6.1 Fitness Test : SAI Khelo India Fitness Test in School
Multiple Choice Questions
50 meter Dash is conducted to test : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Strength
(b) Acceleration
(c) Flexibility
(d) Endurance
Which test can be applied to test endurance ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Sit and Reach
(b) Push Ups
(c) 600 Meter Run/Walk
(d) Plate Tapping Test
Partial curl up is to test : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) agility and speed
(b) leg strength and endurance
(c) abdominal strength and endurance
(d) upper body strength and endurance
Sit and reach test measures (CBSE TBQ)
(a) endurance
(b) flexibility
(c) strength
(d) speed
Sit and reach test is conducted for (6.1) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Flexibility
(b) Motor fitness
(c) Endurance
(d) Speed
Circuit training is an effective method for developing (6.1) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Speed
(b) Strength, endurance and flexibility
(c) Agility
(d) All of the above
Name the component which is measured by this test? (6.1) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Endurance
(b) Speed
(c) Flexibility
(d) Coordinative ability
Mr. Lakshman, aged 65 years worked as a civil engineer in a construction company. He had to walk and climb a lot as part of his job. After retirement, he settled with his son and spent time with his grand children. Nowadays he is experiencing difficulty in doing certain chores which involve physical movement.
The test shown in the picture is performed to assess which component ? (6.1) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) agility
(b) endurance
(c) speed
(d) strength
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Name any motor fitness test. (6.1) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. One motor fitness test is the Flamingo Balance Test.
What do you mean by motor development? (6.1) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. Motor development refers to the progression of a person’s ability to control and coordinate their muscles and movements.
Name the test used for strength measurement. (6.1) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The test used for measuring strength is the Arm Curl Test.
Define motor development. (6.1) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Motor development means the development of child’s bones, muscles and the ability to move around. They learn to sit, walk, stand and run. It is the study of changes in movement behaviour.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Enlist the general equipment used for measuring SAI Khelo India Fitness Test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The general equipment used for measuring the SAI Khelo India Fitness Test includes a weighing machine, a stadiometer or measuring tape pasted on a wall for measuring height accurately, and a digital scale for measuring weight accurately.
Explain the procedure to test strength. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Strength can be tested using various methods, but one common method is the arm curl test.
- In this test, the individual sits on a chair with their back straight and feet on the floor.
- They hold a dumbbell in their dominant hand and perform as many arm curls as possible in 30 seconds.
- The number of complete arm curls is recorded as a measure of upper body strength.
Write down the process to determine the upper body endurance. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The process to determine upper body endurance is through the Arm Curl Test. Here is the procedure:
- Sit on the chair with your back straight and feet on the floor.
- Hold a dumbbell in your dominant hand using a handshake grip.
- On the command “Go,” start curling the dumbbell towards your shoulder, bending your elbow.
- Lower the dumbbell back down to the starting position.
- Repeat the arm curl motion as many times as possible in 30 seconds.
- Count the number of complete arm curls performed within the given time.
- The maximum number of arm curls completed in 30 seconds is the score that determines upper body endurance.
Explain the process of 600 meter run/walk. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The process for the 600 meter run/walk is as follows :
- Participants are instructed to run or walk 600 meters at the fastest possible pace.
- The participants begin on the signal “ready, start”.
- As they cross the finish line, the elapsed time should be announced to the participants.
- Walking is permitted, but the objective is to cover the distance in the shortest possible time.
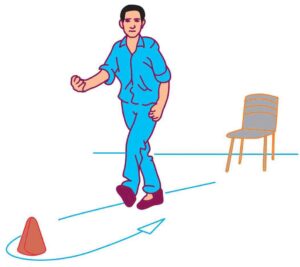
Write any two items of the test battery of motor fitness test and explain the procedure of a test to measure agility. (6.0) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Items of Motor Fitness Test :
- 50 m standing start
- 600 yard run-walk
- Sit and reach test
- 4 × 10 m shuttle run
- Standing long/broad jump
- Pushups (Boys)/modified Pushups (Girls)
- Partial curl up. (any 2 test items)
Test to measure agility : 4 × 10 m shuttle run.
Procedure : Two lines are drawn parallel to each other with a distance of 10 mts. in between. The subject is required to stand behind one line and two blocks are kept behind the line on the other end.
On the signal ‘Ready’ ‘Go’ subjects should run to pick up one block, run back to the starting line and place the block at the line. He should again run back to pick up the second block and bring it also to the starting line. Two successful trials are given.
Scoring : The best time of the 2 trials to the nearest 10th of a second is the score of the subject.
Write in brief about any three physiological factors determining speed? (6.1) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Three physiological factors that determine speed are :
-
Strength : Strength plays a crucial role in generating power and force during movement, which directly affects speed. Strong muscles allow for more forceful and efficient movements, resulting in faster speed.
-
Flexibility : Flexibility refers to the range of motion around a joint. Good flexibility allows for a greater stride length and a more efficient movement pattern, which can contribute to increased speed.
-
Cardiovascular Endurance : Cardiovascular endurance refers to the ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to deliver oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during prolonged physical activity. Improved cardiovascular endurance allows for better oxygen utilization and energy production, enabling an individual to sustain a higher speed for a longer duration.
Describe the method of sit and reach test. (6.1) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Method of sit and reach test :
- The subject is advised to sit on the edge of the chair.
- One foot is kept at the floor while the other leg is extended with knee straight.
- The subject must keep the back straight and head up.
- The subject has to touch the toe with fingertips.
- If the fingertips do not touch than the distance in between fingertips and is measured and the score will be negative.
List the components of Motor fitness test. Explain any two of them in detail. (6.1) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. The components of the Motor fitness test include agility, balance, coordination, power, reaction time, and speed.
- Agility refers to the ability to change direction quickly and efficiently. It involves the coordination of different body parts and requires good balance and coordination. One test to measure agility is the shuttle run, where the individual has to run back and forth between two points as quickly as possible.
