2.1 Exercise Guidelines of WHO for Different Age Groups
Multiple Choice Questions
Minimum duration of activity should be __________ per week at vigorous intensity in adults above 65 years of age. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 75 minutes
(b) 150 minutes
(c) 300 minutes
(d) 450 minutes
Rate at which the activity is being performed is known as _____________. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Volume
(b) Intensity
(c) Type of activity
(d) Frequency
Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)
Name the motor development stages in children. (2.1) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. (i) Infant (0 to 2 years)
(ii) Early Childhood (2 to 6 years)
(iii) Middle Childhood (7 to 10 Years)
(iv) Latter Childhood (11 to 12 years)
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Write down physical activities exercise guideline for under 5 of age. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Physical Activity Guidelines for Children Under 5 Years of Age:
- Infants should have ample space and open environments for movement and exploration.
- Encourage reading and storytelling during sedentary time, and aim for 14-17 hours of good quality sleep.
- Toddlers should limit sedentary activities to one hour, encourage fundamental physical activities, avoid screen time, and engage in reading and storytelling.
- Children aged 3-4 should aim for at least 180 minutes of daily physical activity, including moderate to vigorous intensity activities.
- Consult with health professionals before undertaking these activities.
Briefly write about physical activities/exercises guidelines for adults above 65 of age. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Physical Activity Guidelines for Adults above 65 of Age:
- Physical activity guidelines for adults over 65 include 150-300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activities, 75-150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activities, two or more days of major muscle strengthening activities, and three or more days of balance-enhancing exercises for older adults with poor mobility.
- It’s crucial for individuals with specific health conditions to take precautions and seek medical advice before attempting recommended levels.
- Gradually increase frequency, duration, and intensity based on individual ability and conditions.
Write about two fundamental skills of your game of choice. (2.1) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
Explain any four general rules of the game/sport of your choice. (chap 2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
What are the major muscles involved in running, jumping and throwing? Explain. (2.1) (CBSE 2018)
Ans.

Write about any six terminologies of your game of choice. (chap 2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
Draw play/field/court table with the specifications of the game/sport of your choice. (chap 2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
Enlist any two stages of growth and development. Explain exercise guidelines for any one of them. (2.1) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. Two stages of growth and development are :
- Children and Youth (5-17 years)
- Adults (18-64 years)
Children and Youth (5-17 years) :
- During this stage, the exercise guidelines focus on improving cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, bone health, cardiovascular and metabolic health biomarkers, and reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- The guidelines recommend progressive activities, starting with simple exercises and gradually increasing the frequency, duration, and intensity.
- The type of activities changes at different stages of growth.
- Children and youth should engage in at least one hour of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity every day.
Explain three gender differences in detail. (2.1) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. (a) Physical Differences : Till the age of 14 the boys and girls are not different in body size. Endocrine system start changes at puberty. In women estrogen plays important role in broadening of pelvis, develops breast size. In men estrogen affect on sperm count.
(b) Strength : The muscular strength in women is found to be lesser than men.
(c) Cardiovascular functions : The size of heart is smaller in women than men. During vigorous workouts men have better cardiac output than women.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Describe physical activities/exercise guidelines for all groups. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The physical activity/exercise guidelines for different age groups are as follows:
- Children and Youth (5-17 years) :
- At least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity every day.
- Progressive increase in frequency, duration, and intensity of activities.
- Aim to improve cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, bone health, and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Adults (18-64 years) :
- At least 150 to 300 minutes of moderate intensity aerobic activity or 75 to 150 minutes of vigorous intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Progressive increase in frequency, duration, and intensity of activities.
- Aim to improve cardiorespiratory fitness, maintain healthy weight and body composition, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
- Older Adults (65 years and above) :
- Similar guidelines as adults, but with a focus on balance-enhancing exercises to prevent falls.
- Activities should be done on 3 or more days per week.
- Aim to improve cardiorespiratory fitness, maintain healthy weight and body composition, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases and cognitive decline.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
How physical activities are helpful for children with special need ? Explain strategies to make physical activities assessable for them. (2.1) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Physical activities are very helpful for children with special needs.
(1) Physical improvement
(2) Mental improvement
(3) Cognitive benefits
(4) Social interactions
(5) Self-esteem
Physical improvement : Exercise improve muscle strength coordination and flexibility. They help combat obesity and reduce risk of life style diseases like diabetes, asthma etc. Bone density improves due to exercises. Children experience better balance, improve motor skills and become aware of their body and become physically fit.
Mental improvement : General mood of children improves and children tend to become happier.
Social interactions : Physical activities improve social interactions and improve the psychological and emotional ability of such children.
Cognitive benefits : Sports are a learning tool for self-regulation and decision making. Children learn to communicate when they get to interact with other children.
Self-esteem : Confidence is developed which results in improvement of positive self-image such children start feeling that they can also contribute to the growth of society.
Strategies :
(1) Different playing rules
(2) Specialised equipment
(3) Trained educators
(4) Individual needs
(5) Regular medical check-ups
(6) Safety supervision
(7) Positive learning environment
(8) Modified games (etc.)
Describe exercise guidelines at different stages of growth in children. Give suitable examples for every stage. (2.1) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Different stages of growth in children
Infancy (1-2 years)
- Gross motor developmental skills
- Head control
- Sitting
- Crawling
- Moving arms, legs
- Reaching to various object
- Infants should be provided with objects, toys and games
- Throwing, catching and kicking a ball (Explain any one)
Early Childhood (3-7 years)
- Fine motors developmental skills i.e., coordinative activities.
- Movement skills (throwing, jumping, catching or kicking the ball)
- Emphasis on participation and not on competition.
- Structured as well as unstructured physical activities should be performed daily for at least sixty minutes daily.
- They may be allowed to watch quality programmes on T.V. for one to two hours. (Explain any two)
Later childhood (8-12 years)
- Stunts, throwing, jumping, catching, running etc. so that they can acquire body control, strength and coordination.
- Participation in organized or team games which aim to develop social consciousness in them.
- Children should be introduced to competitive sports and taught the basic rules of sports competition.
- Introduction of concept of endurance, strength, agility, coordination and balance. (Explain any two)
Exercises have numerous physiological and physical benefits on children. Explain in detail. (2.1) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Physical benefits :
- Good motor development
- Posture alignment and good body image, improves physical appearance
- Reduces fatigue
- Increases alertness
- Weight management, prevents obesity
- Increases bone density and prevent from osteoarthritis
- Tolerance of hot and cold climatic conditions.
- Improves muscle Tone and minimizes the risk of injuries
- Improves neuromuscular co-ordination.
Physiological benefits :
- Stronger immunity, reduces the chances of diseases
- Increase lactic acid tolerance
- Increase in size of fibres and connective tissues
- More blood supply
- Density of blood vessels increases
- Myoglobin increases.
- Oxidation of carbohydrate increases
- Improves muscle composition (Any 5 points to be explained)
What is the difference between Running and Walking ? Explain mechanical analysis of ‘Running’. (2.1) (CBSE 2017)
Ans.
|
Running |
Walking |
|
|
(Any two differences)
Mechanical analysis of running :
(1) Stance phase
- Initial contact stage
- Absorption stage
- Mid stance stage
- Propulsive stage
(2) Swing phase
Explain ‘weight training’ as one of the oldest methods for development of strength. Describe its advantages and disadvantages. (2.1) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Weight training are those exercise which are designed to strengthen specific muscles by causing them to overcome a fixed resistance, usually in the form of bar-bells or dumb-bells.
Advantages of weight training :
(i) Help in getting good shape
(ii) Increase in muscle strength
(iii) Increase in bone strength
(iv) Better appearance and correct body posture
(v) Reduces stress and tension
(vi) Best means of providing fitness (Explanation of any two)
Disadvantage of weight training :
(i) Risk of injuries
(ii) Less flexibility
(iii) Risk of doing in early age (Explanation of any two)
Elucidate the meaning of motor development in childhood. Discuss in detail about various factors affecting motor development. (2.1) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Motor development refers to changes in children’s ability to control their body’s movements like walking, jogging, running, climbing, jumping, throwing etc.
Factors affecting motor development :
(1) Growth of the child
(2) Gender
(3) Biological factors
(4) Environmental factors
(5) Immunization
(6) Nutrition
(7) Cultural factors
(8) Physical activities
(9) Opportunities
(10) Sensory impairments
(11) Postural deformities
(12) Obesity (Any four to be explain)
Write in details about the physical and physiological advantages of physical exercise during the childhood stages. Explain any Five. (2.1) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. The advantages are :
(a) Prevents and reduce obesity
(b) Develops bones
(c) Muscle development
(d) Prevention from diseases
(e) Increased blood flow
(f) Develop grace and efficiency in movement/ motor development
(g) Strengthens the heart
(h) Strengthens the lungs
(i) Improves energy levels
(j) Changes in brain structure
(k) Reduces blood sugar level
(l) Improves digestive system
(m) Neuromuscular co-ordination
Differentiate mechanically between walking and running. Explain in detail mechanical analysis of walking. (2.1) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. (A) Difference between walking and running
|
Running |
Walking |
|
|
(B) Walking mechanical analysis in details :
(1) Stance phase
- Heel strike
- Early flat-foot
- Late flat-foot
- Heel rise
- Toe-off.
