10.1 Concept of Talent Identification and
Talent Development in Sports
Multiple Choice Questions
The performance enhancement in the future can be predicted based on (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Physiological factor
(b) Physical factor
(c) Talent indicators
(d) All of the above
Psychological factors contributing to talent identification is (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Cognitive
(b) Emotional
(c) Personality traits
(d) All of the above
Talent identification is a ________ process. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) General process
(b) Scientific process
(c) Specific process
(d) None of the above
Match the Columns :
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer from the code given below : (chap 10) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
|
List I |
List II |
|
(i) Sit and reach test (ii) Standing broad jump (iii) 600 metre run/walk (iv) 50 metre run |
1. Speed 2. Endurance 3. Strength 4. Flexibility |
(a) (i) – 1; (ii) – 2; (iii) – 3; (iv) – 4
(b) (i) – 3; (ii) – 4; (iii) – 1; (iv) – 2
(c) (i) – 4; (ii) – 2; (iii) – 3; (iv) – 1
(d) (i) – 4; (ii) – 3; (iii) – 2; (iv) – 1
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
List the names of components of talent identification in sports. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The main components of talent identification in sports are :
- Physiological attributes
- Physical attributes
- Psychological attributes
- Technical/Tactical attributes
- Results
- Intangibles
Identify the importance of talent identification in sports and games ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The importance of talent identification in sports and games is significant for several reasons :
- Discovery of potential : Talent identification allows for the discovery of individuals with exceptional abilities and potential in a specific sport or game.
- Early recognition : Identifying talent at an early stage allows for proper nurturing and development of skills, maximizing the athlete’s potential.
- Optimum development : Talent identification helps in providing athletes with suitable training and development opportunities.
- National asset : By recognizing and nurturing talented individuals, countries can build a strong pool of athletes who can represent them at national and international levels, bringing pride and success to the nation.
- Resource allocation : By identifying athletes with potential, resources such as coaching, training facilities, and financial support can be directed towards their development, ensuring efficient utilization of resources.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Adopting components of talent identification will enhance performance factors in games and sports. Discuss. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Adopting components of talent identification can enhance performance factors in games and sports in several ways :
- Physiological attributes : Identifying and assessing physiological attributes such as strength, speed, endurance, and flexibility can help coaches and trainers tailor training programs to improve these specific areas. This targeted approach can lead to improved physical performance and overall athletic ability.
- Physical attributes : Recognizing and developing specific physical attributes like height, body composition, and coordination can contribute to better performance in certain sports. For example, height may be advantageous in basketball or volleyball, while agility and coordination are crucial in sports like gymnastics or soccer.
- Psychological attributes : Identifying psychological attributes such as motivation, mental toughness, focus, and resilience can help athletes develop the mental skills necessary for optimal performance. Mental training techniques, such as visualization and goal-setting, can be implemented to enhance mental performance and improve overall game strategy.
- Technical/Tactical attributes : Assessing and developing technical and tactical skills specific to a sport can greatly enhance performance. Identifying strengths and weaknesses in technique and game strategy allows coaches to provide targeted training and practice sessions to improve these areas.
‘Talent identification is the first step in the progression from beginner to successful international athlete.’ Elaborate. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Talent identification plays a crucial role in the progression from a beginner to a successful international athlete. Here’s how it contributes:
- Early Recognition : Talent identification helps in recognizing individuals with potential at an early age. By identifying talented individuals early on, coaches and sports organizations can provide them with specialized training and development opportunities from a young age.
- Targeted Development : Once identified, talented athletes can be provided with a suitable learning environment and targeted development programs. Coaches and trainers can focus on enhancing the specific skills and abilities of these athletes, tailoring their training programs to maximize their potential.
- Specialized Coaching : Talent identification allows for the allocation of specialized coaching and resources to talented athletes. These athletes can receive personalized coaching and guidance from experienced coaches who understand their unique needs and abilities.
- Competitive Opportunities : Talent identification opens doors to competitive opportunities for athletes. Identified talents can be selected for elite junior programs or national teams, where they can compete against other talented athletes at a higher level.
- Pathway to International Success : Talent identification acts as a stepping stone towards international success. By identifying and nurturing talented athletes, sports organizations can provide them with a clear pathway to progress through various levels of competition, from regional to national to international.
Classify the process of talent identification and development in detail. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The process of talent identification and development can be classified into five stages :
- Talent Detection : This stage involves the discovery of potential performers who are not currently involved in the sport in question. It focuses on identifying individuals who may have the talent and aptitude for the sport but have not yet been recognized or given the opportunity to participate.
- Talent Identification : This stage involves recognizing participants with the potential at an earlier age to become elite performers in the future. It aims to identify individuals who show promising skills, abilities, and attributes that indicate their potential for success in the sport.
- Talent Development : This stage provides athletes with a suitable learning environment to accelerate or realize their potential. It focuses on providing training, coaching, and support to help athletes develop their skills, physical abilities, and mental attributes necessary for elite performance.
- Talent Selection : This stage is an ongoing process of identifying individuals at various stages of development who demonstrate prerequisite performance levels. It involves evaluating athletes based on their performance, potential, and suitability for higher levels of competition or elite programs.
- Talent Transfer : This stage focuses on transferring athletes from one sport to another sport where there are more significant opportunities to succeed. It involves identifying athletes who may have the potential to excel in a different sport and providing them with the necessary support and training to make the transition.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Talent Identification : Talent can be defined as adequate aptitude or ability in one direction, above the normal average. Thus, someone who has talent can do something without trying hard.
Talent identification can also be defined as “the process by which children are encouraged to participate in the sport they are most likely to succeed, based on selected parameters. These parameters are designed to predict performance capacity, considering the child’s current level of fitness and maturity.” As talent identification is often confused with latent development, keeping the above definition clearly in mind is necessary. Identifying is the first step in progressing from beginner to a successful international athlete; talent development follows this as the next critical phase in achieving sporting success.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Talent Identification and Development : Process of Talent Identification and Development is classified into five stages as follows :
- Talent Detection : This is the discovery of potential performers who are not currently involved in the sport in question.