- Balance is the ability to maintain stability and control over the body’s position. It is essential for activities that require maintaining a steady posture, such as standing on one leg or performing yoga poses. The flamingo balance test is a common test to assess balance. In this test, the individual stands on one leg and tries to maintain balance for a certain period of time.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Describe the procedure of SAI Khelo India Fitness Test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The procedure for the SAI Khelo India Fitness Test varies depending on the age group.
For Age Group 5-8 years (Class 1-3) :
- Body Composition (BMI) : Measure the height and weight of the child and calculate the Body Mass Index (BMI).
- Coordination (Plate Tapping) : The child taps a plate as many times as possible in a given time period to measure coordination.
- Balance (Flamingo Balance) : The child stands on one leg and maintains balance for a certain duration to measure balance ability.
For Age Group 9-18 years (Class 4-12) :
- Body Composition (BMI) : Measure the height and weight of the student and calculate the Body Mass Index (BMI).
- 50m Speed Test : The student runs a distance of 50 meters as fast as possible to measure speed.
- 600m Run/Walk : The student runs or walks a distance of 600 meters to measure cardiovascular endurance.
- Sit & Reach Flexibility Test : The student sits on the floor with legs extended and reaches forward as far as possible to measure flexibility.
- Strength Test : The student performs specific exercises to measure strength. Boys perform abdominal partial curl-ups and push-ups, while girls perform modified push-ups.
Write down the procedure to conduct SAI Khelo India Fitness Test in school for 5 to 8 years old students. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The procedure to conduct the SAI Khelo India Fitness Test for 5 to 8 years old students in school includes the following steps :
-
Body Composition (BMI) : Measure the height and weight of the students to calculate their Body Mass Index (BMI). This will help assess their body composition.
-
Coordination (Plate Tapping) : Set up a plate tapping test where the students tap a plate as many times as possible within a given time frame. This will assess their coordination skills.
-
Balance (Flamingo Balance) : Conduct a flamingo balance test where the students stand on one leg and maintain their balance for a certain duration. This will assess their balance abilities.
By conducting these three tests, you can measure and track the fundamental movement skills (FMS) of the 5 to 8 years old students, which are important for their overall physical development.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Define motor development? Discuss in detail the factors that affect motor development in children? (6.1) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Motor development refers to the progression of a child’s ability to control and coordinate their muscles and movements. It involves the development of both gross motor skills (such as crawling, walking, and running) and fine motor skills (such as grasping objects and writing).
There are several factors that can affect motor development in children:
-
Genetic factors : Some children may have a genetic predisposition to certain motor skills. For example, some children may naturally have better coordination or balance than others.
-
Environmental factors : The environment in which a child grows up can greatly impact their motor development. Factors such as access to safe and stimulating play spaces, opportunities for physical activity, and exposure to different types of movement can all influence motor development.
-
Physical health : A child’s physical health can affect their motor development. For example, children with certain medical conditions or physical disabilities may experience delays or difficulties in developing motor skills.
-
Nutrition : Adequate nutrition is important for proper muscle and bone development, which in turn can impact motor development. Malnutrition or deficiencies in certain nutrients can hinder motor development.
-
Stimulation and practice : Motor development requires practice and repetition. Children who are provided with opportunities to engage in physical activities and practice their motor skills are more likely to develop these skills at a faster rate.
-
Socioeconomic factors : Socioeconomic factors, such as access to quality healthcare, education, and resources, can also influence motor development. Children from disadvantaged backgrounds may face barriers to optimal motor development.
Design a training programme for improvement of components of motor fitness. (6.1) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The key components of a training program designed to improve motor fitness include :
-
Agility : This component focuses on the ability to change direction quickly and efficiently. Training exercises may include ladder drills, cone drills, and shuttle runs.
-
Balance : Balance training aims to improve stability and control over body movements. Exercises like single-leg stands, yoga poses, and balance boards can be incorporated into the training program.
-
Coordination : This component focuses on the ability to synchronize movements of different body parts. Training exercises may include ball throw and catching, kicking and stopping a ball, and ladder drills.
-
Power : Power training aims to improve explosive movements and strength. Exercises like jumps, throws, and weight training can be included in the program.
-
Reaction Time : This component focuses on the ability to respond quickly to stimuli. Training exercises may include reaction drills, agility ladder drills, and quick direction changes.
-
Speed : Speed training aims to improve the ability to move quickly over a specific distance. Exercises like sprints, shuttle runs, and interval training can be incorporated into the program.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Measuring Height Accurately : Remove the participant’s shoes, bulky clothing, and hair ornaments, and unbraid hair that interferes with the measurement. Take the height measurement on flooring that is not carpeted and against a flat surface such as a wall with no moulding. Have the participant stand with feet flat, together, and back against the wall. Make sure legs are straight, arms are at sides, and shoulders are level. Make sure the participant is looking straight ahead and that the line of sight is parallel with the floor. Take the measurement while the participant stands with head, shoulders, buttocks, and heels touching the flat surface (wall). Depending on the overall body shape of the participant, all points may not touch the wall. Use a flat headpiece to form a right angle with the wall and lower the headpiece until it frmly touches the crown of the head. Make sure the measurer’s eyes are at the same level as the headpiece. Lightly mark where the bottom of the headpiece meets the wall. Then, use a metal tape to measure from the base on the floor to the marked measurement on the wall to get the height measurement. Accurately record the height to the nearest 0.1 centimeter.
W ________
Ans. –
2. 600 MTR RUN/WALK :
Purpose : Cardiovascular Fitness/Cardiovascular Endurance
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Stopwatch, whistle, marker cone, lime powder, measuring tape, 200 or 400 mts with 1.22 mt (minimum 1 mt) width preferably on a flat and even playground with a marking of starting and fnish line.
Procedure : Participants are instructed to run 600 mts. at the fastest possible pace. The participants begin on signal, “ready, start”. As they cross the fnish line, the elapsed time should be announced to the participants. Walking is permitted but the objective is to cover the distance in the shortest possible time.
Scoring : Time taken for completion (Run or Walk) in min and sec.