(2) Swing phase (Explain any four)
“Involvement in physical activities for longer period of time with moderate intensity can improve the quality of life.” Justify your answer. (2.1) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Involvement in physical activities for a longer period of time with moderate intensity can improve the quality of life in several ways :
-
Physical Health : Regular physical activity helps to lower the risk of various chronic diseases such as heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, colon and breast cancers. It also helps to maintain a healthy weight, improve cardiovascular fitness, and enhance bone health.
-
Mental Health : Physical activity has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression, anxiety, and stress. It can also improve mood, boost self-confidence, and enhance overall mental well-being.
-
Cognitive Function : Engaging in physical activities has been linked to improved cognitive function, including better memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. It can also help to reduce the risk of cognitive decline and improve brain health as we age.
-
Social Interaction : Participating in physical activities often involves social interaction, whether it’s playing team sports, joining fitness classes, or exercising with friends and family. This can help to build social connections, improve social skills, and enhance overall social well-being.
-
Overall Quality of Life : Regular physical activity can increase energy levels, improve sleep quality, and enhance overall quality of life. It can also provide a sense of accomplishment, purpose, and enjoyment, leading to a more fulfilling and satisfying life.
It’s important to note that the benefits of physical activity are not limited to just moderate intensity. Engaging in any form of physical activity, whether it’s moderate or vigorous, can have positive effects on health and well-being.
What is SGFI? Explain its organizational set-up with functions. (chap 2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
Briefly write historical development of the game/sport of your choice. (chap 2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. —
What are the benefits of physical activity for children with special needs ? (2.1) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. —
Create a table and explain : Different Stages of Growth and Development; Characteristics of Development and Exercise Guidelines. (2.1) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Different stages of a human life :
- Infancy (1-2 years)
- Toddler (2-4 years)
- Early school age (5-7 years)
- Middle school age (8-12 years)
- Early adolescence (13-17 years)
- Later adolescence (18-25 years)
- Early adulthood (25-30 years)
- Middle adulthood (30-50 years)
- Later adulthood (50 and up)

Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Children and Youth 5-17 Years : Children and youth with a specific medical condition or disability may follow these recommendations under advice of a medical official or with the help of the school special education teacher. Activities should be done in a progressive manner, for example starting the session with simple exercises to complex, gradually increasing the frequency, duration and intensity of the activities. There are various stages of growth in this age group, wherein at every stage the type of activities changes. The chief aim of activities during this age group is to improve cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness, bone health, cardiovascular and metabolic health biomarkers and to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Activities should be done in a progressive manner, starting the session with simple exercises to _____.
Ans. complex
At every stage of growth, the type of activities _____.
Ans. changes
The chief aim of activities during this age group is to improve _____ and muscular fitness.
Ans. cardiorespiratory
By gradually increasing the frequency, duration, and intensity of the activities, the goal is to improve cardiovascular and metabolic health _____ and reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
Ans. biomarkers
Children and youth with a specific medical condition or disability may follow these recommendations under advice of a medical official or _____.
Ans. with the help of the school special education teacher
2. Adults 18-64 Years : These recommendations are relevant to healthy adults aged between 18 to 64 irrespective of gender, race, ethnicity or socio-economic status. Adults/youth with disabilities may follow these recommendations with adjustment as per capacity or limitations. An adult having any medical condition should follow the advice of medical official. Activities should be done in a progressive manner, for example, start the session with simple exercises and move to complex, gradually increasing frequency, duration and intensity of the activities.
An adult having any ____________ should follow the advice of medical official.
Ans. medical condition
These recommendations are relevant to healthy _______ aged between 18 to 64.
Ans. adults
Activities should be done in a __________ manner.
Ans. progressive
Adults/youth with ____________ may follow these recommendations with adjustment as per capacity or limitations.
Ans. disabilities
Start the session with ________ exercises and move to complex.
Ans. simple
3. Older Adults 65 Years and Above : These recommendations are relevant to healthy older adults aged above 65 years, irrespective of gender, race, ethnicity or socio-economic status. These recommendations are also relevant for individuals suffering from chronic NCD conditions. Adults, youth with disabilities may follow these recommendations with adjustment as per capacity or limitations. Individuals with specific health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, may need to take extra precautions and seek medical advice before trying to achieve the recommended levels of
physical activity for older adults. Activities should be done in progressive manner, for example, starting the session with simple exercises and moving to complex, gradually increasing frequency, duration and intensity of the activities as per their ability and as conditions allow.
These recommendations are relevant to healthy _____ adults aged above 65 years.
Ans. older
Individuals suffering from chronic NCD conditions may follow these recommendations with adjustment as per _____ or limitations.
Ans. capacity
Individuals with specific health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes, may need to take extra precautions and seek medical advice before trying to achieve the recommended levels of physical activity for _____ adults.
Ans. older
Activities should be done in _____ manner.
Ans. progressive
Starting the session with simple exercises and moving to complex, gradually increasing frequency, duration and intensity of the activities as per their ability and as conditions _____
Ans. allow
2.2 Posture
Multiple Choice Questions
Deformity of the legs is known as (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Scoliosis
(b) Lordosis
(c) Knock knees
(d) Kyphosis
Lordosis is a problem of the (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Lower back
(b) Middle back
(c) Upper back
(d) Shoulders
Scoliosis is a postural deformity related to (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Muscles
(b) Shoulders
(c) Legs
(d) Spine
Kyphosis is a deformity found in (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Shoulders
(b) Lumber region
(c) Hips
(d) Thoracic region
Scoliosis is a postural deformity related with (2.2) (CBSE 2020)
(a) foot
(b) leg
(c) vertebral column
(d) hand
Which one of the following is not the corrective measure for round shoulders ? (2.2) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
(a) Hanging on horizontal bars
(b) Chakrasana
(c) Vajrasana
(d) Dhanurasana
Which of the following is not a spinal curvature deformity? (2.2) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Kyphosis
(b) Scoliosis
(c) Lordosis
(d) Flatfoot
Gomukhasana and padmasana are performed to rectify which postural deformity? (2.2) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Flatfoot
(b) Scoliosis
(c) Knock-knees
(d) Bow legs
What is the name of the postural deformity caused due to increase in the curve at the lumbar region? (2.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Knock knees
(b) Bow legs
(c) Kyphosis
(d) Lordosis
Which postural deformity has Convexities right or left? (2.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Flat foot
(b) Knock knees
(c) Kyphosis
(d) Scoliosis
Which of the following is not a spinal curvature deformity? (2.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Kyphosis
(b) Scoliosis
(c) Lordosis
(d) Flatfoot
Which exercise should be done to cure this deformity? (2.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Skipping
(b) Walking on heels
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Hanging on horizontal bar
Sandy is diagnosed with postural adaptation of the spine in lateral direction. The curve is identified as convexity right. It happened due to Sandy’s underdeveloped legs and carrying heavy loads on one side only.
What kind of postural deformity doctors found in Sandy? (2.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Scoliosis
(b) Kyphosis
(c) Bow Legs
(d) Flatfoot
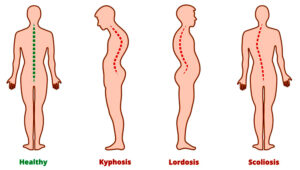
Posture plays a very significant role in our daily activities. Correct posture means the balancing of the body in an accurate and proper manner. Various types of postural deformities can be identified in individuals. (2.2)
From the above given picture, the deformities seen on the left most is caused due to deficiency of which nutrient? (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) Iron
(b) Calcium
(c) Vitamin D
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Identify the asana : (2.2) (SQP 2022-23)
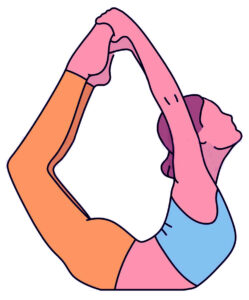
(a) Paschimottanasana
(b) Halasana
(c) Vajrasana
(d) Dhanurasana
Which asana amongst these can be done just after having meals? (2.2) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) Bhujangasana
(b) Dhanurasana
(c) Vajrasana
(d) Ardhmatsyendrasana
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Which type of deformity is ‘Kyphosis’ ? (2.2) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Kyphosis implies an increase of a backward posterior curve or a decrease of a forward curve. It is also called round upper back. Depression of chest is common in Kyphosis.
What is an abnormal curvature of spine at front termed as? (2.2) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Lordosis
What is the main cause of ‘Scoliosis’? (2.2) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans.
- Injury of the bones and joints
- Faulty posture
- Weakness or paralysis of the muscles
- Diseases like TB or Rickets
- Carrying/lifting heavy loads
- Heredity (Any one)
What is Lordosis ? Explain. (2.2) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Lordosis is a postural deformity of the spine. In this deformity, the spine curvature is increased inward in the lumbar region.
State the common postural deformities. (2.2) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. (i) Round shoulder
(ii) Spinal curvature
(a) Khyphosis (b) Lordosis (c) Scoliosis
(iii) Knock-knees
(iv) Bow legs
(v) Flat foot (Any two)
Suggest two exercises for correcting flat-foot. (2.2) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Exercise for correcting flat foot :
(1) Picking up marbles with toes
(2) Place a towel under the feet and role the towel with toes towards body.
(3) Sand walk
(4) Perform up and down the heels
(5) Walking on toes/heels/on inner and outer side of feet
(6) To perform Vajrasana
(7) Jumping on toes/skipping rope (Any two points from the list)
Suggest any two free hand exercises for correcting round shoulder? (2.2) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. (1) Keep your tips of fingers on your shoulder and encircle your elbow clockwise and anticlockwise direction for same number of times.