- Talent Identification : Recognizing participants with the potential at an earlier age to become elite performers in the future.
- Talent Development : Provides athletes with a suitable learning environment to accelerate or realize their potential
- Talent Selection : The ongoing process of identifying individuals at various stages of development who demonstrate pre-requisite performance levels.
- Talent Transfer : Focuses on transfer from one sport to another sport where there are more significant opportunities to succeed
These five steps are common across sporting in Talent Identification and Development System and are often operationalized within the everyday practice.
What ______
Ans. –
10.2 Introduction to Sports Training Cycle :
Micro, Meso, Macro Cycle
Multiple Choice Questions
Meso cycle is training of (CBSE TBQ)
(a) one week
(b) 4 to 10 days
(c) 3 to 6 weeks
(d) Three 3 months
Transitional phase is a (CBSE TBQ)
(a) rest and recovery period
(b) training period
(c) competition period
(d) fitness period
Micro cycle is (CBSE TBQ)
(a) 3 to 10 weeks
(b) 3 to 10 days
(c) 3 to 10 hrs
(d) None from above
The word meso in mesomorph is related to (10.2) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Fat
(b) Lean
(c) Muscular
(d) None of the above
Match the Columns :
Match the following : (10.2) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
(a) 3 1 4 2
(b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 3 2 4 1
(d) 4 2 3 1
Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)
Explain the term ‘Sports Training’. (10.2) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. • Process of preparation, in sports person to achieve a desired goal is called sports training.
• A technical and systematic process of training a sports person, to achieve the utmost level of performance is called sports training. (Any one)
Short Answer Type-I Question (2/3 Marks)
What do you understand by macro cyclicity ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Macro cyclicity :
- Macro cyclicity refers to the longest cycle of training, which typically lasts from 3 to 12 months.
- It is designed to improve the overall performance capacity of an athlete or sportsperson in order to achieve optimal performance during a specific competition.
- A macro cycle consists of several mesocycles, with the last mesocycle focusing on recovery and relaxation to smoothly transition into the next macro cycle.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
All players diligently follow the periodization process. Why do coaches and players follow periodization cycles during training to attain good results in a championship ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Coaches and players follow periodization cycles during training to attain good results in a championship because it allows for systematic and structured planning of training.
By following periodization, coaches and players can :
- Prevent overtraining : Periodization allows for proper rest and recovery periods, which helps in preventing overtraining and reducing the risk of injuries.
- Optimize performance : By focusing on specific training tasks in each phase, such as strength, endurance, and speed, periodization helps in developing and improving the necessary physical and motor fitness components required for the sport.
- Peak at the right time : Periodization ensures that the athletes reach their peak performance level at the right time, usually during the championship or competition.
- Avoid burnout : By incorporating periods of active recovery and relaxation, periodization helps in preventing burnout and maintaining the athletes’ motivation and enthusiasm throughout the training process.
- Adapt to individual needs : Periodization allows for individualization of training programs based on the specific needs and abilities of each player.
Identify the specific training tasks in mesocycle ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The specific training tasks in the mesocycle include :
- Learning and acquiring mastery of skills
- Maintenance and stabilization of performance
- Development of physical and motor fitness components
- Preparation for a specific competition
- Attainment of optimal level of performance
- Preparation for the next mesocycle by providing recovery and relaxation.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Give a brief outline of the factors that help in identifying a suitable sport for a child. (10.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The factors that can help in identifying a suitable sport for a child include :
- Health and physique : Screening the child’s health and physical condition can help determine their suitability for different sports.
- General physical performance capacity : Assessing the child’s overall physical abilities can provide insights into which sports they may excel in.
- Motives and interests : Understanding the child’s interests, motivations, and mental capabilities can help identify a sport that aligns with their preferences.
- Interests of parents : Considering the parents’ preferences and support for a particular sport can also play a role in identifying a suitable sport for the child.
- Physique and motor abilities : As the child progresses in their training, their physique and motor abilities can be assessed to determine their suitability for specific sports.
- Ability to tolerate load : Evaluating the child’s ability to handle physical demands and training loads can help determine their suitability for certain sports.
- Performance : Assessing the child’s performance in their chosen sport can indicate their potential and suitability for further development.
- Cognitive, emotional, and personality traits : Considering the child’s cognitive abilities, emotional resilience, and personality traits can provide insights into their suitability for different sports.
Ram is going regularly to the park near his home in the morning. He found that many old people have some or the other type of fitness problem in terms of flexibility and strength. He decides to check the fitness level of such people in the park. Explain the steps/test used by Ram for measuring the fitness. (10.2) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. ………………………………………
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Several planning systems are available in sports training; a sportsperson has to follow all the procedures to ensure high performance in a specific sport. When we look into the sports training planning format, we will be able to find plans like a long-term plan, Olympic plan, annual plan, sectional plan, and day’s plan. All the projects form a unified training basis, and the pursuit of several years indicates the main line of development. Training content is more concrete and specific in a plan of shorter duration. All the short duration sports training plans are worked according to the requirements of more extended duration plans, called long-term plans. It is the largest unit in the system of planned training. The duration of this plan is approximately 8 to 15 years. This plan begins with the basic training of the sportsperson and continues until the attainment of optimum performance standards in a specific sport.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Micro Cycle : The duration of this cycle is 3 to 10 days and is thus considered the shortest cycle of training. In the case of an intermediate and high performance sportsperson, this cycle lasts 5 to 10 days. The last day of the micro cycle provides active recovery and relaxation to the sportsperson to prepare him for training in the next micro cycle. Even though 5 to 10 days is not adequate to achieve most training tasks, it forms an integral part of the entire training process. The following three proportions of high and medium or low load are adopted in the microcycle.
- 1:1, i.e., every day of the high load is followed by a day of medium
load. - 2:1, i.e., every two days of high load are followed by a day of
medium load. - 3:1, i.e., every three days of high load are followed by a medium or
low load day.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Meso Cycle : P The duration of this training cycle is 3 to 6 weeks and is thus termed a cycle of medium duration. The purpose of this cycle is to tackle specific training tasks. These tasks are :
- Learning and acquiring mastery of skills
- Maintenance and stabilization of performance
- Development of physical and motor fitness components
- Preparation for a specific competition
- Attainment of optimal level of performance
- Preparation for the next mesocycle by providing recovery and
relaxation.