W ________
Ans. –
3. PUSH UPS (BOYS)/MODIFIED PUSH UPS (GIRLS) : Purpose : Upper body strength endurance, and trunk stability.
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : Flat clean cushioned surface/Gym mat
Procedure : A standard push up begins with the hands and toes touching the floor, the body and legs in a straight line, feet slightly apart, the arms at shoulder width apart, extended and at a right angles to the body. Keeping the back and knees straight, the subject lowers the body to a predetermined point, to touch some other object, or until there is a 90-degree angle at the elbows, then returns back to the starting position with the arms extended. This action is repeated, and the test continues until exhaustion, or until they can do no more in rhythm or have reached the target number of push-ups. For Girls: push-up technique is with the knees resting on the ground.
Scoring : Record the number of correctly completed pushups.
W ________
Ans. –
6.2 Measurement of Cardio-Vascular Fitness
Multiple Choice Questions
Rock Port one mile test is conducted to measure (6.2) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Cardio-vascular fitness
(b) Senior citizen’s fitness
(c) Vital capacity
(d) Muscular strength
Who developed the Harvard Step Test ? (6.2) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Muller
(b) Miller
(c) Brouha
(d) Jackson
The correct formula for computation of fitness index is (6.2) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)

Ans. (d)
What is the height of the box used by boys in Harvard step test? (6.2) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) 16 inch
(b) 18 inch
(c) 20 inch
(d) 22 inch
Harvard step test is also called the Aerobic Fitness Test. It was developed by Brouha and others in 1943. It is used to measure aerobic fitness by checking the recovery rate. Few students were asked to conduct Harvard step test for their classmates and they were asked to note down the complete details of their aerobic capacity. For conducting tests they required a bench separate for boys 20 inches and girls 16 inches with one stop watch to note down the timing and their recovery rate.
How many times is the reading taken for calculating a long term fitness index ? (6.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 4
What will be the fitness index score of a girl if the test duration was 300 sec and the pulse count (1 min – 1.5 min) was 80. (6.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 73.2
(b) 62.8
(c) 68.1
(d) 85.3
Harvard step is performed to check which kind of fitness? (6.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Cardiovascular
(b) Explosive strength
(c) Muscular strength
(d) Reaction ability
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
What is the formula for computation of the Fitness Index? (6.2) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans.

Calculate the Physical Fitness Index using short formula for a 12 year old boy having completed Harvard Step Test for a duration of 3 minutes and a pulse rate of 54 beats for 1 to 1.5 minute. (6.2) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Use the following formula :
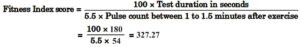
Therefore, the Physical Fitness Index for the 12-year-old boy is 327.27.
What do you mean by Cardiovascular Fitness ? (6.2) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Cardiovascular fitness refers to the ability of the cardiovascular system (heart, blood vessels, and lungs) to supply oxygen and nutrients to the muscles during physical activity.
What is the purpose of Harvard Step-Test ? (6.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The purpose of the Harvard Step Test is to determine aerobic fitness.
What is rockport one mile walk Test? (6.2) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Rockport 1 mile test is a test for measuring cardio-respiratory fitness. The objective of this test is to check/observe the development of the individual’s VO2 max. i.e., maximum volume of oxygen.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Explain the procedure of Harvard step test in detail. (6.2) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Equipment : A bench or box 20” for male or 16” for female, stop watch.
Administration : (1) A tester gives a demonstration of the stepping-up style to be followed by the subjects during the test.
(2) After the command ‘Go’ the stop watch is started and athlete steps-up and down for five minute at the rate of 30 steps per minute.
(3) The stop watch is stopped after 5 minutes and athlete is asked to stop.
(4) The heart-rate is measured between 1 to 1.5 minutes, after finishing the exercise.
(5) The same is repeated after 2 to 2.5 minutes and 3 to 3.5 minutes.
The pulse of all the 3 half minute counts are recorded together and computed in the fitness index.
Write a detail note on Harvard Step Test. (6.2) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Harvard Step Test was developed by Brouha in 1943. It measures the cardiovascular fitness or aerobic fitness by checking the recovery pulse rate. In this test an athlete stands in front of a box or bench which is 16 inches (female) to 20 inches (male) in height and steps up and down for 5 minutes at a rate of 30 steps/minute. The pulse rate is counted 1-1½ minutes, 2-2½ minutes and 3-3½ minutes immediately after the test is administrated.
The fitness Index score is calculated by a simple formula :
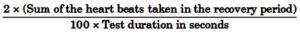
Explain the Rockport test. (6.2) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Rock Port : (Explanation of the test in detail)
(i) Purpose : To measure cardiovascular fitness.
(ii) Equipment required : Stop watch, weighing scale, track.
(iii) Procedure : Measure body weight, run one mile, timing taken, measure heart rate.
(iv) Calculation : Using this data cardiovascular endurance is calculated.
What is the height of a bench for men in Harvard step test ? By using short-term method, calculate the fitness index, if duration of exercise is 300 seconds and heart rate is 70 for 1 to 1.5 minutes. (6.2) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. The height of the bench for men in the Harvard step test is 20 inches.
The fitness index score can be calculated using the following formula :
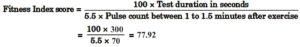
Therefore, the fitness index calculated using the short-term method, with a duration of exercise of 300 seconds and a heart rate of 70 for 1 to 1.5 minutes, is approximately 77.92.
Discuss the procedure of Rockport One Mile Test. (6.2) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Rock Port One Mile Test : The purpose of this test is to measure cardio-vascular fitness or VO2 max (maximum volume of oxygen). The objective of the test is to walk as fast as possible for 1 mile.
Procedure : The test is organised on a track/open area marked for this purpose.
(1) Body weight of the subject is recorded.
(2) Then the subject is made to walk a distance of 1 mile.
(3) Time is recorded when the subject crosses the finish line.
(4) Immediately after finishing the walk, the pulse rate of the subject is recorded for 10 seconds.
