capacity of the lungs, which can increase almost 100% compared to that of a normal individual.
- This increase in lung volume allows for a greater intake of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide from the body.
(b) Heart rate :
- The effects of training on heart rate include a decrease in resting heart rate and an increase in maximum heart rate.
- Regular exercise and training can improve the efficiency of the heart, allowing it to pump more blood with each beat.
- Additionally, training can increase the heart’s capacity to pump blood during intense exercise, resulting in an increase in maximum heart rate.
- Overall, training can help regulate and improve heart rate response during physical activity.
What is blood pressure? Briefly explain its response to exercise. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Exercise can have both short-term and long-term effects on blood pressure.
- In the short term, exercise can cause an increase in systolic blood pressure, which is the top number in a blood pressure reading.
- This increase is due to the increased demand for oxygen by the muscles during exercise.
- However, there is usually minimal change in diastolic blood pressure, which is the bottom number.
- In the long term, regular exercise can lead to a substantial reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- This is because exercise improves the efficiency of the heart, allowing it to pump blood more effectively.
- Additionally, exercise helps to keep the blood vessels healthy and flexible, which can contribute to normal blood pressure levels.
Define and explain the effect of exercise on :
(a) Total volume (b) Stroke volume (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. (a) Total volume :
- The effect of exercise on total volume refers to the changes in the volume of blood in the cardiovascular system during and after exercise.
- During exercise, the total volume of blood increases as the body requires more oxygen and nutrients to meet the increased demand.
- This increase in total volume helps to deliver more oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and organs.
- Additionally, regular exercise can lead to an increase in total blood volume over time, which can improve overall cardiovascular function and endurance.
(b) Stroke volume :
- The effect of exercise on stroke volume is that it increases.
- During exercise, more oxygen is required by the muscles, and the heart responds by pumping more blood with each contraction.
- This increase in the volume of blood pumped per beat is known as stroke volume.
- Regular exercise can lead to an increase in stroke volume, allowing the heart to pump more efficiently and deliver oxygen to the muscles.
Discuss in detail two long term and two short term effects of exercise on cardio respiratory system. (7.3) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Two long-term effects of exercise on the cardiorespiratory system are :
-
Increased lung volume :
- Continuous exercises done for a long duration help to increase the capacity and volume of the lungs.
- This is because regular exercise strengthens the respiratory muscles, such as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which allows for deeper and more efficient breathing.
- This increased lung volume improves overall respiratory function and enhances the body’s ability to deliver oxygen to the muscles during exercise.
-
Increased efficiency of respiratory muscles :
- Regular exercise also improves the efficiency of the respiratory muscles.
- This increased efficiency helps to meet the demand for oxygen during exercise and reduces the feeling of breathlessness.
- It also allows for better control of breathing, which is important for activities that require precise breath control, such as singing or playing wind instruments.
Two short-term effects of exercise on the cardiorespiratory system are :
-
Increased heart rate :
- This sudden increase in oxygen demand is met by an increase in blood circulation, which is achieved by the heart.
- In response to the increased demand, the heart rate increases to pump more blood and deliver oxygen to the working muscles.
- This increased heart rate helps to supply the muscles with the necessary oxygen and nutrients during exercise.
-
Increased respiratory rate :
- Our body requires more oxygen during exercise, and to meet this increased demand, the respiratory rate (breathing rate) increases.
- The increased respiratory rate allows for a greater intake of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide from the body.
- This increased rate of exchange of gases in the lungs helps to meet the increased oxygen demand of the muscles and remove waste products efficiently.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
What is the effect of exercise on cardio respiratory system and muscular system ? (7.3) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Effects of exercise on cardio-respiratory system : When we do exercise there are some immediate effects and long term effects on cardio-respiratory system as — stroke volume increases, cardiac output increases, blood flow increases, heart rate decreases, depth of respiration increases, Strengthen the diaphragm muscles, unused alveolus becomes active, aerobic capacity increases, increase in tidal volume, vital capacity increases and increase in the size of lungs and heart etc. (Any other relevant point)
Effects of exercise on muscular system : When we do exercise regularly there are some changes that take place in our muscular system like — it strengthens the muscles fiber, change in the shape and size of muscles, muscle tone improves, reduces extra fat, improves reaction time, efficiency in the movement of muscles, non-functioning fibers become active, delays fatigue and body posture remains correct etc. (Any other relevant point)
(Explain any 5 points with at least 2 points for each system)
What are the effects of exercise on Respiration System ? Write in detail. (7.3) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Short-term effects of exercise on the respiratory system include :
- Increased Respiratory Rate : During exercise, the body requires more oxygen to meet the increased demand. The normal respiration rate for an adult at rest is 12 to 20 breaths per minute, but during exercise, it can increase to 40 breaths per minute.
- Increased Tidal Volume : Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one breath. During exercise, tidal volume increases to take in more oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
- Increased Rate of Exchange of Gas : Regular exercise increases the rate of exchange of gases in the lungs. This means that oxygen is taken in more efficiently, and carbon dioxide is expelled more effectively.
Long-term effects of exercise on the respiratory system include :
- Increased Efficiency of Respiratory Muscles : Regular exercise improves the efficiency of the respiratory muscles, making inhalation and exhalation more fluent. This helps to meet the increased demand for oxygen during exercise.
- Increased Lung Volume : Continuous exercises done for a long duration help to increase the capacity and volume of the lungs. Vital capacity, which is the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation, increases almost 100% compared to that of a normal individual.