A mesocycle of 4 weeks is considered the best because this is the minimum period within which significant change is affected in the physiological and psychological factors. The last week of the training mesocycle is considered a transitional phase that ensures recovery and relaxation.
What ______
Ans. –
10.3 Strength
Multiple Choice Questions
The isokinetic method was developed by (CBSE TBQ)
(a) H.C. Buck
(b) Joy Perrny
(c) J.J. Perrine
(d) J.J. Coubertin
An exercise in which movement is visible. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Isometric
(b) Isotonic
(c) Isokinetic
(d) Isonomic
Under which kind of strength would you put Shotput? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Strength endurance
(b) Explosive strength
(c) Maximum strength
(d) Speed strength
Barrow Fitness Test does not include : (10.3) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Medicine Ball Put
(b) Zig-zag Run
(c) 600 metres run
(d) Standing Broad Jump
If a muscle contracts and changes its length to produce force, the contraction type is : (10.3) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Isotonic
(b) Isometric
(c) Isokinetic
(d) None of these
Pushing against a stationary wall is an example of (10.3) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
(a) Eccentric exercise
(b) Isometric exercise
(c) Isotonic exercise
(d) Isokinetic exercise
Which of the following is not involved in barrow three item tests? (10.3) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Standing Broad Jump
(b) Zig-Zag Run
(c) Medicine Ball Put
(d) Shuttle Run
Acceleration runs are used to improve __________. (10.3) (SQP 2019-20)
(a) Strength
(b) Endurance
(c) Speed
(d) Flexibility
Interval training is used for developing (10.3) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Flexibility
(b) Agility
(c) Endurance
(d) Speed
Resistance ability against fatigue is called (10.3) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Strength
(b) Speed
(c) Endurance
(d) Agility
Ability to achieve maximum speed from stationary position is called ____________? (10.3) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) Speed endurance
(b) Acceleration ability
(c) Locomotors ability
(d) Movement speed
What is the value placed for male in VO2MAX formula? (10.3) (SQP 2020-21)
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 0.85
(d) 0.72
Identify the component of fitness which is tested through this exercise : (10.3) (SQP Term-I, 2021-22)
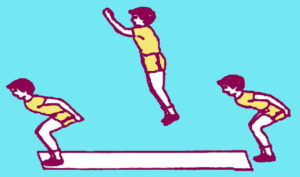
(a) Maximum strength
(b) Explosive strength
(c) Strength endurance
(d) Static strength
Slow twitch fibres are ______________ in colour. (10.3) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) White
(b) Red
(c) Transparent
(d) Brown
Jumping on the spot is an example of __________. (10.3) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) Iso-metric
(b) Iso-tonic
(c) Iso-kinetic
(d) Iso-kinesthetic
Take-off in long jump is an example of _______________ strength. (10.3) (SQP 2022-23)
(a) Explosive strength
(b) Maximum strength
(c) Strength endurance
(d) Static strength
Assertion & Reason Question :
Given below are two statements labelled Assertion (A) and Reason (R) : (10.3) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Assertion (A) : Strength is the force that a muscle or group of muscles can exert against a resistance in one maximum effort.
Reason (R) : There are two types of strength dynamic and static.
In the context of above two statements, which one of the following is correct ?
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Ans. –
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Suggest any two Isometric exercises for shoulder region. (10.3) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Two isometric exercises that can be suggested for the shoulder region are : (a) Shoulder Press Hold and (b) Wall Push-Up Hold.
What are isometric exercises ? (10.3) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. Isometric exercises are a type of strength training exercise where the muscles are contracted without any visible movement in the joints. In other words, there is no change in the length of the muscles during these exercises.
Define strength. (10.3) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Strength is the ability of a group of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance. It is the capacity of the whole body or any of its parts to exert force.
Pace-run method of training is used to develop for which motor component ? (10.3) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. The pace-run method of training is used to develop the motor component of speed endurance.
Define endurance. (10.3) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Endurance is the ability of the body to work for a long time without getting fatigue.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Define strength ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Strength :
- Strength is the ability of a group of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance.
- It is the capacity of the whole body or any of its parts to exert force.
- It is the force that a muscle or group of muscles can exert against a resistance in one maximum effort.
Explain isometric exercise with suitable examples. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Isometric exercise is a type of exercise where the muscles are contracted without any visible movement in the joints.
Examples of isometric exercises include :
- Plank : In this exercise, you hold a push-up position with your body straight and your forearms on the ground.
- Wall Sit : In this exercise, you lean against a wall with your feet shoulder-width apart and slide down until your knees are bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Static Bicep Curl : In this exercise, you hold a dumbbell or resistance band in your hand with your elbow bent at a 90-degree angle.
- Glute Bridge Hold : In this exercise, you lie on your back with your knees bent and feet flat on the ground. You lift your hips off the ground, creating a straight line from your knees to your shoulders, and hold the position.
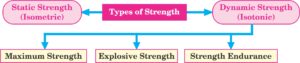
Write a short note on the different types of strength. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The different types of strength are :
- Maximum Strength : This is the ability of the muscles to overcome maximum resistance in a single repetition or muscular contraction.
- Explosive Strength : This is the ability of the muscles to overcome resistance as fast as possible.
- Static Strength : Also known as isometric strength, this is the ability of the muscles to act against resistance without any visible movement.
- Dynamic Strength : Also known as isotonic strength, this is the ability of the muscles to overcome resistance with visible movement.
- Strength Endurance : This is the ability of the muscles to overcome resistance under fatigue or for as long as possible.
- Speed Strength : This is the ability to exert force at a high speed. It is important in sports like sprinting and jumping.
- Isokinetic Strength : This is the ability to exert force at a constant speed. It is often measured using specialized equipment.
- Isonomic Strength : This term is not commonly used in the context of strength training and its definition is unclear.