(5) VO2 max score can be calculated using the formula.
Write down the formula for calculating fitness index both for short term and long term. (6.2) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans.

Name the tests used to calculate cardiovascular fitness. Write the formula for short term and long term fitness index and calculate long term fitness index if duration of exercise is 300 sec and sum of heart rate is 230. (6.2) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Rockport Walk Test (One Mile Test) The formula used to calculate VO2 max is :
132.853 – (0.0769 × weight) – (0.3877 × age) + (6.315 × gender) – (3.2649 × time) – (0.1565 × Heart Rate)
Harvard Step Test : The Harvard Step test is a test of aerobic fitness, developed by Brouha and his associates (1943) in the Harvard Fatigue Laboratories during WWII for college students. It was a very simple and promising field test for measuring cardiovascular endurance of human beings by using easily available and inexpensive equipment.

Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
What do you know about Harvard Step Test ? Explain its procedure and administration. (6.2) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Cardiovascular fitness is the ability of the heart and lungs to supply oxygen-rich blood to the working muscle tissues and the ability of the muscles to use oxygen to produce energy for movements. Harvard Step Test is a cardiovascular fitness test. It is also called aerobic fitness test.
Administrative procedure of Harvard Step Test
Purpose : To measure the general capacity of the heart and circulatory system for measurement of cardiovascular efficiency.
Time Allotment : 5 minutes
Facilities and Equipment : A stop watch, 20¢¢ height bench, partners, stethoscope, metronome, score sheet.
Procedure : The athlete stands in front of the bench or box. On the command ‘Go’ the athlete steps up and down on the bench or box at a rate of 30 steps per minute (one second up one second down) for 5 minutes (150 steps). Stopwatch is also started simultaneously at the start of the stepping. After that the athlete sits down immediately after completion of the test i.e., after 5 minutes. The total number of heartbeats are counted between 1 to 1.5 minutes after completion of the last step. The heartbeats are counted for 30 seconds period. Again the heartbeats are noted for 30 seconds after the finishing of the test. After that third time the heartbeats are noted after 3 minutes of completion of the test for 30 seconds period. The same foot must start the step up each time, and an erect posture must be assumed on the bench.
Calculation of the Score : The athlete’s fitness index score is calculated with the help of following formula :
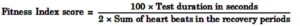
“Students own view relevant to this question also acceptable.”
How the Cardiovascular fitness is measured with the help of “Harvard Step Test” ? Write in details about its administrative procedure. (6.2) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. After completion of administrative procedure of test the data will be put up in the formula for calculation of scores
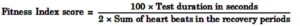
After above calculation fitness rating will be measured.
Procedure : The athlete stands in front of the bench or box (Height of the bench between 18” to 20”). On the command ‘Go’ the athlete step up and down on the bench or box at a rate of 30 steps per minutes (One second up and one second down) for 5 minute (150 steps). Stopwatch is also started simultaneously at the start of stepping after that the athlete sit down immediately after completion of the test i.e., after 5 minutes. The total number of heart beats are counted between 1 to 1.5 minutes after completion of the last step. The heart beats are counted for 30 seconds period. Again heart beats are noted for 30 seconds after the finish of the test. After that 3rd time the heart beats are noted after 3 minutes of completion of the test for 30 seconds period. The same foot must start the step up each time and an erect posture must be assumed on the bench.
Name the test used to measure cardio-vascular fitness and explain its procedure. (6.2) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. The test used to measure cardiovascular fitness is the Harvard Step Test.
The procedure for the Harvard Step Test is as follows :
- The participant steps up and down on a 20-inch step or bench at a rate of 30 steps per minute for a total of 5 minutes.
- After completing the exercise, the participant sits down and the tester takes the participant’s heart rate between 1 to 1.5 minutes.
- The tester notes the duration of the exercise in seconds.
- The fitness index score is determined using the following equation: Duration of the Exercise in Seconds x 100 / 5.5 x Pulse count of 1-1.5 min after Exercise.
- The fitness index score is then compared to the norms to determine the participant’s cardiovascular fitness level.
Norms for the Harvard Step Test are as follows :
- Up to 49 : Poor
- 50-80 : Average
- 81 or above : Good
What is Harvard Step Test? Mention the equipment required to perform it and explain its procedure? (6.2) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Harvard Step Test : The Harvard Step Test is a test used to determine aerobic fitness. It was developed by Brouha in 1943 and was originally designed for young men of college age. The test involves stepping up and down a step for a set period of time.
Equipment required for the Harvard Step Test includes a step or bench that is 20 inches high, a stopwatch, and a wall or tape for marking the wall.
The procedure for the Harvard Step Test is as follows :
- The participant stands next to the wall while a mark is placed on the wall at the level corresponding to midway between the patella (knee cap) and illiac crest (top of the hip bone).
- The participant starts the stopwatch and begins stepping up and down the step at a rate of 30 steps per minute.
- The participant continues stepping for a total of 5 minutes or until exhaustion.
- After the test, the participant immediately sits down and the heart rate is measured for 1 minute.
- The recovery heart rate is recorded and used to calculate the Fitness Index score using the formula :
- Fitness Index = (100 × 5) / (2 × recovery heart rate in beats per minute).
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Harvard Step Test : Harvard step test was developed by Brouha in 1943 for the purpose of measuring physical ftness for work and the ability to recover from work. The test was originally designed for young men of college age. In the original validation of the step test Brouha tested 2200 males.
Procedure : Student will start test at the command “Go” and will step up and down, on and off the wooden block or bench at the rate of 30 steps per minutes for 5 minutes.
Participant is given instructions that on the command ‘up’ or the frst sound of the metronome, he/she should place one foot on the bench; on the second command ‘up’ or the second sound of the metronome, he/she should place both feet fully on the bench with the body erect straightening the legs and back.
Exactly five minutes of steps, on the signal ‘stop’, the participant immediately sits down on the bench. If the student is unable to maintain the pace, then she/he is considered to be exhausted and the test is brought to an end before completion of 5 min.