- Increased Pulmonary Diffusion : Pulmonary diffusion refers to the capacity of the lungs to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood. Regular sub-maximal exercise training increases the scope of increasing the exchange of gases, and in this process, the size of the alveoli also increases.
- Increased Residual Volume : Residual volume is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after forceful expiration. Regular exercise increases residual volume, which helps to maintain the exchange of gases within normal limits.
What are the long term effects of regular exercise on the cardio-vascular system? Explain. (7.3) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. The long term effects of regular exercise on the cardiovascular system include :
- Increased Size and Strength of the Heart : Continuous aerobic exercises help to increase the strength and size of the heart. This allows the heart to pump blood more efficiently, resulting in better overall cardiovascular performance.
- Decrease in Resting Heart Rate : Due to the improved efficiency of the heart, it is required to pump less blood to meet the needs of the body. As a result, the heart rate at rest decreases.
- Normal Blood Pressure : Regular exercise can lead to a substantial reduction in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. This helps to keep the blood pressure within a normal range, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Increase in Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output : With regular exercise, the size and strength of the heart increase. This allows the heart to pump blood more efficiently, resulting in an increase in stroke volume and cardiac output.
- Increase in Capillary Network : Regular exercise leads to an increase in the capillary network. This allows for greater oxygen being transported to the muscles, improving their ability to perform intense exercise. Additionally, exercise helps in preventing the decline in capillary function that happens with age.
What do you mean by ‘Oxygen-Intake’ and ‘Oxygen-Uptake’ ? Explain the effects of exercise on respiratory system. (7.3) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Oxygen intake : The amount of oxygen intake by an athlete from the atmosphere is called oxygen intake. It depend upon lungs size, strength of muscles and number of alveoli.
Oxygen uptake : The amount of oxygen which can be absorbed and consumed by the working muscles from the blood is called oxygen uptake.
Effect of exercise on respiratory system :
- Increase depth of respiration
- Decrease rate of respiration
- Improve vital capacity
- Improve tidal volume capacity
- Increase pulmonary diffusion
- Supply more O2 to muscles
- Strengthen the respiratory muscles
- Unused alveoli become active
- Avoid second wind with strong will power
- Faster recovery rate
- Increases residual air volume
- Increase size of lungs and chest
- Maximum minute ventilation increased
- Strengthens diaphragm muscles
(Any three to be explained in second part)
Explain in detail about the effects of regular exercise on respiratory system. (7.3) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. The effects of regular exercise on the respiratory system include :
-
Increased respiratory rate : During exercise, the body requires more oxygen, so the respiratory rate (breathing rate) increases to meet this demand.
-
Increased tidal volume : Tidal volume refers to the amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one breath. During exercise, tidal volume increases to take in more oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body.
-
Increased rate of gas exchange : Regular exercise increases the rate of gas exchange in the lungs, allowing for more efficient exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
-
Increased efficiency of respiratory muscles : Regular exercise improves the efficiency of the respiratory muscles, making inhalation and exhalation more fluent and helping to meet the demand for oxygen.
-
Increased lung volume : Continuous exercises done for a long duration can increase the capacity and volume of the lungs. This increase in lung volume allows for a greater intake of oxygen.
-
Increased pulmonary diffusion : Pulmonary diffusion refers to the capacity of the lungs to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood. Regular exercise training can increase the scope of gas exchange and also increase the size of the alveoli.
-
Increased residual volume : Residual volume is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after forceful expiration. Regular exercise can increase residual volume, which helps to maintain gas exchange within normal limits.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Cardiorespiratory System : Cardiorespiratory system consists of two parts. They are –
Cardiovascular system : It consists of three parts: the heart, blood vessels and blood. Its major function is to deliver oxygen and nutrients, remove CO2 and other metabolic waste products, to transport hormones and other molecules, to support thermoregulation and control of body fluid balance and lastly to regulate immune function.
Respiratory system : The important parts of the respiratory system are the nose, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Air can also enter the respiratory system through the oral cavity. Its major functions include, transporting air to the lungs, exchanging gases (O2 and CO2) between the air and blood, and regulating blood pH.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Short Term Effects of Exercise in Respiratory System :
Respiratory Rate Increases : Our body requires more oxygen during exercise, and to meet this increased demand, the respiratory rate (breathing rate) increases. The normal respiration rate for an adult at rest is 12 to 20 breaths per minute, but during exercise it increases to 40 breaths per minutes.
Tidal Volume Increases : The amount of air inhaled and exhaled in one breath is known as tidal volume. Tidal volume increases as a result of exercise to take in more oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from our body.
Rate of Exchange of Gas Increases : Regular exercise increases the rate of exchange of gas in lungs.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Long Term Effects of Exercise in Respiratory System :
Increased Efficiency of Respiratory Muscles : Due to regular exercise efficiency of respiratory muscles increases, inhalation and exhalation become fluent. This helps to meet the demand of oxygen.
Increased Lung volume : Continuous exercises done for long duration help to increase the capacity and volume of lungs. Vital capacity increases almost 100 % as compared to that of a normal individual.
Increased Pulmonary Diffusion : Pulmonary Diffusion refers to the capacity of the lungs to allow oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in and out of the blood. Regular sub-maximal exercise training develops the scope of increasing the exchange of gases, and in this process the size of the alveoli also increases.