Define explosive strength with help of example. (10.3) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. Explosive strength : Explosive strength is the ability of the muscles to overcome resistance as quickly as possible. It is a combination of strength and speed.
Example : Explosive strength is seen in volleyball spiking, where the player needs to generate a quick and powerful movement to hit the ball forcefully over the net.
What is the meaning of the Isotonic method and it is used for developing which ability. (10.3) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. Isotonic method : The Isotonic method refers to exercises in which movements can be seen directly.
Used for developing :
- It is used for developing toned muscles and increased muscle length.
- It is particularly important for developing strength, especially in sports.
List down any four advantages of fartlek training method. (10.3) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Advantages :
- Develops strength and endurance.
- Appropriate form of training for most sports.
- be adjusted to suit age, fitness and health of the athlete.
- Exercises are simple enough to make each athlete feel a sense of achievement in completing them.
- A wide range of exercises to select from which will maintain the athlete’s enthusiasm.
- Can be done in the group. (Any four)
Disadvantages :
- Many exercising require specialised equipment, e.g., gym equipment.
- Ample space required to set up the circuit exercises and equipment.
- In general can only be conducted where appropriate facilities/equipment are available.
- Use of addition equipment requires appropriate health and safety monitoring. (Any four)
Differentiate between Isometric and Isotonic exercise with suitable example. (10.3) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Isometric exercise :
- Isometric exercise is a type of exercise in which there is no visible movement of the muscles or joints.
- The muscles contract and generate force, but there is no change in the length of the muscle or movement at the joint.
- An example of an isometric exercise is the plank, where you hold a position and contract your muscles without any movement.
Isotonic exercise :
- Isotonic exercise is a type of exercise in which there is visible movement of the muscles and joints.
- The muscles contract and there is a change in the length of the muscle and movement at the joint.
- For example, performing bicep curls with dumbbells or doing squats are isotonic exercises because there is movement and change in muscle length.
What is endurance ? Explain its types. (10.3) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. The ability to sustain a physical activity over longer period of time resisting fatigue is called endurance.
(a) Endurance according to nature of activity :
- Basic endurance
- General endurance
- Specific endurance
(b) Endurance according to duration of activity :
- Long term endurance
- Medium term endurance
- Short term endurance (Explain any two)
Explain, what is strength and write the methods for improving strength ? (10.3) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. Strength : Ability of the muscles to overcome the resistance/Capacity of the body to exert force/Force that muscle can exert against resistance
The methods for improving strength include :
- Isometric Exercise : These exercises involve muscles carrying out tension against another group of muscles. There is no change in muscle length during these exercises.
- Isotonic Exercise : These exercises involve visible movements and result in toned muscles and increased muscle length.
- Isokinetic Exercise : This method involves a specific type of muscle contraction called isokinetic contraction, which is used in sports like rowing and swimming. These exercises are performed on specially designed instruments.
What do you understand by relative strength ? Explain the importance of body weight in determining relative strength. (10.3) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Relative strength : Relative strength refers to the strength of an individual in relation to their body weight. It is an important measure because it allows for a fair comparison of strength between individuals of different sizes.
Body weight is important in determining relative strength because :
- It provides a context for comparing strength levels among individuals.
- It takes into account the fact that individuals with larger body weights generally have the potential to lift heavier loads due to their increased muscle mass and overall size.
- However, comparing absolute strength between individuals of different body weights can be misleading.
- By considering relative strength, we can better assess and compare the strength levels of individuals, regardless of their body weight.
State any three differences between isotonic and isometric exercises. (10.3) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. Three differences between isotonic and isometric exercises are :
Movements :
- Isotonic exercises involve visible movements, such as running, jumping, or weightlifting, where the muscles change in length.
- Isometric exercises do not involve visible movements, as the muscles contract without changing in length, such as pushing against a wall or holding a plank position.
Muscle Length :
- Isotonic exercises result in increased muscle length, as the muscles are stretched and contracted during the movements.
- Isometric exercises do not change the muscle length, as the muscles are contracted without any movement.
Equipment and Time :
- Isotonic exercises can be performed with various equipment, such as weights or resistance bands, and can be done for a specific duration or number of repetitions.
- Isometric exercises require minimal equipment and can be performed practically anywhere and anytime, as they involve holding a static position for a certain period of time.
Illustrate the differences between iso-kinetic and iso-metric exercises ? (10.3) (SQP 2015-16)
Ans. Differences between iso-kinetic and iso-metric exercises :
Muscle Contraction :
- In isokinetic exercises, the muscles apply maximal force throughout the range of motion around the joint.
- In isometric exercises, the muscles act against resistance without any visible movement.
Equipment :
- Isokinetic exercises are performed on specially designed instruments that provide resistance at a constant speed.
- Isometric exercises can be performed using bodyweight or with the help of external objects like a wall or a resistance band.
Muscle Length :
- Isokinetic exercises do not involve any change in muscle length during contraction.
- Isometric exercises involve holding a static position, which can result in increased muscle length over time.
Explain fartlek training method along with its advantages. (10.3) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. Fartlek is a Swedish term meaning speed play. Used for development of endurance. Blend of continuous training and interval training.
Duration : 45 min; Heartbeat : 140-150 beats/min
Advantages :
- Good aerobic and anaerobic fitness
- Flexible in nature
- More number of athletes can take part
- Easily adapted
- No equipment required
- Versatile
What are the salient features of the Fartlek training method? (10.3) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. The salient features of the Fartlek training method are :
- Speed Variation : In Fartlek training, the athlete changes the speed of their own accord during the activity.
- Heart Rate and Duration : The heart rate and duration of the training in Fartlek method are similar to the variable pace method.
- Weight Loss : Fartlek training promotes weight loss as it is a high-intensity exercise that incorporates speed variations.
- Strength and Endurance : Fartlek training is an excellent test for strength and endurance.
- Speed and Race Tactics : Fartlek training improves speed and race tactics.
- Mind Over Matter : Fartlek training improves the mind over matter game.
- Energy and Flexibility : Fartlek training increases physical and mental energy.
- Fast and Slow Twitch Muscle Response : Fartlek training improves both fast and slow twitch muscle response, enhancing overall muscle performance.