(2) Pull the shoulders backward and see upward.
(3) Chakra Asana, Dhanur Asana, Bhujang Asana
(4) Hold the hanging position on horizontal bar for sometime (Any two)
Explain correct sitting posture. (2.2) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. • The correct sitting posture involves keeping your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and feet flat on the floor.
• It is important to sit with your weight evenly distributed on both hips and avoid crossing your legs.
What do you understand by postural deformities ? (2.2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. • Postural deformities refer to abnormal alignments or positions of the body that deviate from the ideal posture.
• Corrective measures, such as exercises and proper body alignment, are often recommended to address these deformities.
What is flat foot ? (2.2) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Flat foot, also known as pes planus or fallen arches, is a condition where the arch of the foot is either very low or completely absent, causing the entire sole of the foot to touch the floor in a standing position.
Name any two postural deformities. (2.2) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. Two postural deformities mentioned in the context are Lordosis and Scoliosis.
What do you mean by correct posture ? (2.2) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. • Correct posture refers to the alignment of the body in such a way that puts the least amount of stress on the joints and muscles.
• It involves having all body parts properly aligned, including the spine, shoulders, hips, and neck.
What is scoliosis ? (2.2) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. • Scoliosis is a position in which the spine is tilted to either side of the body.
• In this disorder, the spine bends, twists or rotates in a way that it makes a C or an S shape.
What is a good posture? (2.2) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. • Good posture refers to the alignment of the body in a way that puts the least amount of stress on the joints and muscles.
• Good posture while sitting, studying, writing, standing, and walking helps to prevent fatigue, maintain productivity, and reduce the risk of postural deformities.
Name the deformity for which horse riding can be used as corrective measure. (2.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. Horse riding can be used as a corrective measure for Genu valgum (knock knees).
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What is meant by Round Shoulders? Mention a few exercises to correct it. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. • Round shoulders is a postural deformity in which the shoulders are bent forward from the ideal alignment, giving a narrow curve to the upper back.
• It can lead to other postural deviations such as hyperkyphosis (hunchback) and anterior head carriage (forward head posture).
• To correct rounded shoulders, some exercises that can be helpful include:
- Chest stretches
- T stretch
- Wall stretch
- Handclasp stretch
- Planks, pull-ups, and reverse shoulder stretches:
What is the Lordosis? Write in brief. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Lordosis is a spinal deformity characterized by an excessive inward curvature of the lower back. It is also known as sway back.
- Lordosis can cause pain and discomfort, and if left untreated, it can become more serious.
- In some cases, the cause of lordosis is unknown.
- Treatment for lordosis may include exercises to strengthen the back muscles, physical therapy, swimming, using exercise/gym balls or bands, and practicing yoga asanas like Dhanurasana, Chakrasana, and Bhujangasana.
- Weight loss, maintaining good posture, and a balanced diet are also beneficial in reducing the problem of lordosis.
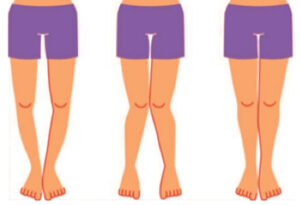
Write in brief the causes and symptoms of Knock Knees. CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The causes of Knock Knees, also known as Genu valgum, can include an injury or infection in the knee or leg, rickets, severe lack of vitamin D and calcium, obesity, or arthritis in the knee.
- It can also be a natural misalignment that occurs in early childhood and usually corrects itself by the age of 7-8.The symptoms of Knock Knees include the knees turning inward, causing them to touch or knock against each other while there is a gap of 3-4 inches between the ankles.
- In some cases, there may be stiff joints, knee pain, walking with a limp, and pain in the hips, ankles, or feet.
Explain corrective measures for Flatfoot. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The corrective measures for flatfoot include exercises like walking, standing or jumping on toes and heels in all four directions, skipping rope, and strengthening the muscles of the foot to help develop the arch.
- Activities like picking up marbles with toes and writing numbers in the sand with the toes can also help in developing the arch.
- Yoga asanas like Adhomukhsavasana performed in Surya Namaskar, Vajrasana, and other therapeutic massages are also helpful in developing the arch.
Identify the following postural deformities and write their names : (2.2) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
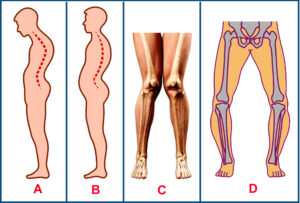
Ans. —
What are the advantages of correct posture ? (2.2) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Maintaining correct posture has several advantages:
- Reduced stress on joints and muscles : When the body is properly aligned, it puts less strain on the joints and muscles, reducing the risk of pain, stiffness, and injury.
- Improved physical and mental well-being : Proper posture helps to prevent fatigue and promotes a sense of physical and mental well-being.
- Prevention of postural deformities : Maintaining good posture can help prevent the development of postural deformities such as lordosis, scoliosis, and round shoulders.
- Enhanced appearance and confidence : Good posture gives a more upright and confident appearance, which can positively impact self-esteem and how others perceive you.
Design a free hand four exercises programme for curing round shoulders. (2.2) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans.Here is a free hand exercise program that can help in correcting rounded shoulders:
- Chest Stretch : Stand tall with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Gently lift your arms up and away from your body, keeping your back straight.
- Hold this stretch for 20-30 seconds, feeling a stretch in your chest and shoulders.
- Repeat 3-4 times.
- T Stretch : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Extend your arms out to the sides, forming a “T” shape.
- Wall Stretch : Stand facing a wall, about an arm’s length away.
- Planks : Start in a push-up position, with your hands directly under your shoulders and your body in a straight line.
Write about the deformities of spinal curvature? (2.2) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Deformities of spinal curvature : Lordosis, Scoliosis, Kyphosis.
- The deformities associated with spinal curvature are Lordosis and Scoliosis.
- Lordosis is a spinal deformity in which the lower back curves inward excessively, creating an exaggerated arch in the lower back.
- Scoliosis is a spinal deformity in which the spine curves sideways, forming either a C or an S shape.
Explain any three corrective measures for ‘scoliosis’. (2.2) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. Three corrective measures for scoliosis are wearing a brace to stop the curve from worsening, undergoing surgery to straighten the spine, and performing exercises like hanging on horizontal bars and swinging on the opposite side of the C-shaped curve.
What do you mean by ‘round shoulders’ ? Suggest any four exercises as corrective measures. (2.2) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Round shoulders : It is the postural deformity in which shoulders are projected forward. In this deformity the shoulders become round and sometimes they seem bent forward.
Corrective exercises :
(1) Perform yogic asanas such as Dhanurasana, Bhujangasana, Chakrasana and Ushtrasana.
(2) Backward bending exercises.
(3) Shoulder rotation.
(4) Sit on chair and stretch both hands backward, hold each other behind your back.
(5) Holding horizontal bar. (Any four)
Correct posture is a reflection of a good personality. Comment. (2.2) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Correct posture plays a significant role in relation to personality.
- Confidence : Maintaining good posture can make a person appear more confident and self-assured.
- Presence : Correct posture helps in creating a strong presence.
- It makes a person stand out in a crowd and gives them a commanding presence.
- Professional Image : In professional settings, having good posture is often associated with professionalism and competence.
- It gives the impression of being attentive, focused, and capable, which can enhance one’s professional image and career prospects.
- Mental Well-being : Maintaining good posture can also have a positive impact on mental well-being.
- This, in turn, can contribute to a more positive and confident mindset.
What are the causes of bad posture ? (2.2) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. The factors that contribute to bad posture include heredity, disease, injury, poor habits, improper clothing, unhygienic living conditions, improper diet, improper exercise, lack of exercise, obesity, and socio-economic status.
What are the advantages of keeping correct posture ? Explain. (2.2) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Maintaining correct posture has several advantages.
- It helps to prevent fatigue by reducing stress on joints and muscles.
- Good posture also promotes better productivity and efficiency in work.
- It can contribute to a physically and mentally stress-free condition.
- Additionally, maintaining good posture can help prevent postural deformities caused by factors such as heredity, disease, injury, poor habits, improper clothing, unhygienic living conditions, improper diet, improper exercise, lack of exercise, obesity, and socio-economic status.
What is scoliosis? Mention any two corrective exercises for it. (2.2) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans.
- Scoliosis is a condition where the spine is tilted to either side of the body, creating a sideways curvature.
- Two corrective exercises for scoliosis are hanging on horizontal bars and swinging, and performing Trikonasana and Adhomukhasana in yoga.
- These exercises can help to strengthen the muscles and improve the alignment of the spine.
Personality and posture are the two opposite sides of the same coin. Comment. (2.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans.
- There is a relationship between personality and posture, although it is not fully understood.
- Some studies suggest that certain personality traits may be associated with specific postural characteristics.
- For example, individuals with confident and assertive personalities may exhibit an upright and open posture, while individuals with shy or introverted personalities may have a more closed or slouched posture.
- However, it is important to note that posture can also be influenced by factors such as muscle strength, body structure, and habits, so it is not solely determined by personality.
Enlist the spinal postural deformities? Explain the causes of kyphosis and the precautions to avoid it. (2.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans.
- The spinal postural deformities mentioned in the context are scoliosis, bow legs (genu varum), and lordosis.
- Lordosis, also known as sway back, is a spinal deformity where the angle of the lower back is reduced, leading to an exaggerated concavity of the lumbar region of the spine.
- In some cases, the cause of lordosis is unknown.