W ________
Ans. –
6.3 Computing Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Multiple Choice Questions
The test duration for the Harvard fitness test is : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 3 minutes
(b) 4 minutes
(c) 5 minutes
(d) 6 minutes
The Harvard step test is developed by (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Harvard
(b) Brouha
(c) Kansal
(d) SAI
What is BMR ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Bodily Mass Index
(b) Body Mass Index
(c) Boldy Mass Index
(d) Bodley Mass Index
Which parameter is not required to assess the BMR ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Weight
(b) Height
(c) Age
(d) Name
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Write down the procedure of Harvard fitness test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The procedure of the Harvard fitness test is as follows :
- Step height selection : The first step is to select an appropriate step height for the test.
- Warm-up : Before starting the test, it is important to warm up the body.
- Test execution : The test involves stepping up and down on the selected step at a rate of 30 steps per minute for a total duration of 5 minutes.
- Recovery : After completing the 5-minute stepping period, the individual should immediately sit down and remain seated for exactly 1 minute.
- Heart rate measurement : At the end of the 1-minute recovery period, the individual’s heart rate should be measured using a heart rate monitor or by manually counting the pulse for 15 seconds and multiplying by 4.
What is a formula to find out Fitness Index score? And enlist equipment which can be used in Harvard fitness test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The formula to calculate the Fitness Index score in the Harvard fitness test is :
![]()
The equipment that can be used in the Harvard fitness test includes a step or bench that is 20 inches in height, a metronome or timer to maintain the stepping rhythm, and a heart rate monitor or stopwatch to measure the heart rate after the test.
How can BMR be assessed ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The method for assessing Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is through the use of the Mifflin-St Jeor BMR Equation.
- This equation takes into account factors such as weight, height, age, and gender to calculate the number of calories needed to maintain basic life-sustaining functions.
- Other factors that may affect BMR include muscle mass, state of mind, genetics, body composition, and environmental changes.
- To assess BMR, you would need a stadiometer to measure height, a weight machine to measure weight, and pen and paper to record the measurements.
Explain the procedure of any one cardio-vascular fitness test in detail. (6.2) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans.
- Preparation : Ensure that the step used for the test is 20 inches high.
- Have a chair or bench nearby for the participant to sit on after the test.
- Warm-up : Begin with a 5-10 minute warm-up, such as light jogging or brisk walking, to prepare the body for exercise.
- Test Execution : The participant stands facing the step.
- The participant continues stepping for 5 minutes without any breaks, maintaining the pace of 30 steps per minute.
- Recovery : Immediately after the 5 minutes of stepping, the participant sits down on the chair or bench.
- The final result is the participant’s cardiovascular fitness score.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Briefly describe the test used for assessing aerobic fitness. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The purpose of the Harvard Step Test is to determine an individual’s aerobic fitness level.
- The objective of the test is to perform continuous step exercises without a break for a duration of 5 minutes or until exhaustion.
- During the test, the participant steps up and down on a platform or step at a set rhythm or pace.
- The participant is required to maintain the pace and rhythm throughout the test.
- After completing the 5-minute step exercise, the participant’s heart rate is measured immediately at the end of the test and at specific intervals during the recovery period.
- The recovery heart rate is an important indicator of aerobic fitness.
- The test results are calculated using a formula that takes into account the duration of the exercise in seconds, the pulse count at specific intervals during the recovery period, and a constant value.
- The Harvard Step Test is a widely used and reliable test for assessing aerobic fitness.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) : The Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) is the number of calories needed to maintain body function and resting condition. In another words BMR is the number of calories burnt by the body while performing basic life sustaining functions. That is, a person, who does not engage in any work, still requires energy for the functioning of their internal organs. This energy is called Basal Metabolic Rate. Unit of BMR is calculated in Kcal. There are factors that may affect BMR like Muscle Mass, age, state of mind, Gender, Genetics, Body composition etc. Environment changes like change in heat and cold may change the requirement of the body.
Purpose : determine Basal Metabolic Rate
Equipment : Stadiometer, Weight machine, Pen and paper
Procedure : method to measure height and weight is given at BMI
Formula used : The mifflin-St Jeor BMR Equation
Male calculation = (10 * weight(kg.)) + (6.25 * height(cm)) – (5 * age) + 5
Female calculation = (10 * body weight(kg.)) + (6.25 * height(cm)) – (5 * age) – 161
W ________
Ans. –
6.4 Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test
Multiple Choice Questions
Which is not an item of Rikli and Jones Test? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 8 Foot Up and Go
(b) Sit and Reach Test
(c) 6 Minute Walk Test
(d) Arms Curl Test
What is the weight of dumbbell for men in arm curl of Rikli and Jones Test? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 5 pounds
(b) 6 pounds
(c) 8 pounds
(d) 10 pounds
Which test is developed to test fitness in senior citizens? (6.4) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Harvard step
(b) Rikli and Jones
(c) AAHPER
(d) Rockport
Which test is used to test the functional ability amongst senior citizens? (6.4) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Rockport one mile test
(b) Harvard step test
(c) Rikli and Jones test
(d) Fitness index score
What is the test duration for the arm curl test? (6.4) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 1 min
(b) 2 min
(c) 30 sec
(d) Number of repetitions
Identify the test for which this pattern is followed : (6.4) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
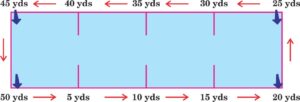
(a) 600 metre
(b) 50 yard dash
(c) 400 metre
(d) 6 minute walk
Identify the odd one. (6.4) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 2
(d) 1
Match the Column :
*Match the following : (6.4) (SQP 2022-23)
|
Column – A |
Column – A |
|
I. Chair stand test |
1. Lower body strength |
|
II. Arm curl test |
2. Aerobic endurance |
|
III. Back scratch test |
3. Upper body strength |
|
IV. Six minute walk test |
4. Upper body flexibility |
(a) I-1, II-3, III-4, IV-2
(b) I-2, II-3, III-1, IV-4
(c) I-1, II-3, III-2, IV-4
(d) I-2, II-3, III-4, IV-1
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
What motor quality does a senior citizen lack, who finds difficulty in tying the shoe laces while sitting on a chair ? (6.4) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Lower body flexibility/flexibility.