Explain any three physiological factors determining strength. (10.3) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Strength : Strength component has varied sub-types like maximum strength, Explosive strength, Strength, Endurance etc. Each has different types of exercise, intensity and duration so physiological factors vary. In games like weightlifting, jumps, sprint or power, agility and strength dominating sports where force production is high, fatigue is quick, and fast twitch fibre percentage must be high in muscles. ATP-CP system or anaerobic system works to produce energy for strength training. Stroke volume (the volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle of the heart during each systolic cardiac contraction) is a vital parameter as far as cardiovascular system is concerned.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Explain the preventive measures to be kept in mind during strength training. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The preventive measures to be kept in mind during strength training are :
- Proper warming up : It is important to warm up before starting strength training to prepare the muscles and joints for the workout.
- Ensure strong and stable joints : Before engaging in strength training, it is essential to ensure that the musculoskeletal system is strong and stable.
- Use correct technique : When exercising with heavy weights, it is crucial to use the correct technique to avoid serious injuries.
- Perform a variety of exercises : A strength training program should include a variety of exercises that target different muscle groups.
- Gradually increase the load : The load or weight used in strength training should be increased gradually according to the athlete’s ability and requirement.
- Allow for proper recovery : Rest and recovery play a vital role in strength training.
- Use safety equipment when necessary : Safety equipment such as belts, boots, and wristbands should be used when necessary to provide additional support and protection during strength training.
- Be cautious with children : In the case of children, the load or weight used in strength training should be kept low until the age of 16, as their chances of injuries are higher.
What is Strength ? What are various methods for developing strength ? Write in detail. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Strength is a crucial component of fitness and plays a significant role in sports. It refers to the ability of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance.
These methods can be categorized into three main types :
- Resistance Training : This method involves using external resistance, such as weights or resistance bands, to challenge the muscles and stimulate strength gains. There are different types of resistance training techniques : (a) Traditional Strength Training (b) Circuit Training and (c) Bodyweight Training
- Isometric Training : Isometric exercises involve contracting the muscles without any visible movement. These exercises are performed by exerting force against an immovable object or by holding a static position. Isometric training helps improve strength at specific joint angles and can be beneficial for rehabilitation purposes.
- Plyometric Training : Plyometric exercises involve explosive movements that utilize the stretch-shortening cycle of muscles. These exercises focus on developing power and speed, which are essential for activities that require quick and explosive movements. Plyometric exercises include box jumps, medicine ball throws, and depth jumps.
Define strength and explain any two methods to develop it. (10.3) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Strength is a crucial component of fitness and plays a significant role in sports. It refers to the ability of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance.
Two methods to develop are :
- Isometric Training : Isometric exercises involve contracting the muscles without any visible movement. These exercises are performed by exerting force against an immovable object or by holding a static position. Isometric training helps improve strength at specific joint angles and can be beneficial for rehabilitation purposes.
- Plyometric Training : Plyometric exercises involve explosive movements that utilize the stretch-shortening cycle of muscles. These exercises focus on developing power and speed, which are essential for activities that require quick and explosive movements. Plyometric exercises include box jumps, medicine ball throws, and depth jumps.
Discuss physiological factors determining speed. (10.3) (SQP Term-II, 2021-22)
Ans. The physiological factors that determine speed include the mobility of the nervous system, explosive strength of an individual, correct technique of performing a task, bio-chemical reserves and metabolic power of an individual, flexibility, and certain psychic factors like optimum arousal, attention, motivation, concentration, ability to relax, etc.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Write in detail about strength improving methods — Isometric, Isotonic and Isokinetic. (10.3) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Strength is the capacity of the whole body or parts of to exert force. There are two types of strength — Dynamic and Static strength. Following methods are used to improve strength :
(1) Isometric exercise : Means where we do these exercises work is done cannot be observed. In these exercises, work is performed but it is not seen directly. In these exercises a group of muscles carry out tension against the other group of muscles. For example : Pushing against the sturdy wall, we will not be able to move it from its place. So, we should not consider it as work. Our muscle exert force, while pushing wall, but we see that work is not done.
When we do exercise expenditure of energy is usual phenomenon. Some time body temperature may increase while performing these exercises. Muscles may feel a slight tremor if exercise is done for a prolonged time. Regular performing these exercises muscle size and shape can be changed.
(2) Isotonic Exercise : Isotonic exercises are those exercises in which movement can be seen directly. Work is done in these exercises. The lengthening and shortening of muscle can be called eccentric contraction and concentric contraction accordingly.
Examples are : Calisthenic exercises, running and jumping on the spot, lifting of weights or exercise with medicine ball. These exercise can be done with or without equipment.
(3) Iso-kinetic exercise : In Iso-kinetic exercise contraction of muscle apply maximum forces throughout the complete range of movements. According to individual’s capacity, the speed of contraction can be adjusted. The Iso-kinetic excise can be used effectively for the development of strength.
What are the types of ‘strength’ ? Explain isotonic method to improve strength. (10.3) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans.
Isotonic strength (Dynamic strength) : The word isotonic is comprised of two word ‘ISO’ means ‘same’ and tonic means tone. Involves movement of muscles i.e., shortening and lengthening of muscles. In these type of exercise we can observe movements directly. The length of muscle can be seen and called, eccentric contraction and concentric contraction accordingly. e.g., when we throw a ball, jump, run, weight training.
We can observe these type of movement widely in games and sports. These exercises can be done with or without equipments. They are best for strength development and are good for conditioning in sports like, calisthenics exercise, light rhythmic exercise, exercise with light weight. (or any relevant answer)
Write in detail about ‘Barrow’s Motor Ability Test’ to measure motor fitness components. (10.3) (CBSE 2018, Delhi)
Ans. Three item test battery/purpose of test/requirement/Result :
(1) Standing broad jump/leg strength/mat 5 × 12 ft./3 trial — best jump recorded.
(2) Zig Zag Run/agility and speed/stop watch, 5 obstacles, space 16 × 10 ft./3 complete circuit — time recorded.