- To avoid kyphosis, which is an excessive forward curvature of the upper back, it is important to maintain good posture while sitting, standing, and walking.
- Regular exercise, especially exercises that strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility, can also help prevent kyphosis.
Explain the physical activities that can be undertaken to correct flatfoot deformity. (2.2) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. Exercises and physical activities can be undertaken to correct flatfoot deformity. Some of these activities include :
- Walking, standing, or jumping on toes and heels in all four directions : This helps to strengthen the muscles of the foot and develop the arch.
- Skipping rope : Jumping rope helps to strengthen the muscles of the foot and improve the arch.
- Picking up marbles with toes : This activity helps to strengthen the muscles of the foot and improve the arch.
- Writing numbers in the sand with the toes : This activity helps to improve the flexibility and strength of the foot muscles, which can contribute to developing the arch.
- Yoga asanas like Adhomukhsavasana performed in Surya Namaskar and Vajrasana : These yoga poses help to stretch and strengthen the muscles of the foot, promoting the development of the arch. (any three)
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Explain any five postural deformities with their corrective measures. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Here are five common postural deformities and their corrective measures :
- Knock knees (Genu valgum) : Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knees, such as squats and lunges. Wearing orthotic devices or shoe inserts may also help.
- Flat foot (Pes planus) : Arch support insoles or orthotic devices can provide support. Strengthening exercises for the muscles of the feet and ankles, such as toe curls and calf raises, can also be beneficial.
- Round shoulders (Kyphosis) : Strengthening exercises for the muscles of the upper back, such as rows and shoulder retractions. Stretching exercises for the chest muscles can also help improve posture.
- Lordosis (Sway back) : Strengthening exercises for the abdominal and lower back muscles, such as planks and back extensions. Stretching exercises for the hip flexors and hamstrings can also be beneficial.
- Scoliosis (Sideways curvature of the spine) : Physical therapy exercises to strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve posture. In severe cases, bracing or surgery may be necessary.
Describe corrective measures of some common spinal postural deformities. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Common spinal postural deformities such as Lordosis, Kyphosis, and Scoliosis, the following corrective measures can be taken:
- Lordosis :
- Strengthening exercises for the back muscles.
- Physical therapy.
- Swimming.
- Exercise/gym ball exercises.
- Exercises with bands.
- Yoga asanas like Dhanurasana, Chakrasana, and Bhujangasana.
- Using a flat bed with a thin pillow while sleeping.
- Kyphosis :
- Exercises to strengthen the upper back muscles.
- Stretching exercises for the chest muscles.
- Physical therapy.
- Swimming.
- Yoga asanas like Bhujangasana, Dhanurasana, and Shalabhasana.
- Using a flat bed with a thin pillow while sleeping.
- Scoliosis :
- Physical therapy.
- Exercises to strengthen the core muscles.
- Bracing (in severe cases).
- Surgery (in severe cases).
- Yoga asanas like Dhanurasana and Halasana.
- Maintaining a good posture.
- Weight reduction.
- Balanced diet.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Explain ‘Flat Foot’ and ‘Knock Knees’ and also suggest corrective measures for both postural deformities. (2.2) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. • Flat foot : It is a deformity in the feet. There is no arch in the foot and the foot is completely flat which may cause pain in the foot. An individual with this deformity faces problem in standing, walking, jumping and running.
Corrective measures :
- Jumping on toes
- Rope skipping
- Walk on toes
- Stand up and down on heels
- Walk on heels
- Walking on inner and outer side of foot
- Perform Vajrasana and Yogic exercises.
• Knock knees : It is a postural deformity in which both the knees touch or overlap each other in normal standing position. Due to this deformity an individual usually faces difficulty in walking.
Corrective measures :
- Horse riding is one of the best exercise
- Keep a pillow between the knees and stand for some time every day.
- Use of walking caliper may be beneficial.
- Perform Padmasana and Gomukhasana.
Explain the causes and corrective measures for knock-knee and scoliosis. (2.2) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Causes of knock-knee :
- Faulty standing posture
- Rickets
- Obesity
- Weakness of muscles and ligaments of knee region.
- Wearing improper shoes.
- Carrying heavy weight at early age.
- Deficiency of vitamin-D, calcium and phosphorus. (Any two points with explanation.)
Corrective measures for knock-knee :
- Horse riding
- Padmasana and Gomukhasana
- Keeping pillow between the knee while standing
- Use of walking calipers
- Walking along a straight line with knee facing outwards
- Side kicking in football
- Supplements as advised by doctor (Any three points with explanation.)
Causes of scoliosis :
- Weakening of spinal muscle in one side
- Due to infantile paralysis, rickets
- Heavy load on shoulder
- Due to some diseases or injuries such as cerebral palsy
- Due to poor light
- Wrong habit of sitting/Wrong sitting posture
- Partial deafness
- May be congenital or acquired abnormalities of vertebras (Any two points)
Corrective measures for scoliosis :
- Breast stroke in swimming
- Pull-ups/Hanging on Horizontal Bar
- Banding exercise on the opposite side of ‘C’ curve
- Flexion, extension, side ward flexion of the spine (Any three points)
What are the causes of ‘Flat-Foot’ and ‘Knock-Knees’ ? Suggest physical activities as corrective measures for these deformities. (2.2) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Cause of flat-foot :
- Genetic
- Weak muscles
- Over weight
- Improper foot wear
- Carrying heavy weight
- Forcing child to stand up at very early stage.
Cause of Knock-knee :
- Chronic illness
- Deficiency of calcium, vitamin-D
- Mal nutrition
- Flat-foot
- Carrying heavy weight at early age (Any two causes)
Corrective measures for flat-foot :
- Walking on heels
- Walking on toes
- Rope skipping
- Jumping on toes
- Perform vajrasan, Tadaasana
- Picking pebbles by toes
- Running on inclined plane/stairs
- Cycling
Corrective measures for knock knees :
- Horse riding
- Kicking football by instep kick
- Putting a pillow between the knees
- Padmasana, Gomukhasana
- Walking on inner side of the foot (Any three corrective measures)
What do you mean by correct posture ? Explain the standing and sitting postures. What are the causes of bad posture ? (2.2) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Correct posture means the balancing of body in accurate and proper manner while sitting, standing, reading, writing or during any other action of body.
Explanation of sitting and standing posture :
Standing : Heals together, toes apart, body erect. Knee straight, chin inside, chest forward, belly backward, body weight equally on both feet.
Sitting : Hips as far back as possible on the chair, legs rest on the floor, thigh horizontal head, spinal column, shoulder and hips should be in straight line and erect.
Causes of bad posture :
- Improper diet
- Heredity
- Accident
- Disease
- Obesity
- Due to improper exercise,
- Nature of job
- Fatigue
- Wearing tight clothes
- Unsuitable furniture
- Muscle weakness
- Unawareness of correct footwear/Improper footwear. (Explain any two)
What are the causes of Bad Postures ? Write in brief. (2.2) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Causes of bad posture are as follows :
(1) Hereditary/Congenital
(2) Improper diet/Low nutritional diet
(3) Muscle weakness/Poor core stability
(4) Joint stiffness/Very high toned muscle
(5) Accident/Diseases
(6) Lifestyle/Fashion
(7) Lack of education/awareness of correct posture
(8) Delicacy and imitation
(9) Bad habits
(10) Obesity
(11) Fatigue
(12) Lack of rest and sleep
(13) Lack of proper exercise
(14) Unsuitable furniture/poor ergonomic
(15) Poor way of carrying weight (Any three to be explain)
Suggest physical activities as corrective measures for correcting round shoulders. (2.2) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. Some physical activities that can be suggested as corrective measures for correcting round shoulders include :
-
Chest stretches : Stretching the chest muscles can help to counteract the forward rounding of the shoulders. This can be done by standing in a doorway and placing your forearms on either side of the door frame, then leaning forward gently.
-
T stretch : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and raise your arms out to the sides, forming a “T” shape. Gently squeeze your shoulder blades together while keeping your arms straight.
-
Wall stretch : Stand with your back against a wall and your feet about 6 inches away from the wall. Place your forearms against the wall at shoulder height and gently lean forward, feeling a stretch in your chest and shoulders.
-
Handclasp stretch : Interlace your fingers behind your back and gently lift your arms away from your body, feeling a stretch in your chest and shoulders.
-
Planks : Planks are a great exercise for strengthening the core and improving posture. Start in a push-up position, with your hands directly under your shoulders and your body in a straight line. Hold this position for as long as you can, focusing on keeping your shoulders pulled back and down.
-
Pull-ups : Pull-ups can help to strengthen the muscles in your upper back and improve posture. If you don’t have access to a pull-up bar, you can use resistance bands or a TRX suspension trainer to simulate the movement.
-
Reverse shoulder stretch : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and extend your arms straight out in front of you. Cross your arms so that your palms are facing away from you, then gently lift your arms up and back, feeling a stretch in your shoulders and upper back.
How can physical activities be corrective measures for the common postural deformities ? (2.2) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Common postural deformities are various corrective measures that involve physical activities. Here are some examples:
-
Knock Knees : Exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles around the knees, such as squats, lunges, and leg presses, can help correct knock knees. Stretching exercises for the inner thigh muscles (adductors) can also be beneficial.
-
Flat Foot : Activities that strengthen the arches of the feet, such as toe curls, arch lifts, and calf raises, can help improve flat foot. Walking barefoot on sand or grass can also provide natural arch support.