Increased Residual Volume : Residual volume is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after forceful expiration. Regular exercise increases residual volume that helps to exchange the gases in normal limits
What ______
Ans. –
7.4 Physiological Changes Due to Ageing
Multiple Choice Questions
Men and women usually attain their highest strength levels between the ages of (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 5 and 7
(c) 7 and 11
(d) 20 and 40
It is a measure of the amount of minerals (mostly calcium and phosphorous) contained in a certain volume of bone, (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Body composition
(b) Bone mass
(c) Pulmonary function
(d) Neural function
The chemical substances synthesized by specific host glands, secreted into the blood, and carried throughout the body are called (CBSE TBQ)
(a) hormones
(b) sugar
(c) electrolytes
(d) capillaries
It is a disease in which bone weakening increases the risk of a broken bone (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Measles
(b) Osteoporosis
(c) Atherosclerosis
(d) Beriberi
Decrease in size of a body part, cell, organ, or other tissue is called (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Myopia
(b) Atrophy
(c) Cardiac arrest
(d) Cardiac cycle
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
On the basis of physiological parameters, mention any two gender differences. (7.4) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. (1) Muscular strength
(2) Cardiovascular fitness
(3) Bones and ligament
(4) Respiratory organs (Any two)
What is the relationship between muscular size and strength ? (7.4) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The relationship between muscular size and strength is generally positive.
What do you mean by ageing ? (7.4) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The definition of ageing refers to the progressive degeneration of organ systems and tissues in the body over time.
What is osteoporosis? (7.4) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Osteoporosis is a disease in which bone weakening increases the risk of a broken bone.
Write one physiological change due to ageing? (7.4) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. One physiological change that occurs due to aging is a decline in muscular strength.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Describe the changes in endocrine system due to ageing. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The changes in the endocrine system due to ageing include impaired glucose tolerance leading to Type 2 diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, and a decrease in growth hormone secretion.
- Approximately 40% of individuals aged between 65 and 75 years and 50% of those older than age 80 have impaired glucose tolerance leading to Type 2 diabetes.
- Thyroid dysfunction, primarily from lowered pituitary gland release of the thyroid-stimulating hormone thyrotropin (and reduced output of thyroxine), is common among the elderly.
- This directly affects metabolic function, including decreased glucose metabolism and protein synthesis.
- Mean pulse amplitude, duration, and fraction of secreted growth hormone (GH) gradually decrease with ageing, a condition termed somatopause.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Write in detail about the physiological changes taking place due to ageing. (7.4) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. Some of the major physiological changes that occur with ageing include :
- Muscular Strength : There is a decline in muscular strength, both concentric and eccentric, due to a reduction in muscle mass and loss of motor units.
- Neural Function : There is a decline in the number of spinal cord axons and nerve conduction velocity, leading to a reduction in neuromuscular performance and slower reaction and movement times.
- Endocrine Changes : The endocrine system undergoes changes, such as impaired glucose tolerance leading to Type 2 diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, and a decrease in growth hormone secretion.
- Pulmonary Function : There is a deterioration in static and dynamic lung function measures, resulting in slower pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange kinetics during exercise.
- Cardiovascular Function : Maximum heart rate and cardiac output typically decrease with age, leading to reduced peripheral blood flow capacity and a decline in aerobic capacity.
- Body Composition : Total body mass decreases, while body fat increases, especially after the age of 60.
- Bone Mass : Osteoporosis becomes a major concern, causing a loss of bone mass and increased risk of fractures, particularly among postmenopausal women.
What do you understand by ‘ageing’ ? Explain the following :
(a) Physiological changes due to ageing.
(b) Contribution of exercise to maintain functional fitness in aged population. (7.4) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Ageing refers to the natural and gradual process of getting older and the associated changes that occur in the body and mind over time.
(a) Physiological changes due to ageing :
- Muscular Strength : There is a decline in muscular strength, both concentric and eccentric, starting at a later age.
- Neural Function : There is a decline in the number of spinal cord axons and nerve conduction velocity, leading to a reduction in neuromuscular performance, reaction time, and movement time.
- Endocrine Changes : The endocrine system undergoes changes with ageing, including impaired glucose tolerance leading to Type 2 diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, and a decrease in growth hormone secretion.
- Pulmonary Function : There is a deterioration in static and dynamic lung function measures, as well as a slowing of pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange kinetics during exercise.
- Cardiovascular Function : Ageing affects cardiovascular function and aerobic capacity.
- Body Composition: Total body mass decreases, while body fat increases after the age of 60.
- Bone Mass : Osteoporosis becomes a major concern, leading to a loss of bone mass and increased risk of fractures, particularly among postmenopausal women.
(b) Contribution of exercise to maintain functional fitness in aged population :
- Muscular Strength and Endurance : Regular exercise, particularly resistance training, helps to improve muscular strength and endurance.
- Balance and Stability : Exercise programs that include balance and stability exercises can help to reduce the risk of falls in the elderly.
- Cardiovascular Health : Exercise improves cardiovascular health by strengthening the heart and improving circulation.
- Bone Health : Weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or weightlifting, help to maintain bone density and reduce the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Cognitive Function : Exercise has been shown to have positive effects on cognitive function and can help to reduce the risk of cognitive decline and dementia in the elderly.
- Mental Health: Regular exercise has been shown to have positive effects on mental health, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety in the elderly.