(3) Medicine ball throw/arm and Shoulder strength/(boys — 3 kg; girls — 1 kg)/3 trials best recorded.
Define strength and discuss means and methods for strength development. (10.3) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. Strength is a crucial component of fitness and plays a significant role in sports. It refers to the ability of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance.
Here are some common means and methods for strength development:
- Resistance Training : Resistance training involves using external resistance, such as free weights, weight machines, resistance bands, or bodyweight exercises, to challenge and strengthen the muscles.
- Progressive Overload : Progressive overload is a principle in strength training that involves gradually increasing the demands placed on the muscles over time.
- Compound Exercises : Compound exercises involve multiple muscle groups and joints working together, which can lead to greater overall strength gains.
- Specificity : Strength development can be specific to the movements and demands of a particular sport or activity.
- Periodization : Periodization is a training approach that involves dividing training into specific phases or cycles, each with different goals and intensities.
- Rest and Recovery : Adequate rest and recovery are essential for strength development.
- Proper Technique : Using proper technique during strength training exercises is crucial for both safety and effectiveness.
Define strength. Explain any two methods of improving strength. (10.3) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. Strength is a crucial component of fitness and plays a significant role in sports. It refers to the ability of muscles to overcome resistance or act against resistance.
Two methods to develop are :
- Isometric Training : Isometric exercises involve contracting the muscles without any visible movement. These exercises are performed by exerting force against an immovable object or by holding a static position. Isometric training helps improve strength at specific joint angles and can be beneficial for rehabilitation purposes.
- Plyometric Training : Plyometric exercises involve explosive movements that utilize the stretch-shortening cycle of muscles. These exercises focus on developing power and speed, which are essential for activities that require quick and explosive movements. Plyometric exercises include box jumps, medicine ball throws, and depth jumps.
Elaborate the physiological factors determining endurance and strength. (10.3) (SQP 2017-18)
Ans. Physiological factors determining endurance and strength :
Endurance :
- Slow twitch muscle fibre
- Dehydration
- Blood volume
- Cardiac output
- Pulmonary diffusion
- Lactic acid tolerance
- Muscle composition
- Aerobic capacity
Strength :
- Gender
- Muscle size
- Lean body mass
- Energy level
- Nerve impulses
- Age
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Dynamic Strength : Dynamic strength is also known as isotonic strength. In pull-ups and push-ups, we required dynamic strength. In performing such a workout, there is a diminishing tendency in dynamic strength, and as a result, muscles refuse to do work after some time. The man cannot do even one extra pull-up or push-up at this stage. Movements are visible when someone uses dynamic strength. It is recognized by rhythmic muscular contractions with changes in muscle length, using a relatively small force. Example: push up and full squats.
Dynamic strength can be divided into three parts : (a) Maximum Strength, (b) Explosive Strength, and (c) Strength Endurance.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Isometric Exercise : These are the exercises that are not visible as there are no direct movements. Therefore, isometric exercises cannot be observed. In these exercises, work performed cannot be seen directly, like pushing a wall. While pushing a wall, work is done, i.e., the force is being exerted, but the work done cannot be seen as the wall is still at the same place and doesn’t move a bit. These exercises involve muscles carrying out tension against the other group of muscles. There is no change in the muscle length when such exercises are done, hence they are called “iso” metric. These exercises need less time and equipment and can be performed practically anywhere and everywhere. Moreover, isometric exercises can prove to be of great value for maintaining strength in case of an injury. These exercises, if performed regularly, may result in a change in muscle size and shape.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Isokinetic Exercise : P this method was introduced by J.J. Perrine in 1968 and involves a particular type of muscle contraction called isokinetic contraction, generally used in sporting events like rowing and swimming. These exercises are performed on specially designed instruments. In isokinetic contraction, the muscles apply maximal force throughout the range of motion around the joint. Whereas in isotonic contraction, the pressure is applied at a particular angle. The use of isokinetic contraction is minimal. Hence, the contribution of isokinetic contraction in developing strength is yet to be scientifically proved.
What ______
Ans. –
10.4 Endurance
Multiple Choice Questions
Which is not a type of endurance according to the nature of activities (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Basic endurance
(b) General endurance
(c) Specific endurance
(d) Speed endurance
400 m sprint event comes under (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Speed endurance
(b) Short endurance
(c) Medium endurance
(d) Long endurance
There will be no variation in the pace of inactivity in (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Fartlek method
(b) Continuous method
(c) Interval method
(d) None of the above
The Swedish word meaning speed play is ____________. (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Fartlek method
(b) Continuous method
(c) Pace method
(d) None of the above
Fartlek training was developed in (10.4) (CBSE 2020)
(a) Sweden
(b) The USA
(c) India
(d) The U.K.
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
Which method will you suggest to develop endurance ? (10.4) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. (i) Fartlek method
(ii) Continuous method
(iii) Interval training method (Any one)
What does the term ‘Fartlek’ mean and who developed this training method ? (10.4) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. The word ‘Fartlek’ is Swedish word means ‘speed play’. Gosta holmer developed it in 1937.
Maintaining physical activities for a longer period, brings desirous changes in circulatory system. Justify your answer by highlighting three benefits of exercise. (10.4) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. (1) Improved cardiovascular health, (2) Increased capillarization, and (3) Enhanced aerobic capacity, these benefits of exercise contribute to a healthier circulatory system, promoting better overall health and well-being.
Define coordinative ability. (10.4) (SQP 2016-17)
Ans. Coordinative abilities are the abilities of an individual to control and regulate their movements in a specific manner, allowing them to perform various activities accurately and efficiently.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Define endurance. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Endurance : Endurance can be defined as the ability of an individual to sustain physical activity or resist fatigue over a period of time. It is a measure of one’s stamina and the capacity to continue performing a task or exercise without experiencing excessive tiredness or exhaustion.
- According to Harre, endurance is the ability to resist fatigue.
- Barrow and McGee define it as the result of a physiological capacity to sustain movement over a period of time.
- H. Singh defines endurance as the ability to sustain an activity.