-
Round Shoulders : Exercises that target the muscles of the upper back and shoulders, such as rows, reverse flyes, and shoulder retractions, can help correct round shoulders. Stretching exercises for the chest muscles (pectoralis) can also be beneficial.
-
Lordosis : Strengthening exercises for the abdominal muscles, such as planks, crunches, and pelvic tilts, can help correct lordosis. Stretching exercises for the hip flexor muscles can also be beneficial.
-
Kyphosis : Exercises that focus on strengthening the muscles of the upper back and shoulders, such as rows, reverse flyes, and shoulder retractions, can help correct kyphosis. Stretching exercises for the chest muscles can also be beneficial.
-
Scoliosis : Physical therapy exercises that target the muscles around the spine can help improve scoliosis. These exercises may include stretches, strengthening exercises, and postural correction exercises. Yoga asanas like Dhanurasana, Chakrasana, and Bhujangasana can also be beneficial.
Suggest five exercises as corrective measures for round shoulders and kyphosis. (2.2) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. Round shoulders and kyphosis, here are five exercises that can be used as corrective measures :
-
Chest stretches : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, interlace your fingers behind your back, and gently lift your arms upward while squeezing your shoulder blades together. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat.
-
T stretch : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, raise your arms to shoulder height, and extend them out to the sides in a T shape. Gently squeeze your shoulder blades together and hold for 20-30 seconds.
-
Wall stretch : Stand facing a wall, place your hands on the wall at shoulder height, and slowly walk your feet back while keeping your hands on the wall. Lean forward, keeping your back straight, until you feel a stretch in your chest and shoulders. Hold for 20-30 seconds.
-
Handclasp stretch : Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, clasp your hands behind your back, and gently lift your arms upward while squeezing your shoulder blades together. Hold for 20-30 seconds and repeat.
-
Planks : Start in a push-up position, with your hands directly under your shoulders and your body in a straight line. Hold this position for 30-60 seconds, engaging your core and keeping your shoulders pulled back.
Explain the causes, precautions and remedies of bow legs. (2.2) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Bow legs, also known as Genu varum, is a condition where the legs curve outward at the knees while the feet and ankles touch.
Causes :
- Lack of Vitamin D, Phosphorus, and Calcium : Deficiency in these nutrients can contribute to the development of bow legs.
- Underlying diseases : Conditions like Blount’s disease, rickets, or arthritis can cause bow legs.
- Genetic factors : In some cases, bow legs may be inherited.
Precautions :
- Balanced diet : Ensuring sufficient intake of Vitamin D, Phosphorus, and Calcium through a balanced diet can help prevent or improve bow legs.
- Modified shoes and braces : Using braces and modified shoes can provide support and help correct the alignment of the legs.
- Walking on the inner edge of the feet : Encouraging walking on the inner edge of the feet may help improve the alignment of the legs.
Remedies :
- Observation : In most cases, bow legs resolve on their own as the child grows, so observation and monitoring may be sufficient.
- Braces : In some cases, the use of braces can help correct the alignment of the legs and prevent further progression of bow legs.
- Modified shoes : Wearing shoes with proper support and alignment can aid in correcting bow legs.
- Balanced diet : Ensuring a balanced diet with sufficient intake of Vitamin D, Phosphorus, and Calcium can support healthy bone development.
- Walking on the inner edge of the feet : Encouraging walking on the inner edge of the feet may help improve the alignment of the legs.
Explain the causes of any five postural deformities in detail. (2.2) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Causes of five postural deformities :
Knock knee : The knock is commonly caused by irregular growth of the lower leg bones and weak ligaments.
Rickets is also a cause of knock knee.
Flat foot :
- Faulty posture
- Prolonged standing
- Excessive body weight
- Lack of exercise
Round shoulder :
- Poor posture
- Faulty furniture
- Lack of physical exercise
- Carrying heavy loads on shoulders
Lordosis :
- Weakening of the bones
- Due to lose abdominal muscles
- Due to bad posture/habits
Bow legs :
- Due to the deficiency of Vitamin-D, Calcium and Phosphorous
- Due to Blount’s disease
- Due to overstraining on bones because of long standing of hours.
Define spinal curvature deformities and list their causes and precautions. (2.2) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Spinal curvature : Spinal curvature deformities refer to abnormal curvatures of the spine, which can include conditions such as scoliosis, lordosis, and kyphosis. Here are the causes and precautions for each of these deformities:
- Scoliosis : Scoliosis is a sideways curvature of the spine. The cause of most cases of scoliosis is unknown, but it can be caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy, muscular dystrophy, or diseases like arthritis, paralysis, or rickets. Some precautions for scoliosis include:
- Regular exercise, including activities like hanging on horizontal bars and swinging, which should be done on the opposite side of the C-shaped curve.
- Aerobic activities with a slow pace and breaststroke in swimming can be helpful.
- Yoga asanas like Trikonasana and Adhomukhasana can help straighten the spine.
- Lordosis : Lordosis is an excessive inward curvature of the lower back. It can be caused by factors such as obesity, improper development of muscles, skeletal or muscular diseases, poor posture while standing, sitting, and walking, or malnutrition. Precautions for lordosis include:
- Weight loss to help improve posture.
- Daily physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve range of motion.
- Exercises to develop strength in the pelvic region, such as sit-ups, sitting against the wall and pushing the trunk backward, and lying on the back and raising upper extremities and legs together.
- Yoga asanas like Dhanurasana and Halasana can be helpful.
- Kyphosis : Kyphosis is an excessive outward curvature of the upper back, resulting in a rounded or hunched posture. It can be caused by factors such as poor posture, osteoporosis, spinal fractures, or certain medical conditions. Precautions for kyphosis include:
- Exercises that help strengthen back muscles, provide stability, and improve flexibility.
- Physical therapy, swimming, exercise/gym ball exercises, exercises with bands, and yoga asanas like Dhanurasana, Chakrasana, and Bhujangasana can be beneficial.
- Using a flat bed with a thin pillow while sleeping can also help.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Posture : Posture is defined as the attitude assumed by the body either with support during the course of muscular activity, or as a result of the coordinated action performed by a group of muscles working to maintain the stability. Posture is classified into two categories.
- Dynamic posture is how one holds oneself when moving, for example, walking, running, or bending over to pick up something. It is usually required to form an efficient basis for movement. Muscles and non-contractile structures have to work to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Static posture is how one holds oneself when stationary or not moving, For example, sitting, standing, or sleeping. Body segments are aligned and maintained in fixed positions. This is usually achieved by co-ordination and interaction of various muscle groups which are working statically to counteract gravity and other forces.
Dynamic posture is _____ one holds oneself when moving.
Ans. how
Static posture is how one holds oneself when _____ or not moving.
Ans. stationary
_____, standing, or sleeping are examples of static posture.
Ans. Sitting
Muscles and non-contractile structures have to work to _____ to changing circumstances.
Ans. adapt
Body segments are aligned and maintained in _____ positions.
Ans. fixed
2. Bow Legs : Bow Legs, also known as Genu varum, is a position of knees in which legs look like a bow, when the legs curve outward at the knees while the feet and ankles touch. Infants and toddlers often have bow legs. It may be caused due to lack of Vitamin D, Phosphorus and Calcium and can be easily cured at an early stage. The condition doesn’t cause pain or discomfort and is rarely serious. It does not affect running,
standing, crawling etc. Bow legs is a condition that usually goes away without treatment, often by the time a child is 3–4 years old and does not affect a child’s ability to crawl, walk, or run. However, parents might worry about the appearance of their child’s legs, or an awkward walking pattern.
A
3. Knock Knees : Knock Knees, also known as Genu valgum, is a knee misalignment that turns the knees inward. As a result, both knees touch or knock against each other in a normal standing posture but there is a gap of 3-4 inches between the ankles. It is generally first noticed in early childhood, but in most cases, it usually corrects itself naturally by the time children are 7-8 years old. However, in some cases it continues till adolescence. In some cases Genu valgum can also develop due to an injury or infection in the knee or leg, rickets, severe lack of vitamin D and calcium, obesity, or arthritis in the knee.
It negatively effects walking and running and impedes other legs movement which hinder performance. In case Genu valgum persists beyond childhood, it may have other symptoms besides misaligned knees. They include stiff joints, knee pain and walking with a limp. Stressed ligaments and muscles can also cause pain in the hips, ankles, or feet. If only one knee is out of line, the stance may be unbalanced.
A) Controlling
2.3 Women Participation in Sports —
Physical, Psychological and Social Benefits
Multiple Choice Questions
Sports is a important tool for social empowerment for women as it develops the folowing : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Aggression
(b) Isolation
(c) Stress
(d) Leadership
Psychological benefits of women particapation in sports includes : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Coopration
(b) Emotation Control
(c) Physical Fitness
(d) Communication
Weakening of bones due to loss of bone density and improper bone formation is known as _________. (2.3) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) Amenorrhea
(b) Anorexia nervosa
(c) Osteoporosis
(d) Lordosis
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Define the term ‘Emotions’. (2.3) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. • Emotions are feelings which result in physical and psychological changes that influence our behaviour.
• Emotions are strong feelings deriving from one’s circumstances, moods or relationship with others. (Any one)
Define leadership. (2.3) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Leadership may be defined as the quality of the person to lead others or direct others.