Explain in detail physiological changes which occur due to ageing. (7.4) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. Physiological changes which occur due to ageing
(1) Change in muscle size and strength
(2) Change in metabolism and body composition
(3) Change in bone density
(4) Change in respiratory system
(5) Change in cardiovascular system
(6) Change in gastro-intestinal system
(7) Changes in senses
(8) Change in flexibility
(9) Change in nervous system
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Muscular Strength : It is defned as the maximal force that a muscle or muscle group can generate. Men and women usually attain their highest strength levels between ages 20 and 40, the time when muscle cross-sectional area is largest. Concentric strength of most muscle groups declines, slowly at first and then more rapidly after middle age. Decline in eccentric strength begins at a later age and progresses more slowly than those in concentric strength.
Strength loss begins at a later age for women than for men. A 40% to 50% reduction in muscle mass from muscle fibre atrophy and actual loss of motor units between ages 25 and 80 is the primary cause of reduced strength, even among healthy, physically active men and women.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Endocrine Changes with Ageing : The endocrine system consists of a host organ (gland), minute quantities of chemical messengers (hormones), and a target or receptor organ. Approximately 40% of individuals aged between 65 and 75 years and 50% of those older than age 80 have impaired glucose tolerance leading to Type 2 diabetes. Thyroid dysfunction, primarily from lowered pituitary gland release of the thyroid-stimulating hormone thyrotropin (and reduced output of thyroxine), is common among the elderly. This directly affects metabolic function, including decreased glucose metabolism and protein synthesis. Mean pulse amplitude, duration, and fraction of secreted growth hormone (GH) gradually decrease with ageing, a condition termed somatopause.
What ______
Ans. –
7.5 Sports Injuries
Multiple Choice Questions
A sprain is an injury to : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Muscle
(b) Tendon
(c) Ligament
(d) Bone
A fracture is an example of injury to (CBSE TBQ)
(a) skin
(b) soft tissue
(c) hard tissue
(d) eyes
A soft tissue injury damages (CBSE TBQ)
(a) ligaments and tendons
(b) bone
(c) cartilage and muscles
(d) carpals
A fracture in which the bone breaks diagonally is called a _________ fracture. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Greenstick
(b) Impacted
(c) Oblique
(d) Transverse
When the bone is broken into more than one piece, it is called (7.5) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Comminuted fracture
(b) Compound fracture
(c) Simple fracture
(d) Greenstick fracture
PRICE treatment is for (7.5) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Fractures
(b) Abrasions
(c) Sprains
(d) Lacerations
Dislocation is related to (7.5) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Bone injury
(b) Skin Injury
(c) Muscular Injury
(d) Joint injury
Fracture where a part of broken bone enters another bone (7.5) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Simple fracture
(b) Compound fracture
(c) Impacted fracture
(d) Green stick fracture
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Which type of sports injury is known as ‘Strain’ ? (7.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. It is a soft tissue injury.
What do you mean by soft tissue injuries ? (7.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body. Soft tissue injury includes sprain, strain, contusion, abrasion and bruises.
What type of sports injury can be termed as ‘Laceration’ in sports? (7.5) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Laceration is an irregular cut on the skin with a sharp object or sharp edged sports equipment.
What type of fracture is known as Greenstick Fracture? (7.5) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. Greenstick fracture is a bend or crack in a bone usually found in children.
What is contusion ? (7.5) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. A soft tissue injury in which blood vessels in the muscles are broken and internal bleeding may occur on the injured part generally caused by direct hit with blunt object.
What is incision ? (7.5) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Incision is a soft tissue injury. It may occur due to sharp edged object of sports equipments or spikes etc. Sometimes arteries or veins may be cut. Blood usually comes out freely from incision.
What is ‘Laceration’ ? (7.5) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. A laceration is an irregular and jagged wound from a sharp object or sports equipment.
What kind of sports injury can be termed as ‘Abrasion’. (7.5) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Abrasion is soft tissue injury. It is the injury of skin in which skin is scrapped or rubbed by friction
Define any one soft tissue injury. (7.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. A soft tissue injury is the damage to muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the body.
What do you understand by P.R.I.C.E. ? (7.5) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. P.R.I.C.E. stands for Protection, Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation.
What do you understand by SPRAIN and STRAIN ? (7.5) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. A sprain is an injury to the ligaments, which are the fibrous tissues that connect bones in the joints.
A strain is an injury to the muscles or tendons that are attached to a bone.
Mention the various types of soft tissue injuries? (7.5) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The various types of soft tissue injuries are : Abrasion, Contusion, Laceration, Strain, Sprain, and Incision.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What is comminuted fracture? Write its cause, prevention and treatment. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. A comminuted fracture is a type of fracture in which a bone is broken, splintered, or crushed into multiple pieces.
- Causes : Comminuted fractures are usually caused by direct or indirect trauma or violence to the bone. This can occur from accidents, falls, or other forms of physical impact.
- Prevention : Maintaining strong bones through a diet rich in calcium and regular exercise can help prevent comminuted fractures.
- Treatment : An X-ray is important for diagnosing a comminuted fracture. This procedure is performed to stabilize the bone and promote proper healing.
What is a sprain? Write its cause, prevention and treatment. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. A sprain is the stretching or tearing of ligaments, which are the fibrous tissues that connect bones in the joints.
- Causes of a sprain include overextending or tearing a ligament while severely straining a joint. This can happen during activities such as sports, running, or even a simple misstep.