Your grandmother feels that she has reduced her upper body flexibility and therefore she wants to test herself. Which test would you suggest to her ? (6.4) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Back Scratch Test.
What test would you suggest to measure upper body strength for aged population ? (6.4) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. The Arm Curl Test is to measure upper body strength for aged populations.
Explain the procedure for Eight Foot Up and Go Test? (6.4) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Procedure : Place the chair next to a wall and mark 8 feet in front of the chair. The subject starts by fully seated, hand resting on knees and feet flat on ground. On command ‘Go’ timing is started and the subject stands and walks as quickly as possible around the cone. Back to initial position and sit on to chair. A person sit down stop time. Perform two trials.
Your grandmother feels she has reduced her upper body flexibility and therefore she wants to test herself. Which test would you suggest her ? (6.4) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. I would suggest the Back Stretch test for assessing your grandmother’s upper body flexibility.
Define functional disabilities. (6.4) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. In functional disability the body organs are affected, normally these faults occurs due to chronic diseases and sometimes the reason may be congenital. It can be categorized :
(a) Hearing (b) Visual (c) Motor (d) Organic
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Explain any two test that form part of the Rikli and Jones Test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Two tests that form part of the Rikli and Jones Test are :
-
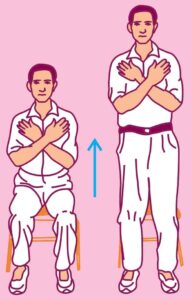
30-Second Chair Stand Test : The participant sits on a chair with their feet flat on the floor and their arms crossed over their chest. On the command “Go,” they stand up and sit back down as many times as possible in 30 seconds. The number of completed chair stands is recorded, and a higher number indicates better lower body strength and endurance.
-
8-Foot Up and Go Test : The participant starts by sitting in a chair and, on the command “Go,” they stand up, walk as quickly as possible around a cone placed 8 feet away, and return to the chair to sit down. The time taken to complete the task is recorded, and a shorter time indicates better agility and balance.
Write down the purpose of all the tests that form a part of Rikli and Jones Test. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The purpose of the tests that form part of the Rikli and Jones Test is to assess the fitness levels of senior citizens.
- These tests are specifically designed to measure various components of fitness, including muscular strength, muscular endurance, cardiovascular endurance, flexibility, speed, coordination, and agility.
- By conducting these tests, health professionals and fitness trainers can evaluate the overall physical fitness and functional abilities of senior citizens, identify areas of improvement, and design appropriate exercise programs to enhance their fitness and quality of life.
List down the test items of Rikli and Jones fitness test and explain the procedure of any one. (6.4) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. The test items of the Rikli and Jones fitness test are :
- Chair Stand Test for lower body strength
- Arm Curl Test for upper body strength
- Chair Sit and Reach Test for lower body flexibility
- Back Scratch Test for upper body flexibility
- Eight Foot Up and Go Test for agility
- Six Minute Walk Test for aerobic endurance
Procedure of Eight Foot Up and Go Test for agility : Place the chair next to a wall (for safety) and the marker 8 feet away in front of the chair. Clear the path between the chair and the marker. The subject starts fully seated, hands resting on the knees and feet flat on the ground. On the command, ‘Go’ stop watch is started and the subject stands and walks (no running) as quickly as possible (and safely) to and around the cone, returning to the chair to sit down. Timing stops as they sit down. Two trials are given to each participant.
What are the components of Rikli and Jones Test? Explain the purpose and procedure of any one test? (6.4) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. The components of the Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test are :
- Chair stand test
- Arm curl test
- Chair sit and reach test
- Back scratch test
- Eight foot up and go test
- Six minute walk test
Six minute walk test :
Purpose : This test helps in early identification of participants at risk. The individuals health and fitness level can be known better with the help of this test or to check aerobic fitness/aerobic endurance of a person.
Procedure : Walking course in a rectangular area of 50 yards or 45.72 mts.

The person has to walk maximum distance as quickly as possible for six minutes. He/she may stop at any time if desires so.
The total distance covered in six minute is recorded to the nearest yards/meters.
Explain the ‘Eight Foot Up and Go’ Test for measuring agility and dynamic balance. (6.4) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Purpose : This test helps to evaluate speed, agility and dynamic balance
Equipment required : A chair about 44 inch high, a stop watch, cone, marker, measuring tape, and an area without any hindrance.
Procedure : Keep a chair next to the wall and place the cone/marker 8 feet away in front of the chair. The participant is initially completely seated, hands resting on the knees and feet. Feet on the ground. On the command go stop watch is switched on and the participant starts walking (no running at all) as quickly as possible towards the cone, turns around and returns to the chair to sit down . Time is noted as he sit down on the chair. Two trials are given per participants.
Illustrate the procedure to measure speed, agility and balance of a senior citizen. (6.4) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. The speed, agility, and balance of a senior citizen can be measured using the Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test. This test includes several components that assess these abilities :
-
Eight Foot Up and Go Test : This test measures agility. The participant is timed as they stand up from a chair, walk eight feet, turn around, and sit back down.
-
30 Second Chair Stand Test : This test measures lower body strength. The participant is asked to stand up from a chair as many times as possible in 30 seconds.
-
Flamingo Balance Test : This test measures balance. The participant stands on one leg and tries to maintain their balance for as long as possible.
Explain the procedure for administering chair sit and reach test and chair stand test in detail. (6.4) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. Chair Sit and Reach Test :
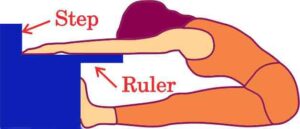
- Equipment : You will need a straight back chair without arms and an 18-inch ruler.
- Set up : Place the chair against a wall or somewhere where it is stabilized.
- Participant Positioning : The participant sits on the chair with one foot flat on the floor and the other leg extended forward with the knee straight.