Suggest any four ways through which women participation in sport across age group can be enhanced. (2.3) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. • Awareness Programs
-
Encourage Family Support
-
Media Coverage and Sponsorship
-
Develop Sports Infrastructure
Define the term sports medicine? (2.3) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. —
Your grandmother has severe pain in the legs. Name the test you will suggest to measure her lower body strength particularly legs? (2.3) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. —
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Write a short note on benefits of participation in sports. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- The benefits of participation in sports include physical, psychological, and social benefits.
- Regular exercise and participation in sports increase muscle tone and strength.
- Participation in sports helps individuals stay in shape and maintain a healthy weight.
- Winning in sports boosts confidence and self-esteem, leading to a sense of achievement.
- Participation in sports can bring out leadership skills and qualities in individuals.
Explain physical benefits of women participation in sports. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The physical benefits of women’s participation in sports include:
- Reduced risk of lifestyle diseases : Regular sports participation helps women stay active, reducing the chances of lifestyle diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity.
- Toned muscles : Regular exercise and sports participation can increase muscle tone in women, helping them stay strong.
- Prevention of obesity : Regular participation in sports helps women stay in shape and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the chances of obesity
What is the role of Yoga in preventing lifestyle diseases ? (2.3) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Yoga helps in improving our flexibility, lower our stress and increases our confidence and finally contributes to a healthier lifestyle on the whole. There are various lifestyle diseases like obesity, Diabetes, Asthma, Hypertension and Backache.
Through regular participation in yoga :
- Bones and joints become strong.
- Muscles becomes stronger and flexible.
- Circulation of blood becomes normal.
- Respiratory organs become efficient.
- Efficiency of digestive system increases.
- Better neuro muscular coordination.
- Strengthen the immune system. (Any three)
Comment on the outlook of Indian society towards the participation of women in sports? (2.3) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. According to Indian Society :
- Sports is a male dominant field.
- Women are expected to stay indoor since society still looks down on women for participation in sports
- Personal safety on road, public transport and sports venues are persistent problems for women.
- The physical stature of female is affected by sports and it is considered that involving in vigorous physical activity makes her infertile. (any other relevant points)
Keeping in view the Indian ideology, critically analyze the sociological aspect of participation by women athletes in sports. (2.3) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Women athletes in sports :
- Family
- School
- Culture
- Lack of facility
- Lack of role model
- Less of coaches (Explain any three)
How does participation in Games and Sports contribute to the psychological development of women athletes in India? Explain. (2.3) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans.
- Gender role orientation
- Self-image and body image
- Self-confidence
- Self-esteem
- Positive-aggression
- Competitiveness
- Overcome depression
- Emotional and mental balance (Explain any 3)
How can women’s participation in sports and games be encouraged in India ? Explain. (2.3) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans.
- Self confidence must be developed in women.
- Female role model to be highlighted.
- More time and facilities to be given to women participation.
- Women should be aware regarding the benefits of sports. (Job opportunities, Personality development etc.)
- Better safety measures to be implemented.
- Legislation regarding women in sports should be more flexible.
- Attitude of spectators and media should be motivating.
- Women coaches should be appointed in more number.
- Equal importance to be given to female in sports. (Explanation of any three)
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Explain the various benefits of women participation in sports? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The various benefits of women’s participation in sports are:
Physical Benefits :
- Helps women stay active and reduces the chances of lifestyle diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity.
- Increases bone density and strengthens bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Improves muscle tone and overall strength.
- Enhances the cardiovascular system by increasing the number of capillaries, allowing for better oxygen intake.
- Helps women stay in shape and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of obesity.
Psychological Benefits :
- Helps in stress management by releasing hormones that promote happiness and reduce stress levels.
- Boosts confidence and self-esteem through achievements in sports.
- Enhances self-image and self-worth, leading to a positive self-perception.
- Develops leadership skills that can be applied outside of sports as well.
Social Benefits :
- Encourages communication and bonding with teammates and other officials.
- Improves coordination and teamwork skills.
- Enhances communication skills through on-field interactions.
- Promotes inter-relationships and respect among team members.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Give your outlook on participation of Indian women in sports. (2.3) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. Sports in India is still dominated by the male world. It is a field where gender inequality still persists. India is a country of villages where education is still at backdrop.
With changing times in the 20th century some states have made rapid progress in women participation but the other states still let back due to various reasons.
(1) Social discrimination : Women are still exploited to be confined in homes, cook, rear the children in family.
(2) Lack of safety : Outdoor sport expose women to all sorts of safety issues. On field, roads or on public transport women always feel unsafe. Lack of protected and safe sports complexes also raise issues and add to their misery. This provides a good reason to the parents to discourage them for participation.
(3) Poor spectator interest : As media coverage of female events is not adequate, people are less interested in seeing the events.
(4) Lack of adequate fitness : Women get little opportunity of being physically fit and active due to major responsibilities of home and family. Inadequate healthy and nutritious food availability takes a toll on their health.
(5) Lack awareness in families : Families are not aware about sports and woman participation and discourage women to pursue sport. This is because they feel that it is not a rewarding career. They feel that sports develop masculine traits and the women will have difficulty in conception and child birth.
(6) Lack of women centric govt. policies : Funding and scholarship are lesser. Recent improvement in woman participation and results at international platform is however changing the thought perceptions.
Keeping in view of the Indian Ideology, critically analyze the sociological aspect of women athletes in sports participation. (2.3) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. The sociological aspect of women athletes in sports participation in India can be critically analyzed by considering the following points:
- Gender Equality : The Constitution of India provides gender equality and ensures the elimination of any type of gender bias or hindrance.
- However, in reality, women athletes still face challenges and discrimination in terms of lower pay, less media coverage, and limited opportunities compared to their male counterparts.
- Empowerment and Social Change : Women’s participation in sports can be seen as a tool for social empowerment and bringing about social change.
- This can lead to a shift in societal attitudes towards gender equality.
- Role Models and Inspiration : Indian women athletes who have achieved success at the international level, such as P.V. Sindhu, Mary Kom, and Hima Das, serve as role models and sources of inspiration for young girls.
- Their achievements not only showcase the talent and potential of women in sports but also encourage other women to pursue their dreams and overcome societal barriers.
- Breaking Cultural and Social Norms : In many parts of India, cultural and social norms restrict women’s participation in sports.
- Support and Infrastructure : To encourage women’s participation in sports, it is crucial to provide adequate support and infrastructure.
- Additionally, awareness programs and campaigns should be conducted to promote women’s participation in sports and to eliminate cultural and social negativity.
Elucidate about the psychological aspects of women athletes for their limited participation in sports. (2.3) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. The psychological aspects that contribute to the participation of women athletes in sports are :
-
Stress Management : Participating in sports helps women manage their stress levels and stay happy.
-
Emotional Control : Women who participate in sports are better equipped to manage their emotions and become emotionally stronger.
-
Confidence : Winning in sports boosts the confidence of women athletes and gives them a sense of achievement, which carries over to other areas of their life.
-
Self-Esteem : Sports help women realize their self-worth and improve their self-image, which is important for personal growth.
-
Leadership : Sports bring out leadership skills in women athletes, enabling them to lead both on and off the field.
Gender beliefs still exist in every society of the world even when so many changes have taken place due to education. Explain any five psychological traits of women athletes? (2.3) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Based on the given context, five psychological traits of women athletes are :
-
Stress Management : Women athletes who participate in sports are better equipped to manage their stress levels compared to those who don’t participate in sports.
-
Emotional Control : Women athletes develop the ability to manage their emotions effectively, especially in challenging situations during the game, which makes them emotionally stronger.
-
Confidence : Participation in sports and winning boosts the confidence of women athletes, leading to a sense of achievement and increased self-confidence in all areas of their life.
-
Self-Esteem : Sports help women athletes realize their self-worth and improve their self-image, which is crucial for their overall well-being.
-
Leadership : Participation in sports helps women athletes develop leadership skills, which can be applied not only within the sports arena but also in other aspects of their lives.
Give five physiological differences between males and females? (2.3) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans.
-
Hormonal Differences : Males have higher levels of testosterone, while females have higher levels of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones play a role in various physiological processes, including reproductive development and function.
-
Reproductive System : Males have testes, which produce sperm, while females have ovaries, which produce eggs. Additionally, females have a uterus for pregnancy and childbirth, while males do not.
-
Body Composition : On average, males tend to have a higher percentage of muscle mass and lower percentage of body fat compared to females. This is influenced by hormonal differences and genetic factors.
-
Metabolism : Males generally have a higher metabolic rate compared to females. This means that they may burn calories more quickly and have a higher energy expenditure at rest.
-
Cardiovascular System : Females tend to have a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases compared to males. This is partly due to the protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. However, after menopause, this difference diminishes.
Comment on the outlook of Indian society towards the participation of women in sports. Give supportive reason against your opinion. (2.3) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The outlook of Indian society towards the participation of women in sports has been evolving positively in recent years. There is a growing acceptance and encouragement for women’s participation in sports at both national and international levels. Some supportive reasons are :
- Gender Equality: The Constitution of India provides gender equality and ensures the elimination of any type of gender bias or hindrance.
- This has created a foundation for promoting women’s participation in sports and treating them on par with their male counterparts.
- Empowerment and Equity : Sports serve as a medium for gender equity and empowerment.
- By participating in sports, women develop skills like communication, teamwork, leadership, respect, and sportsmanship.
- International Recognition : Indian women athletes have been achieving remarkable success in international sports events, bringing pride and recognition to the country.
- Supportive Initiatives : The International Olympic Committee (IOC) encourages women’s participation not only in playing sports but also in administrative roles, coaching, officiating, and journalism.