- Prevention of sprains can be done through regular stretching and strengthening exercises for any kind of sport. This helps to improve the flexibility and strength of the ligaments, reducing the risk of sprains.
- The treatment for a sprain is often referred to as RICE, which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Resting the affected joint allows it to heal, while applying ice helps reduce swelling and pain.
Differentiate between sprain and strain. (any two) (7.5) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Sprain :
- A sprain is an injury to the ligaments, which are the fibrous tissues that connect bones in the joints.
- It occurs when the ligaments are stretched or torn due to overextension or severe stress on a joint.
- The most common location for a sprain is the ankle. (any two)
Strain :
- On the other hand, a strain is an injury to the muscles or tendons that are attached to a bone.
- A strain can range from a simple overstretch of the muscle or tendon to a partial or complete tear.
- It can be caused by overuse, force, or stretching. (any two)
What is Laceration and how can it be managed? (7.5) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans.
- A laceration is an irregular tear-like wound caused by blunt trauma. It is defined as a cut caused by a sharp edge of an object.
- A laceration can be managed by gently washing the affected area with soap and water to remove any dirt.
- After cleaning, the area should be dried with a clean towel before applying a dressing.
- It is important to keep the laceration clean and covered to prevent infection.
- If the laceration is deep or severe, medical attention may be necessary for stitches or further treatment.
Explain any two types of soft tissue injuries with help of examples. (7.5) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. A soft tissue injury is the damage of muscles, ligaments and tendons throughout the body.

Draw diagram and explain the management of any two types of bone injury. (7.5) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Comminuted Fracture : A comminuted fracture is a type of bone fracture where the bone is broken, splintered, or crushed into multiple pieces.
- Diagnosis : An X-ray or other imaging tests are done to determine the extent and location of the fracture.
- Immobilization : The affected limb or area is immobilized using a cast, splint, or external fixation device to prevent further movement and promote healing.
- Surgery : In severe cases, surgery may be required to realign the bone fragments and stabilize them using screws, plates, or rods.
- Rehabilitation : Once the fracture starts to heal, physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected area.
Transverse Fracture : A transverse fracture is a type of bone fracture where the break is straight across the bone.
- Diagnosis : An X-ray or other imaging tests are done to confirm the presence and location of the fracture.
- Immobilization : The affected limb or area is immobilized using a cast, splint, or external fixation device to prevent movement and promote healing.
- Rehabilitation : Once the fracture starts to heal, physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are recommended to restore strength, flexibility, and function to the affected area.
Discuss the preventive measure of sports injuries. (7.5) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Preventive measure of sports injuries :
- Proper warm up
- Proper conditioning
- Balanced diet
- Adequate knowledge about the sport skills
- Use of protective equipments
- Good sports facilities
- Unbiased officiating
- Avoid over training
- Proper Techniques
- Obeying the rules
- Proper cooling down
- Levelled ground (Or any 3 relevant point explained)
Mention briefly about the common sports injuries and their prevention. (7.5) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Common sports injuries :
|
Soft tissue injuries |
Bone injuries |
Joint injuries |
|
• Contusion • Strain • Sprain • Abrasion • Bruises (Mention all the injuries only and describe any one) |
• Simple fracture • Compound fracture • Complicated fracture • Communicated fracture • Impacted fracture • Greenstick fracture (Mention all the injuries only and describe any one) |
• Dislocation of lower jar • Dislocation of shoulder joint • Dislocation of hip joint • Dislocation of wrist (Mention all the injuries only and describe any one) |
Prevention :
- Warming up
- Proper conditioning
- Discontinue to play during the state of fatigue
- Good officiating (Any three in brief)
- Sports equipment
- Playfield/Count
- Scientific knowledge of game
- Protective equipment
- Equipment of good quality
- Protective equipment should be used
What do you understand by ‘First-Aid’? How will you manage joint injuries? Explain. (7.5) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. First-Aid : First-Aid is the immediate and temporary care given to a victim of accident or sudden illness before the arrival of the Doctor.
Joint injuries : Dislocation of the joints – in which adjoining bones are displaced from their normal position.
Management :
- Call for immediate medical help.
- Do not move the joint to replace it.
- Keep the person in a comfortable position.
- Apply cold packs around the area to reduce swelling.
- Immobilize the area with a splint.
- Pain killer as advised by doctor. (Any 2 points)
Explain PRICE procedure as a treatment for soft tissue injury. (7.5) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Protection : Protect the injured area by using a support.
Rest : In the initial phase it is best to give complete rest to the injured part for at least 48 hours.
Ice : Ice should be applied on the injured area as soon as possible to reduce swelling and limit internal bleeding.
Compression : Applying pressure on the injured part , such as ankle, wrist or muscle is helpful in reducing internal bleeding and swelling. This can be done by wrapping the injured part with elastic bandage or cloth.
Elevation : If possible elevate the injured part immediately, this will reduce the flow of blood towards the injured part and thus reduce swelling.
List down different type of bone injuries (joints dislocation and fractures) and explain any two. (7.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Types of bone injuries include :
-
Joint dislocation : This occurs when the ends of bones in a joint are forced out of their normal position.
-
Fractures : A fracture is a break in the continuity of a bone. There are different types of fractures, including :
- Open/compound fracture
- Closed/simple fracture
- Stress fractures
- Greenstick fracture
- Comminuted fracture
- Transverse fracture
- Oblique fracture
- Impacted fracture
- Comminuted Fracture : The management of a comminuted fracture involves several steps.