- Test Execution : The participant tries to touch the toe of the extended foot by bending at the hip and sliding their hands towards the toes.
- Scoring : Measure the distance between the extended long finger and the tip of the toe.
Chair Stand Test :
- Equipment : You will need a straight back chair without arms and a stopwatch.
- Set up : Place the chair against a wall or somewhere where it is stabilized.
- Participant Positioning : The participant sits on the chair with their back straight, arms crossed, and feet firmly on the floor, shoulder-width apart.
- Test Execution : On the command “Go,” the participant stands up completely and then returns back to the initial sitting position.
- Scoring : Count the maximum number of complete stands performed by the participant.
Explain the procedure of six minute walk test. (6.4) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. The subject is asked to walk for six minute around the 50 yards dimensional area. The cones are placed at regular intervals to indicate distance covered. The maximum distance covered in six minutes. Measure the distance covered in six minutes to the nearest metre.
Explain the procedure for administering any three test items of Rikli and Jones Test. (6.4) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. To administer the Chair Stand Test :
- Set up a straight back chair without arms against a wall or in a stable position.
- Encourage the individual to perform as many stands as possible in 30 seconds.
- Count the number of complete stands the individual was able to perform.
- Record the maximum number of complete stands as the score for the Chair Stand Test.
To administer the Arm Curl Test :
- Place a straight back chair without arms against a wall or somewhere where it is stabilized.
- The individual should sit on the chair with their back straight, feet on the floor, and holding a dumbbell with their dominant hand using a handshake grip.
- The individual can perform as many arm curls as possible in 30 seconds.
- Count and record the maximum number of correct arm curls completed in 30 seconds.
To administer the Back Stretch :
- Have the participant stand in a standing position.
- Instruct the participant to place one hand over the shoulder and the other hand in the middle of the back.
- Ask the participant to try to touch or overlap the fingers of both hands behind the back.
- Measure the distance between the tips of the middle fingers.
- If the fingertips touch, the score is zero.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Discuss any three tests for testing the endurance and agility of senior citizens. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Three tests for testing the endurance and agility of senior citizens are :
-
Six-Minute Walk Test : This test measures cardiovascular endurance and overall fitness. The senior citizen is asked to walk as far as possible in six minutes, at a comfortable pace. The distance covered is recorded, and it reflects the individual’s endurance level. This test is suitable for older adults who may not be able to perform high-intensity activities.
-
Timed Up and Go Test : This test assesses agility, balance, and mobility. The senior citizen is instructed to stand up from a chair, walk a short distance, turn around, and sit back down. The time taken to complete the task is recorded. A shorter time indicates better agility and mobility.
-
Stair Climb Test : This test evaluates lower body strength, endurance, and balance. The senior citizen is asked to climb a set of stairs at a comfortable pace. The time taken to complete the task and any difficulties encountered are noted. This test provides insight into the individual’s ability to perform daily activities that involve climbing stairs.
Long Answer Type Question (5 Marks)
Rudra is working on a project to collect data for assessing Physical Fitness amongst Senior Citizens at his residential complex. He plans to administer test for assessing Lower Body Flexibility; Upper Body Flexibility and Lower Body Strength. List the test(s) he should conduct and also explain in detail the procedure of its administration along with scoring system. (6.4) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. To assess lower body flexibility, Rudra can conduct the Chair Sit and Reach Test. The procedure for administering this test is as follows:
- Place the chair against a wall or somewhere where it is stabilized.
- The participant sits on the chair with one foot flat on the floor and the other leg extended forward with the knee straight, heel on the floor, and ankle bent at 90 degrees.
- The participant then tries to touch the toe of the extended foot by bending at the hip and sliding their hands towards the toes.
- To score, the measurement is taken between the extended long finger and the tip of the toe. A minimum of 0.5 inches will be recorded as the score.
- If the participant’s fingers cross the toe, a “+” sign will be indicated before the score. If the participant is unable to touch the toe, a “-” sign will be indicated.
To assess upper body flexibility, Rudra can conduct the Sit and Reach Test. The procedure for administering this test is as follows:
- The participant sits on the floor with their legs stretched out straight ahead. Shoes should be removed.
- The soles of the feet are placed flat against the Sit and Reach box, with both knees locked and pressed flat to the floor.
- The tester may assist by holding down the knees.
- With the palms facing downwards and hands on top of each other, the participant reaches forward along the measuring line as far as possible.
- The hands should remain at the same level, with neither hand reaching further forward than the other.
- After some practice reaches, the participant reaches out and holds that position for one to two seconds while the distance is recorded.
- Make sure there are no jerky movements during the reach.
To assess lower body strength, Rudra can conduct the Partial Curl-Up Test. The procedure for administering this test is as follows:
- The participant lies on their back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor, about 12 inches from their buttocks.
- The arms are crossed over the chest, with the fingertips touching the opposite shoulder.
- The feet are held down by a partner or secured under a stable object.
- On the command “Go,” the participant flexes the elbow or curls the arm with a full range of motion and then returns back to the initial position.
- The dumbbell used for the arm curl should return to a handshake grip in the down position.
- The participant can perform as many arm curls as possible in 30 seconds.
- The maximum number of correct arm curls in 30 seconds will be counted as the score.


Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Rikli and Jones Senior Citizen Fitness Test : The senior citizen’s ftness test (SFT) was developed by Rikli and Jones for older people aged between 60 to 94 years. The purpose of the test was to evaluate functional ability and monitor the physical ftness status of older people and to identify problems and work on the weakness. This test should not be practiced by those who have any medical conditions like chest pain, dizziness, high blood pressure, heart problems etc. This test is economical and easy to administer. The test includes the following items:
1. Chair Stand Test for lower body strength
2. Arm Curl Test for upper body strength
3. Chair Sit and Reach Test for lower body flexibility
4. Back Scratch Test for upper body flexibility
5. Eight Foot Up and Go Test for agility
6. Six Minute Walk Test for aerobic endurance
W ________
Ans. –
2. BACK STRETCH : Purpose : To determine upper body flexibility
Objective : To touch or overlap the finger of the both hands behind the back.