Write about the different types of endurance based on the duration of activity. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Based on the duration of activity, the different types of endurance are :
- Speed Endurance : This is the ability to resist fatigue in cyclic activities that last up to 45 seconds. Examples include a 400 m sprint in track and field.
- Short Term Endurance : This ability is needed for activities lasting 45 seconds to about 2 minutes. An examples is an 800 m run.
- Medium Time Endurance : This type of endurance is needed to resist fatigue in activities lasting from 2 minutes to about 11 minutes. Examples include a 1500 m run and 3000 m run.
- Long Time Endurance : This type of endurance is needed for activities that last for more than 11 minutes. Examples include marathons and cross country events.
Explain any two physiological factors, help in determining endurance. (10.4) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Two physiological factors that help in determining endurance are :
- Oxygen Utilization : Endurance activities require a continuous supply of oxygen to the working muscles in order to produce energy. The body’s ability to efficiently utilize oxygen plays a crucial role in determining endurance. This is measured by the maximum oxygen uptake or VO2 max, which is the maximum amount of oxygen that an individual can use during intense exercise.
- Muscle Fiber Composition : The composition of muscle fibers in an individual’s body also affects their endurance capacity. There are two main types of muscle fibers : (a) Slow-twitch fibers are more efficient at using oxygen and are resistant to fatigue, making them well-suited for endurance activities. (b) Fast-twitch fibers, on the other hand, are better at generating quick bursts of power but fatigue more quickly.
Explain interval training method. (10.4) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. Interval training method :
- The interval training method is a versatile method used for improving endurance.
- It involves practicing an activity at a high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery.
- The principle behind this method is to work at a speed and duration that raises the heart rate to 180 beats per minute, followed by a short interval until the heart rate drops to 120-130 beats per minute, and then repeating the work.
- This method has several effects, including improved circulatory system, improved aerobic capacity, and improved lactic acid tolerance.
Describe any two types of endurance. (10.4) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Two types of endurance are :
- Basic Endurance : This type of endurance refers to the ability of a person to resist fatigue in activities that involve medium intensity and aerobic muscular metabolism. Examples of activities that develop basic endurance include jogging, cycling, and swimming for more than 30 minutes.
- Specific Endurance : This type of endurance is specific to a particular sport and refers to the ability to perform movements of that sport while resisting fatigue. For example, the specific endurance required for a hockey player would be different from that of a marathon runner or a cyclist.
What is Fartlek training ? Write in brief. (10.4) (CBSE 2017)
Ans. • Gosta Holmer developed Fartlek training in 1937.
- Fartlek training method is used for developing endurance
- It is a combination of Aerobic and Anaerobic/Continuous and internal training.
- Fartlek is derived from Swedish word which means speed play.
- Athletes speed or pace is not preplanned and is decided according to the surroundings
- Self discipline is most important while undertaking the training.
- The range of heart beat should be 140 to 180/minute
- Example :
- Jogging, slow running — 5 to 10 minutes
- Steady, hard running — 1.5 to 2.5/km
- Rapid walking — 5 minutes
- Sprints for about 50 to 60 mts
- Full speed up hill running for 175 to 200 mts
- Free running/easy running
- Fast pace/minute (Relevant information may be considered)
Explain interval training method. (10.4) (CBSE 2017, Outside)
Ans. Interval training method : Interval training method is also called terrace training. It is training of heart, through endurance training. If you run your heart beats at a faster rate.
Dr. Woldemar and Gerschler, introduced this training method in 1930. In this method the athlete used to run 400 m. race, 10 to 20 times daily, instead of running 10 to 20 miles daily. In fact this training method is based on effort and recovery principle. During interval training recovery period is given to the athlete after each speedy workout. Recovery period can be adjusted according to the efficiency of the athlete. The load can be increased by reducing the recovery period or by increasing the workout. For an athlete of 400 m.
Following examples are applicable in his training :
- 400 m race with 80% speed.
- Walking or jogging until his heart rate comes down to 120 to 140 approximately.
- 400 m race with 80% speed. (repetition)
What is endurance ? How endurance can be developed through Fartlek method ? (10.4) (CBSE 2016)
Ans. Endurance is the ability to sustain an activity over a longer period of time, under the condition of fatigue. Endurance can be developed through fartlek method are as follows :
- Endurance develops through continuous and interval training; fartlek combines both training.
- Endurance develops according to duration of activity; fartlek can vary from aerobic walking to anaerobic sprinting.
- Endurance develops according to nature of activity; fartlek can change it according to the surrounding.
- Endurance develops under the condition of fatigue; self discipline plays a vital role in Fartlek training method.
- Fartlek training keeps the heart rate up allowing an athlete to get good cardio-vascular endurance.
- Due to the sprinting interval, it makes the body versatile.
- It is not rigid but flexible in nature.
Define endurance and describe any one method to develop endurance. (10.4) (CBSE 2018, Comptt.)
Ans. Endurance : Endurance can be defined as the ability of an individual to sustain physical activity or resist fatigue over a period of time. It is a measure of one’s stamina and the capacity to continue performing a task or exercise without experiencing excessive tiredness or exhaustion.
One method to develop endurance is the Continuous Method :
- An exercise is performed for a longer duration without any rest.
- The intensity of the training is relatively low, but the duration is long and continuous.
- Within the Continuous Method, there is a subcategory called the Slow Continuous Method.
- The Slow Continuous Method of the Continuous Method helps to develop endurance by allowing the muscles to work for an extended period of time without rest.
Explain any three types of coordinative abilities. (10.4) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. Three types of coordinative abilities mentioned are :
- Orientation Ability : This refers to the ability to determine and change the position and movements of the body in a specific field of action and in relation to a moving object. It involves spatial awareness, body positioning, and visual perception.
- Differentiation Ability : This refers to the ability to achieve a high level of accuracy and fine-tuning of movement phases. It involves precise control and coordination of body movements, requiring a high level of motor skill and experience.
- Coupling Ability : This refers to the ability to coordinate movements of different body parts with each other and with a specific goal-oriented movement.