- The IOC has also announced that 49% of women will take part in the next Olympic Games.
- Legal Framework : The Indian government has implemented various policies and initiatives to promote women’s participation in sports.
- Awareness programs, regular competitions, appointment of women coaches, provision of proper facilities, and incentives in states with social constraints are some of the measures taken to encourage women’s sports participation.
- Changing Social Norms : Society is gradually accepting and recognizing the importance of women’s participation in sports.
- Media coverage and sponsorship have played a significant role in highlighting the achievements and stories of women athletes, thereby creating a positive perception and encouraging more women to participate in sports.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Despite the fact that women have shown a dramatic rise in sports participation, there is still a large disparity in participation rates between women and men. But to deal with this disparity many countries like India run programmes such as Khelo India scheme and National Sports Talent Search Scheme (NSTSS) to mainstream women’s participation in sports in India. While in the past there were certain psychological constraints like low self-confidence and self-esteem, higher levels of stress and anxiety, and social causes like lack of support or positive reinforcement from family and a male-dominated social structure that affect women’s participation in sports, or even, certain economic factors that played a negative role that affected women’s participation in sports, these are all a thing of the past.
A) Controlling
2. Women’s sports, both amateur and professional, have existed throughout the world for centuries in all varieties of sports. There is a rich record of participation of women in sports in India. In the days of Mahabharata, Shakuntala, Madhuri, Kunti all chose physical activities as recreation. As time passed, Indian women, despite having potential and talent, were deprived of participation in sports for a number of reasons. They were put in the back seat and were not allowed to participate in sports. However, female participation and popularity in sports increased dramatically in the last quarter of the 20th century, reflecting changes that emphasize gender parity. Although the level of participation and performance can still be improved, women’s participation in sports is generally accepted and promoted today.
A) Controlling
3. In 2016 Rio Olympics Sakshi Malik won medal in wrestling and P.V. Sindhu won the first ever women’s silver medal in badminton. P.T Usha and Anju Bobby George were athletes who earned a name in Athletics at international level. Saina Nehwal has won 24 international titles, which includes ten Superseries titles. In 2015 that she was able to attain the world no. 1 ranking, thereby becoming the only female player from India to achieve this feat. Saikhom Mirabai Chanu, an Indian weightlifter, lifted a total of 201 kg to win the Gold Medal at the CWG 2022. Lovlina Borgohain is an Indian boxer who won a bronze medal at the 2020 Olympic Games in the women’s welterweight event and the silver medal at the 2020 Tokyo Olympics in Women’s 49 kg category. Our Indian women cricket team, wrestling, badminton, boxing are bringing glory to the country as they achieve new heights.
A) Controlling
2.4 Special Consideration
(Menarche & Menstrual Dysfunction)
Multiple Choice Questions
Frequent menstruation is known as : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Metrorrhagia
(b) Oligomenorrhea
(c) Polymenorrhea
(d) Menorrhagia
If the menstruation cycle does not begin at puberty, the condition is called (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Primary amenorrhea
(b) Secondary amenorrhea
(c) Oligomenorrhea
(d) Dysmenorrhea
Menarche is defined as the (2.4) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Ending of menstrual period in women
(b) Beginning of menstrual period in women
(c) Time of pregnancy
(d) Beginning of pregnancy
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Among females, what type of Menstrual Dysfunction is called Amenorrhea ? (2.4) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Amenorrhea is a menstrual disorder in women where girls of 18 years and above either never began menstruating or there is an absence of menstruation for three months or more than that in woman with a history of normal menstrual cycle.
What is ‘Amenorrhea’ in female athlete triad? (2.4) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. • Amenorrhea is the absence of menstruation/menstrual periods in a woman for more than three months.
• Or a girl above age of 18 years who has not begun menstruating.
• Unnatural absence of menstrual cycle for more them three months. (Any one)
What is menopause ? (2.4) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Menopause is a natural physiological change in women of age between 45-55 years, where there is a permanent cessation of menstruation cycle/primary functions of the ovaries due to hormonal changes.
Explain the term ‘Menarch’. (2.4) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Menarche is the first menstruation and the commencement of cyclic menstrual function in female. It usually occurs between 9 to 17 years of age.
Enlist different types of disorders. (2.4) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Some different types of disorders mentioned in the context are :
- Postural deformities
- Eating disorders
- Menstrual dysfunction
- Low bone mineral density
- Female athlete triad
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What is menstrual dysfunction? Write in brief. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans.
- Menstrual dysfunction refers to any abnormal condition or irregularity in a woman’s menstrual cycle.
- Menstrual dysfunction can be caused by various factors such as hormonal imbalances, stress, dietary disorders, certain medical conditions, changes in exercise routines, or other underlying health complications.
- It is important for women to seek medical attention if they are experiencing menstrual dysfunction, as it can have an impact on their overall health and well-being.
Explain the term Menarche. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The term used to describe the onset of a woman’s first menstrual period is “menarche.”
Write short note on Amenorrhea. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Amenorrhea is a condition characterized by the absence of a normal monthly period or menstrual cycle. There are two types of amenorrhea: 1. Primary and 2. Secondary.
Some common symptoms include :
- Absence of menstrual periods
- Changes in breast size or shape
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Excessive facial hair growth
- Acne
- Vaginal dryness
- Hot flashes
The causes of amenorrhea can also vary and may include:
- Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders
- Extreme weight loss or low body weight
- Excessive exercise
- Stress or emotional factors
- Certain medications or medical treatments
- Structural abnormalities in the reproductive system
- Chronic illnesses or medical conditions
Explain any two causes of anxiety. (2.4) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. —
Write briefly about menstrual dysfunctions and their effect on sports participation of female athletes. (2.4) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. Menstrual dysfunction means the irregularity and uncertainty in menstrual cycle of women.
Effect on sports participation :
- Athletic training and exercise neither affect the menarche nor menstrual periods.
- Heavy and intense training program may result in amenorrhea.
- Exercise is beneficial in relieving pain (dysmenorrhea).
- Sometimes strength decreases during menstrual cycle and affects the performance.
- Less hemoglobin affected oxygen intake, hence sports performance is affected.
- Uncertainty in menstrual cycle may cause stress and anxiety. (Any 2 points)
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Explain menstrual dysfunction. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The common causes of menstrual dysfunction include overweight, stress, dietary disorders, diseases, sudden changes in exercise schedule, travel, and other medical complications.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Menarche : The period of adolescence is marked by certain universal physical and biological changes in the body which lead to the attainment of sexual maturity. The time when sexual maturity is reached is called puberty. Menarche (first menstruation) is usually considered the point of sexual maturity for girls. It is the process in which female reproduction system matures and the body prepares itself for potential pregnancy. It is associated with the development of secondary sexual characteristics. Menarche is one of the most significant milestones in a woman’s life. The average age for a girl to get her first period ranges from 8 to 15 years old. Although the precise determinants of menarcheal age remain to be understood, genetic influences, socioeconomic conditions, general health and well-being, nutritional status, certain types of exercise, seasonality, and family size possibly play a role. Over the past century the age at menarche has fallen due to reasons still unknown.
A
2. Menstrual Dysfunction : Menstrual dysfunction is an abnormal condition in a woman’s menstrual cycle. Normal range of the menstruation cycle is 21 to 35 days. If it happens earlier than 21 days or after more than 35 days, then it’s a problem. Other menstrual problems include missing three or more periods, menstrual flow heavier or lighter in comparison with usual, cycle happening longer than seven days, any pain, cramping or vomiting during period, bleeding after menopause etc. Causes of abnormal menstrual cycles or menstrual order are: overweight, stress, dietary disorder, disease, sudden change in exercise schedule, travel, other medical complications etc.
A
2.5 Female Athlete Triad :
(Osteoporosis, Amenorrhoea, Eating Disorders)
Multiple Choice Question
Which one of the following is not a female athlete triad ? (2.5) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(A) Amenorrhoea
(B) Eating disorder
(C) Obesity
(D) Osteoporosis
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
What do you mean by ‘Bulimia’ ? (2.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Bulimia is an eating disorder in which female athlete eats excessive amount of food and then vomits it in order not to gain weight.
What is Bulimia? (2.5) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Bulimia is an eating disorder in which an athlete/person eats excessive amount of food and then vomits in order not to gain body weight.
What is ‘Bulimia’ ? (2.5) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Bulimia is an eating disorder under psychological condition in which a person overeats uncontrollably and follows this with behavior designed to prevent weight gain, e.g., over-exercising and purging.
What is osteoporosis? (2.5) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Low estrogen levels and poor nutrition, especially low calcium intake makes bone porous.
Or
Osteoporosis is a weakening of the bones due to the loss of bone density and improper bone formation.
Define osteoporosis. (2.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. • Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones and low bone density.
• Osteoporosis increases the risk of injury, stress fractures, and the development of early osteoporosis after menopause.
What is anorexia nervosa ? (2.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Individuals with anorexia have a strong desire to control their weight and often engage in extreme efforts to restrict their food intake.
What are female athlete triad ? (2.5) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. The female athlete triad is a syndrome characterized by three components: low energy availability (with or without an eating disorder), menstrual dysfunction, and low bone density.
Explain the term ‘Eating Disorders’ in brief. (2.5) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Eating disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by abnormal eating habits and attitudes towards food and weight.
Describe the meaning of ‘Amenorrhea’. (2.5) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Amenorrhea refers to the absence or missed periods in women. There are two types : 1. Primary, and 2. Secondary.