Equipment : 18 inches ruler
Procedure : In standing position participant will place one hand over the shoulder and one hand middle of the back and try to touch or overlap each other.
Scoring : Measurement will be taken by measuring the distance between the tips of the middle fingers. If the fingertips touch, then the score is zero. If they do not touch, measure the distance between the finger tips (a negative score), if they overlap, measure by how much (a positive score).

W ________
Ans. –
6.5 Johnson : Metheny Test of Motor Education
Multiple Choice Questions
Johnson-Metheny Test battery has ____ Items. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 10
Johnson-Metheny Test battery does not consist of ________ motor stunts. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Front Roll
(b) Back Roll
(c) Side Roll
(d) Jumping Full-Turns
Fine motor development is involved in : (6.5) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Sitting
(b) Walking
(c) Standing
(d) Catching a ball
AAHPER General Fitness test consists of : (6.5) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Pull-Ups Boys
(b) Sit-Ups (Flexed Leg), Boys and Girls
(c) Shuttle Run (Boys and Girls)
(d) All of these
Motor development only happens when the child is biologically and mentally ready for it. Motor development refers to the development of movement and various motor abilities from birth till death. It is the ability to move around and manipulate his/her environment. The first stage is marked by extremely rapid growth and development, as is the second stage. By the age of 2 years, this development has begun to level out somewhat. The final stage does not have any marked new development; rather it is characterised by the mastering and development of the skills achieved in the first two stages.
Which factor affecting motor development (6.5) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Biological, environmental, nutrition, opportunity
(b) Obesity, postural deformities, physical activities
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Technique, skill and style
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Explain the procedure of Jumping Half-Turns and Jumping Full-Turns in Johnson-Methney battery. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Jumping Half-Turns in Johnson-Methney battery is as follows :
- The subject starts with their feet on the first 3″ line.
- They jump with both feet to the second 3″ wide line, executing a half turn either right or left.
- They continue jumping to the fourth and fifth 3″ wide lines, executing half turns, right or left alternatively.
Jumping Full-Turns in Johnson-Methney battery is as follows :
- The subject starts with their feet outside the marked area, at about the center of the lane.
- They are required to jump with their feet together to the second rectangular space, executing a full turn with the body either right or left.
- They must land on both feet every time.
Write down the objectives and administration of the flamingo test. (6.5) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Objective : The Flamingo Balance Test is conducted to assess an individual’s ability to balance successfully on a single leg.
Administration :
Infrastructure/Equipment Required : The test can be conducted on a non-slippery even surface.
Procedure :
- The participant stands on the beam and may hold the instructor’s hand for balance if needed to start.
- While balancing on the preferred leg, the free leg is flexed at the knee, and the foot of this leg is held close to the buttocks.
- The stopwatch is started as the instructor lets go of the participant/subject.
- The stopwatch is paused each time the subject loses balance, either by falling off the beam or letting go of the foot being held.
- The number of falls in 60 seconds of balancing is counted.
- If there are more than 15 falls in the first 30 seconds, the test is terminated.
Scoring : The scoring is based on the number of falls in 60 seconds of balancing.

Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
How can we test Motor Educability? Explain in detail. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Motor educability refers to the ability of an individual to learn and improve motor skills.
- Testing motor educability involves assessing the neuromuscular components of fitness that contribute to successful performance in specific motor skills, games, or activities.
- One test that can be used to assess motor educability is the Johnson-Metheny Test.
- This test battery was designed to measure neuromuscular skill capacity and consists of four motor stunts: front roll, back roll, jumping half-turns, and jumping full-turns.
- Boys are required to perform all four stunts, while girls perform three stunts.
- The test area for the Johnson-Metheny Test is a mat area that is 15 feet long and 2 feet wide.
- For each stunt, specific instructions and scoring criteria are provided.
- The same procedure and scoring criteria are followed for the other stunts in the Johnson-Metheny Test.
- The total score is calculated based on the points earned in each stunt.
- By conducting the Johnson-Metheny Test or similar tests that assess motor skills and neuromuscular components of fitness, educators can evaluate an individual’s motor educability and identify areas for improvement.
- This information can be used to design appropriate training programs and interventions to enhance motor skills and overall physical fitness.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
How AAPHER youth fitness test is administered ? (6.5) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Administered of AAHPER Motor Fitness Test. The test was administered on school students of 17 ages.
Pull up for boys : To measure arm and shoulder strength. This test measures the total number of repetitions performed without taking rest on a horizontal bar.
Flexed arm hang for girls :
To measure arm and shoulder strength : The test is administered on a adjustable horizontal bar.
Sit-up : To measure abdominal strength and endurance.
The total number of repetitions of sit-ups is noted in one minute only.
Shuttle run : To measure agility and speed. The subject starts race behind the other line. The best of two trials will be noted.
Standing long jump : To measure power.
The best distance will be taken out of three trials.
50 m dash : To measure speed.
The subject is advised to run 50 yards and the time is recorded nearest to 10th of a second.
600 yard run/walk : To measure endurance.
The subject is advised to run/walk 600 yards and the time is recorded in minutes and second.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Johnson – Metheny Test of Motor Education : Johnson- Metheny Test battery is revised version of Johnson Educability
Test which was designed in 1932. The purpose of the Johnson battery was to measure neuromuscular skill capacity which have ten items. In 1938 Methney studied the test and eliminated six items. The test battery consist of four motor stunts are given below :
I. Front Roll
II. Back Roll
III. Jumping Half-Turns
IV. Jumping Full-Turns
Four stunts are to be performed by the boys and three stunts for girls.
Test Area : Mat area length is 15 feet and it is 2 feet wide. The 15 feet length divided in to ten sections for 18” each. The width of transverse line is ¾” and 3” alternatively. Centre of lines remains 18” apart. Another ¾” wide line is marked lengthwise in the middle of the mat area.
W ________
Ans. –