- First, an X-ray is necessary to diagnose the condition and determine the extent of the fracture.
- In severe cases, an open reduction may be required.
- Transverse Fracture : The management of a transverse fracture depends on the severity of the injury.
- In less severe cases, the fracture can be treated at home with rest and medication.
- It is important to follow the prescribed treatment plan and allow the bone to heal properly.
Explain about the management of fracture. (7.5) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Management of fracture : First-aid for closed and open fracture.
The injured part can be immobilized with the help of sling in closed fracture. During open fracture the open wound must be covered by sterile gauze or dressing. The compression and elevation is given to stop the bleeding. The sling is used to immobilize the injured part.
For transporting the injured person to the hospital, sitting position is desirable but in complicated cases person can be transported in a lying position on a stretcher.
Create a flow chart for common sports injuries while enlisting the sub-parts. (7.5) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Common sports injuries
|
Soft tissue injuries |
Bone injuries |
Joint injuries |
|
(a) Contusion (b) Bruises (c) Sprain (d) Strain (e) Abrasion
|
(a) Simple fracture (b) Complicated fracture (c) Impacted fracture (d) Green stick fracture (e) Compound fracture (f) Comminuted fracture |
(a) Shoulder dislocation (b) Hip dislocation (c) Lower jaw dislocation (any two from each) |
Create a flowchart to explain classification of sports injuries. (7.5) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. ……………………………………………..
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Name the more common types of fractures and describe them. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The more common types of fractures are :
-
Comminuted fracture : This is a fracture in which a bone is broken, splintered, or crushed into a number of pieces. Prevention involves maintaining strong bones through a calcium-rich diet and regular exercise. Treatment may require an open reduction, where the bone fragments are surgically joined together using nails or plates.
-
Transverse fracture : This is a fracture where there is a straight break right across a bone. Prevention involves physical activity, weight-bearing exercises, and a calcium-rich diet. Treatment can be done at home with rest and medication, and a back brace or abdominal binder may be prescribed to reduce pain.
-
Oblique fracture : This is a fracture in which the bone breaks diagonally. Prevention involves a calcium-rich diet and regular exercise. Treatment depends on the severity of the fracture and may include anti-inflammatory medication and reduction (resetting the bone).
-
Impacted fracture : This type of fracture occurs when the broken ends of the bones are jammed together by the force of the injury. Prevention involves increased physical activity, weight-bearing exercises, and a calcium-rich diet. Treatment may require a sling or splint to keep the broken bones in place and prevent further damage.
What is a soft tissue injury? Name four types of soft tissue injury and describe it. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. A soft tissue injury refers to damage or injury to the muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the body. These injuries can occur during physical activities, sports, or accidents.
Four types of soft tissue injuries are :
- Contusion : A contusion, commonly known as a bruise, is caused by a direct blow to a part of the body. Prevention includes wearing protective gear and practicing proper techniques. Treatment involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), along with pain management.
- Sprain : A sprain occurs when a ligament, which connects bones to each other, is stretched or torn. Prevention involves proper warm-up, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Treatment includes RICE, immobilization, and rehabilitation exercises.
- Strain : A strain refers to an injury to a muscle or tendon, which connects muscles to bones. Prevention includes proper conditioning, gradual increase in intensity, and using proper techniques. Treatment involves RICE, rest, and physical therapy.
- Avulsion : Avulsion is the tearing away of a part of the skin or soft tissue from its normal position. Prevention includes wearing protective gear and avoiding situations that may lead to such injuries. Treatment involves cleaning the wound, stopping bleeding, and suturing or reattaching the avulsed tissue if possible.
Classify bone injuries. Explain preventive measures to avoid sports injuries. (7.5) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Bone injuries can be classified based on the severity and type of fracture. The severity of the fracture can range from a mild crack in the bone to a severe shattering of the bone into many pieces.
The preventive measures to avoid sports injuries include:
- Proper warm-up : It is important to warm up before engaging in any physical activity.
- Use proper equipment : Wearing appropriate protective gear and using the right equipment for the sport can help prevent injuries.
- Gradual progression : Gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts to allow your body to adapt and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
- Maintain good technique : Using proper technique and form while participating in sports can help prevent injuries.
- Stay hydrated : Proper hydration is important for maintaining optimal performance and reducing the risk of muscle cramps and fatigue, which can lead to injuries.
- Listen to your body : Pay attention to any pain or discomfort during physical activity.
- Cross-training and rest days : Engaging in a variety of physical activities and taking regular rest days can help prevent overuse injuries. Cross-training allows different muscle groups to be used and reduces the strain on specific areas of the body.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle : Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can contribute to overall physical health and reduce the risk of injuries.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
What do you understand by fracture ? How can fractures be classified ? Explain. (7.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Fracture : Broken or cracked bone is known as fracture. It is a very common injury in games and sports.
Fractures can be classified based on various factors such as the location of the fracture, the pattern of the fracture, and the severity of the fracture. Here are some common classifications of fractures :
-
Location-based classification : Fractures can be classified based on the specific bone or body part where the fracture occurs. For example, a fracture in the arm, leg, or spine.
-
Pattern-based classification : Fractures can be classified based on the pattern of the break in the bone. Some common pattern-based classifications include:
- Transverse fracture : A straight break right across the bone.
- Oblique fracture : A diagonal break in the bone.