Define anorexia nervosa? (2.5) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight or a distorted perception of one’s weight.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Define disorder and enlist any two types of disorders. (2.5) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Disorder refers to a disturbance or abnormality in eating behavior or menstrual function that can negatively impact an individual’s health. It can include conditions such as eating disorders (e.g., anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa) and menstrual irregularities.
What are the causes of osteoporosis ? (2.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. (a) Calcium and vitamin deficiency.
(b) Amenorrhoea
(c) Eating disorder
Write briefly about the prevention and management of ‘Anorexia’. (2.5) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Prevention :
- Encourage a healthy view of the self and others means refraining from commenting on the body sizes of other children.
- Make children aware about their genetics, body shape and size.
- Make them to eat healthy, nutritious food and be physically active.
- Stay away from the people, places and activities which induce anorexia.
Management :
- Face the reality.
- Restoring healthy weight.
- Individual psychotherapy.
- Antidepressants to aid the process of recovery.
Explain briefly about eating disorder ‘Bulimia’? (2.5) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Bulimia is eating disorder in which a person (adolescent girl/young women) eats excessive amount of food and vomits it out in order not to gain weight. A person suffering from this disorder feels loss of control on oneself. Does not eat proper food and hence lack proper nutrients.
It is normally of two types :
(1) Purging : When the person self induces vomiting.
(2) Non-purging : When the person uses severe fasting, rigid dieting or excessive exercising to reduce weight.
Causes : (1) Pressure of performance in sports (e.g., Gymnastics, Marathons etc.)
(2) Social factors
(3) Maintain weight category in sports
(4) Genetic factor
(5) Psychological factors (e.g., A person with low self-esteem)
What do you understand by Sports Medicine? Discuss briefly about the scope of Sports Medicine. (2.5) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. Medical knowledge applied to sport with the aim of preserving the health of the athlete while improving the athlete’s performance is Sports Medicine.
Or
Sports Medicine is related to such human problems which usually arise during training and competition in sports and Games. (any one)
Scope :
- Human anatomy and physiology
- Sports and first aid
- Prevention of sports injury
- Rehabilitation
- Female problem associated with women
- Sports performance and ageing
- Scientific promotion of sports and games
- Fitness for sports
- Illness caused by environment, physiological and psychological disturbances.
- Sports nutrition
- Methods of detecting doping
- Sports and traumatology
- Physiotherapy (explain any two)
What is Osteoporosis ? Explain factors, those lead to Osteoporosis in women. (2.5) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. Osteoporosis is weakening of the bones due to the loss of bone density.
Factors those lead to osteoporosis in women :
- Insufficient calcium in diet
- Lack of Vitamin-D
- Sedentary life style
- Side effects of medication
- Thyroid condition
- Due to the menstrual dysfunctioning in women
- Eating disorders like anorexia bulimia/poor nutrition (Any two)
Write in brief about osteoporosis. What are the causes of osteoporosis in women ? (2.5) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Osteoporosis is weakening of bone due to the loss of bone density.
Causes :
- Insufficient calcium in diet
- Amenorrhea
- Poor nutrition
- Sedentary life style
- Thyroid condition
- Lack of vitamin D (Explain any two cause)
‘Women face certain hindrance in sports due to their biological cycle.’ Explain these issues in brief. (2.5) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. Female Athlete Triad : (Osteoporosis, Amenoria, Eating Disorders)
- The Female Athlete Triad is a syndrome (collection of signs and symptoms) that links three health problems including : disordered eating, amenorrhea and osteoporosis.
- Girls may begin to skip periods if they are not getting adequate nutrition for the amount of exercise they do (energy availability).
- Periods also may be irregular.
- Stress lowers estrogen levels, which may cause skipped periods.
- Low estrogen levels and a lack of menstrual periods can lead to low bone mass (low bone mineral density) and stress fractures (small cracks) in their bones.
- The female athlete triad is defined as the combination of disordered eating, amenorrhea and osteoporosis.
- This disorder often goes unrecognised.
- The consequences of lost bone mineral density can be devastating for the female athlete.
- Premature osteoporotic fractures can occur, and lost bone mineral density may never be regained.
What is the meaning of female athletes triad? Explain any two in brief. (2.5) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Female Athlete Triad :
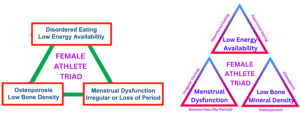
(a) Disordered eating
(b) Amenorrhea and
(c) Osteoporosis
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Discuss in detail about Female Athletes Triad. (2.5) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. The Female Athlete Triad is a syndrome characterized by three components: low energy availability (with or without an eating disorder), menstrual dysfunction, and low bone density.
Symptoms of the Female Athlete Triad may include :
-
Low energy availability : This can manifest as disordered eating behaviors, such as calorie restriction or excessive exercise, leading to inadequate energy intake for the body’s needs.
-
Menstrual dysfunction : This can include irregular or absent periods, known as amenorrhea, or other menstrual irregularities.
-
Low bone density : This refers to decreased bone mineral density, which can increase the risk of stress fractures and osteoporosis.
Risk factors for the Female Athlete Triad include :
-
Participation in sports or activities that emphasize leanness or a specific weight, such as gymnastics, dance, or distance running.
-
Pressure to maintain a certain body weight or shape for performance or aesthetic reasons.
-
Inadequate nutrition, including insufficient calorie intake or nutrient deficiencies.
-
Psychological factors, such as body image concerns, perfectionism, or high levels of stress.
It is important to note that the Female Athlete Triad can have serious long-term health consequences if left untreated, including increased risk of injury, decreased athletic performance, and potential long-term effects on bone health and reproductive function.
Write in detail the symptoms and causes of amenorrhoea. (2.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The symptoms of amenorrhea, which is the absence of a normal monthly period or menstrual cycle, can vary depending on the underlying cause.
Some common symptoms include :
- Absence of menstrual periods for three months or more (secondary amenorrhea)
- Lack of menstruation at puberty (primary amenorrhea)
- Changes in breast size or nipple discharge
- Hair loss or excessive hair growth
- Headaches or vision changes
- Changes in libido or sexual function
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Mood changes or depression
The causes of amenorrhea can also vary and may include :
- Pregnancy
- Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or thyroid disorders
- Excessive exercise or low body weight
- Stress or emotional factors
- Certain medications or medical treatments
- Structural abnormalities in the reproductive system
- Chronic illnesses or medical conditions
What is an eating disorder? Mention its types and explain each. (2.5) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. An eating disorder is a mental health condition characterized by abnormal eating habits and a distorted perception of body weight and shape. It involves extreme efforts to control weight and shape, which can significantly interfere with a person’s life. There are several types of eating disorders, including:
-
Anorexia Nervosa : Individuals with anorexia have an intense fear of gaining weight and a misconception about their weight. They severely restrict their food intake, often to the point of starvation. They may also engage in behaviors such as excessive exercise, vomiting, or misuse of laxatives to prevent weight gain.
-
Bulimia Nervosa : People with bulimia engage in episodes of binge eating, consuming large amounts of food in a short period of time. They then adopt unhealthy ways to compensate for the binge, such as vomiting, using laxatives, or excessive exercise. Unlike anorexia, individuals with bulimia may maintain a relatively normal weight.
-
Binge Eating Disorder : This involves recurrent episodes of binge eating without compensatory behaviors. Individuals with this disorder feel a loss of control during these episodes and often experience guilt, shame, or distress afterward. Binge eating disorder is associated with significant weight gain.
-
Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder (OSFED) : This category includes eating disorders that do not meet the specific criteria for anorexia, bulimia, or binge eating disorder. Examples include atypical anorexia (similar to anorexia but without low body weight), purging disorder (engaging in purging behaviors without binge eating), and night eating syndrome (consuming a significant amount of food during the night).
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Participation in sports and physical activities provides a lot of physical and social benefits like developing leadership qualities, competition, teamwork etc. Regular participation in such activities is associated with a longer and better quality of life, reduced risks of a variety of diseases and many psychological and emotional benefits. Evidence suggests a positive relationship between physical activity and a host of factors affecting girls’ physical health, including diabetes, blood pressure and the ability to use fat for energy, thus preventing obesity. Physical activity could reduce the risk of chronic diseases in later life. Conditions, such as cancer, diabetes
and coronary heart disease, have their origins in childhood, and can be aided, in part, by regular physical activity in the early years. Also, regular activity beginning in childhood helps to improve bone health, thus preventing osteoporosis, which predominantly affects females.
A
2. However, participation in sports is not without certain health risks. Sports like Judo, boxing, wrestling, taekwondo etc. exert a lot of pressure on athletes to maintain their shape and weight. For participation in sports like distance running, cycling, cross country etc. athletes have to take a balanced diet since these demand high levels of energy and a good quantity of dietary intake. Such pressures put the athlete’s health at risk and leads to Female Athlete Triad. The term ‘triad’ was first described by American college of sports medicine in 1992, and the three components
to describe the triad were
(a) disordered eating,
(b) amenorrhoea and
(c) osteoporosis
A
3. Bulimia Nervosa : Bulimia nervosa is an eating disorder in which an individual eats large amount of food with loss of control over eating and then adopts unhealthy ways to cut down calories like vomiting, taking laxatives, weight loss supplements, diuretics, excessive exercises etc. Symptoms of bulimia are dehydration, dental problems, oedema,
electrolyte abnormalities, extreme weight fluctuation, menstrual irregularity, weakness, cramps, depression etc.
A