- Comminuted fracture : A fracture in which the bone is broken, splintered, or crushed into multiple pieces.
- Impacted fracture : A fracture in which the broken ends of the bone are jammed together by the force of the injury.
- Severity-based classification : Fractures can also be classified based on the severity of the break and the displacement of the bone fragments. Some common severity-based classifications include :
- Closed fracture : The broken bone does not pierce through the skin.
- Open fracture : The broken bone pierces through the skin, leading to an open wound.
- Greenstick fracture : A partial fracture in which the bone bends and cracks but does not completely break.
Contusion and dislocation are common sports injuries. Write in detail about the symptoms and management of these injuries. (7.5) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Symptoms of contusion : The symptoms of a contusion include pain, swelling, and discoloration of the skin. The affected area may also feel tender to the touch. In severe cases, there may be difficulty in moving the injured body part.
Management for contusion : The management of a contusion involves the RICE method–Resting the injured area helps prevent further damage and allows the body to heal. Applying ice to the contusion helps reduce swelling and pain. Compression, using a bandage or wrap, helps control swelling and provides support to the injured area. Elevating the injured body part above the level of the heart also helps reduce swelling.
Symptoms of dislocation : The symptoms of a dislocation include severe pain, swelling, deformity of the joint, and loss of movement. The affected joint may also appear visibly out of place.
Management of dislocation : The management of a dislocation involves seeking immediate medical attention. It is important not to try to relocate the joint yourself, as this can cause further damage. A healthcare professional will perform a physical examination and may order imaging tests, such as X-rays, to confirm the dislocation. They will then carefully manipulate the joint back into its normal position, a process called reduction. After the joint is relocated, the healthcare professional may immobilize the joint with a splint or cast to allow for proper healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to regain strength and range of motion in the joint.
What are the causes of ‘Sports-Injuries’ ? How Sports-Injuries can be prevented ? Explain briefly. (7.5) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Causes of Sports-Injuries :
- Personal causes :
- Improper warm up .and cool-down
- Not following the rules and regulation.
- Protective clothing and equipment
- Knowing the limits
- Improper rest and relaxation
- Healing previous injury or inadequate rehabilitation
- Lack of conditioning
- Drug abuse
- Environmental/External causes :
- Improper ground or poorly maintained facilities
- Extreme cold or heat
- Inadequate first-aid care
- Expectation of spectators
- Lack of medical check-up
- Improper diet
- Training causes :
- Without considering individual differences
- Lack of proper supervision
- Wrong method of training/poor coaching
- Lack of systematic and scientific training
- Lack of psychological preparation
- Improper load and recovery
Prevention of Sports Injuries :
- Overall conditioning
- Pre-participation physical examination/medical check-up
- Coaching under expert trainer/physio/coach
- Stress on proper physical fitness
- Balance diet
- Acclimatisation with environment/coaching according to climatic conditions
- Training according to periodisation
- Intake of sufficient fluid
- Adequate clothing and equipments
- Standardised play field/court
- Documentation of injuries
- Knowledge of first-aid
- Protective sport gears
Classify sports injuries. Explain ‘P.R.I.C.E.’ procedure as a treatment of soft tissue injuries. (7.5) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Some common types of sports injuries include :
- Abrasion – injury caused by falling on a rough or firm surface.
- Laceration – tears in the skin.
- Incision – cut caused by a sharp edge of an object.
- Puncture wound – wound caused by piercing by a sharp and pointed object.
- Avulsion – tearing away of a part of the skin.
- Contusion – bruise caused by a direct blow to some part of the body.
- Sprain – injury of ligament of joints, caused by the violent overstretching of ligament in a joint or the movement of the joint in abnormal directions.
- Strain – injury of muscle or tendon, with three types – mild, moderate, severe.
- Joint dislocation – displacement of contiguous surfaces of two or more bones in a joint.
- Fractures – breaks in the continuity of the bone, which can be open/compound or closed/simple fractures.
‘P.R.I.C.E.’ procedure as a treatment of soft injuries :
- Protection : The injured area should be protected from further harm. This may involve using crutches, a brace, or a splint to immobilize the area and prevent any additional stress or strain.
- Rest : Resting the injured area is crucial for allowing the tissues to heal. It is important to avoid any activities or movements that may aggravate the injury.
- Ice : Applying ice to the injured area helps reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. It is important to wrap the ice pack in a towel or cloth to protect the skin from direct contact with the ice.
- Compression : Applying compression to the injured area helps reduce swelling and provides support. This can be done by using an elastic bandage or compression wrap.
- Elevation : Elevating the injured area above the level of the heart helps reduce swelling by allowing fluid to drain away from the injured area. This can be done by propping up the injured limb on pillows or cushions.
Write in detail about the dislocation and fractures among the bones and joints injuries. (7.5) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Dislocation : A dislocation occurs when the ends of bones in a joint are forced out of their normal position. This can happen due to a fall, a blow, or a sudden impact, often seen in contact sports.
- Causes : Dislocations are usually caused by trauma, such as accidents, falls, or sports injuries. Weakening of muscles and tendons surrounding the joint can also lead to dislocations, especially in older individuals.
- Symptoms : Symptoms of a dislocated joint include severe pain, swelling, bruising, instability of the joint, loss of ability to move the joint, and a visibly deformed joint.
- Treatment : Treatment for a dislocation depends on the severity of the injury and the joint involved. Initially, applying ice and elevating the joint can help reduce pain and swelling. Surgery may be necessary if the dislocation caused damage to blood vessels, nerves, bones, or if muscles and ligaments need repair.
Fractures : A fracture is a break in the continuity of a bone. Fractures can range from a mild crack in the bone to a severe shattering of the bone into multiple pieces.
- Causes : Fractures are usually caused by a direct impact, such as a fall or a severe tackle. Stress fractures, on the other hand, develop over time due to repetitive stress or overuse.
- Symptoms : Symptoms of a fracture include severe pain, swelling, deformity, difficulty moving the affected area, and sometimes a visible bone protrusion.
- Treatment : Treatment for fractures depends on the type and severity of the fracture. It may involve immobilizing the affected area with a cast or splint to allow the bone to heal. Rehabilitation through physical therapy exercises is often necessary to regain strength and mobility in the affected area.
Define sports injuries? Write classification, prevention of sports injuries? (7.5) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Sports injuries :
- Sports injuries may be defined as any stress or overstretch put on soft tissues or bone on or off the field resulting in pain and hindering performance.
- They can include cuts, tears, overstretching of tissues, breakage of bones, or dislocation of joints.
Classification :
- The classification of sports injuries can be based on the cause of the injury.
- They can be classified as direct injuries, which are caused by an external force at the point of contact, or indirect injuries, which occur when the athlete damages the soft tissues through internal or external force.
- Sports injuries can also be classified as soft tissue injuries, which involve injuries to the skin, muscles, or ligaments, or hard tissue injuries, which occur in bones and cartilages.
Prevention methods for sports injuries include :
- Proper warm-up : Warming up before engaging in physical activity helps to increase blood flow to the muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce the risk of injury.
- Using proper equipment : Wearing appropriate protective gear and using well-fitted equipment can help prevent injuries.
- Technique and form : Using correct technique and form while participating in sports can reduce the risk of injury.
- Gradual progression : Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of training can help the body adapt and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
- Rest and recovery : Allowing adequate time for rest and recovery between training sessions or competitions is important to prevent overuse injuries.
- Conditioning and strength training : Building strength and conditioning specific to the sport can help prevent injuries.
- Proper nutrition and hydration : Maintaining a balanced diet and staying hydrated can support overall health and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Regular check-ups : Regular medical check-ups can help identify any underlying issues or imbalances that may increase the risk of injury.
Discuss the impact of different types of playing surface on athletes and the steps to over-come the impact for avoiding injuries. (7.5) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. ………………………………
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Sports Injuries : Sports participation and exercise engagement have always witnessed an interruption among athletes towards active participation or lead to painful experience due to some or the other form of injuries. The injuries may be due to incorrect movement, hitting or colliding with equipment or aggressive sporting actions like diving and sliding, overtraining or lack of conditioning. All these injuries caused due to different reasons may not be of the same type, which means they may need different remedies and specific understanding towards each injury to avoid and prevent such injuries. The injury in sports and exercise refers to the physical damage caused to tissue, bone, or any other organ of the body while in action and further leading to withdrawal from participation or experience pain while performing movement actions.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Dislocation : Dislocations are joint injuries that force the ends of bones out of position. The cause is often a fall or a blow, sometimes from playing a contact sport. A joint dislocation, also called luxation, occurs when there is an abnormal separation in the joint, where two or more bones meet. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation. Dislocation can be caused by a trauma (accident or fall) or the weakening of muscles and tendons. A dislocated joint can be treated through medication, manipulation, rest or surgery.
Causes : Trauma that forces a joint out of place causes a dislocation. Accidents, falls, and contact sports such as football are common causes of this injury. Dislocations also occur during regular activities when the muscles and tendons surrounding the joint are weak. These injuries happen more often in older people who have weaker muscles and balance issues.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Stress fracture : Stress fractures may occur because of overuse injuries and the failure to have adequate equipment to protect the body.
Causes : Stress fractures often result from increasing the amount or intensity of an activity too quickly.
Prevention : Low impact activities added to exercise regimen to avoid repetitively stressing a particular part of the body.
Treatment : Rest, cold therapy ice packs, cold compresses, apply ice to the injured area, anti-inflammatory medications such as Ibuprofen, aspirin etc and a recovery time of 6 to 8 weeks is required for healing.
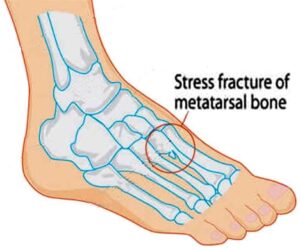
What ______
Ans. –
4. (CBSE TBQ)

Which types of injury is illustrated above?
(a) Soft tissue
(b) Hard tissue
(c) Joint injury
(d) Ligament injury
Recognise the type of facture is illustrated above :
(a) Green stick
(b) Comminuted
(c) Transverse
(d) Oblique
In which of the factures bone ‘breaks diagonally’?
(a) Green stick
(b) Comminuted
(c) Transverse
(d) Oblique
5. Given below is data of soft tissue injuries collected from a training centre after completion of training : (7.5) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
From which injury were the players most affected ?
(a) Abrasion
(b) Contusion
(c) Strain
(d) Sprain
Sprain is related to :
(a) muscle
(b) ligament
(c) skin
(d) bone
From which injury were the players least affected ?
(a) Sprain
(b) Abrasion
(c) Strain
(d) Contusion