Explain the methods to improve flexibility with help of examples. (10.4) (SQP 2019-20)
Ans. There are two common methods to improve flexibility :
- Slow Stretching : This method involves slowly stretching the muscles around the joint without any jerky movements. For example, performing a slow and controlled hamstring stretch by reaching towards your toes and holding the stretch for a few seconds.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : After stretching, this method involves holding the maximum stretching point for about 6-8 seconds. An example would be performing a slow stretch and hold for the quadriceps by bending one knee and bringing your foot towards your glutes, then holding the stretch.
Explain any three types of coordinative abilities. (10.4) (SQP 2020-21)
Ans. Types of coordinative abilities :
- Orientation ability : It is an ability to realize position of the body or its parts in space and time.
- Coupling ability : Coupling ability is the ability to combine the movements of different body parts for performing perfect sports movements.
- Reaction ability : It is the ability to react quickly and effectively to a signal.
- Balance ability : Balanceability is the ability to keep body and its parts in a relatively stable position in both static and dynamic conditions.
- Rhythm ability : It is the ability to understand the rhythm of movement and to do the movement with the required rhythm.
- Adaptation ability : It is the ability to adjust or bring about an effective change in the movement on the basis of changes or anticipated changes in the situation.
- Differentiation ability : The ability to attain a high degree of accuracy and economy of separate body movements and movement phases. (any three)
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Explain types of endurance according to the duration of the activity. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. According to the duration of the activity, endurance can be classified into different types :
- Basic Endurance : This type of endurance is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that involve medium intensity and aerobic muscular metabolism. Examples : jogging, cycling, and swimming for more than 30 minutes.
- General Endurance : General endurance refers to the ability to perform sporting movements for a prolonged duration that are not specific to any particular sport.
- Specific Endurance : This type of endurance is the ability to perform movements specific to a particular sport and resist fatigue. Examples : a hockey player will be different from that of a marathon runner or a cyclist.
- Speed Endurance : Speed endurance is the ability to resist fatigue in cyclic activities that last up to 45 seconds. Examples : 400 m sprint in track and field.
- Short Term Endurance : This type of endurance is needed for activities lasting from 45 seconds to about 2 minutes. Examples : 800m run.
- Medium Time Endurance : Medium time endurance is required to resist fatigue in activities lasting from 2 minutes to about 11 minutes. Examples : 1500 m and 3000 m run, as well as 100 m rowing.
- Long Time Endurance : This type of endurance is needed for activities that last for more than 11 minutes.
Explain types of endurance according to the nature of the activity. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Based on the nature of the activity, the types of endurance can be classified into three categories :
- Basic Endurance : This type of endurance is the ability to resist fatigue in activities that involve medium intensity and aerobic muscular metabolism. It involves movements that engage a large number of muscles at a slow pace for a prolonged period. Examples: jogging, cycling, and swimming for more than 30 minutes.
- General Endurance : General endurance refers to the ability to perform sporting movements for a prolonged duration that are not specific to any particular sport. Unlike basic endurance, general endurance activities may incorporate high-intensity practices. However, the duration for general endurance is much shorter than basic endurance.
- Specific Endurance : This type of endurance is the ability to perform movements specific to a particular sport and resist fatigue. The specific endurance required varies from activity to activity, depending on the nature of fatigue. Example : A hockey player is different from that of a marathon runner or a cyclist, as the demands of the activity are different.
What do you mean by endurance ? Explain methods to develop endurance in detail. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Endurance refers to the ability of an individual to sustain physical activity or resist fatigue over a period of time.
- Continuous Method : This method involves performing an exercise for a longer duration without any rest. There are two subcategories :
- Slow Continuous Method : In this method, the activity is performed at a certain speed without any breaks for a long duration.
- Fartlek Method : In this method, the activity is performed at varying speeds and intensities.
- Interval Method : This method involves practicing the activity at a relatively high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery. The principle behind this method is to work at a speed and duration that raises the heart rate to around 180 beats per minute. The Interval Method helps to improve the circulatory system, aerobic capacity, and lactic acid tolerance.
Define endurance and discuss the methods of endurance development. (10.4) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Endurance : Endurance can be defined as the ability of an individual to sustain physical activity or resist fatigue over a period of time.
The methods to develop endurance are :
- Continuous Method : This method involves performing an exercise for a longer duration without any rest. The intensity of the exercise is low, and it can be further categorized into the Slow Continuous Method, where the activity is performed at a certain speed without any break for a long duration.
- Interval Method : This method involves practicing the activity at a comparatively high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery. The principle is to work at a speed and duration that raises the heart rate to 180 beats per minute, followed by a short interval, and then starting again when the heart rate drops to 120-130 beats per minute.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
Define endurance. Elucidate any two methods of developing endurance. (10.4) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Endurance : Endurance is the ability of an individual to continue the activity for a considerable period of time with a great degree of efficiency. Or Endurance is the ability to resist fatigue.
Any two training methods to develop endurance.
(1) Continuous running methods : An athlete is required to run at a steady pace or speed without any break. This rate can be determined by keeping the heart beat 130 to 160 beats per minutes. Running at such a pace can be continued for about 30 minutes for young athlete and 60 to 120 minutes for mature athlete. The duration can be decided on the basis of the capability of athlete and type of competition. Due to long term of training under aerobic condition, the maximum oxygen uptake or the oxygen utilization of the athlete increases. Glycogen level of muscles, efficiency of heart and lung also increases.
(2) Interval training method : This method is based on the principle of effort, recovery and effort again. In this method the recovery period is called interval. This interval period help an athlete to recover from increased respiratory rate. Blood pressure and accumulation of waste product such as load can be decided according to the capability of athlete. Many variables can be considered like — increase distance, decrease time, increase number of repetition and decrease recovery time. Accordingly, there may be a need to change speed, repetitions and recovery period. Care should also be taken while increase in the load gradually. Decrease the load if the athlete feels difficulty in performing.
A micro cycle (weekly schedule) should be prepared and can be altered. This training is important for the athlete, especially engaged in endurance development as it helps in proper cardio vascular adjustments.
(3) Fartlek training : Fartlek is Swedish word which means ‘speed play’. It is variation of variable pace running .This method is based on cross country running with varying speed according to the dictates of terrain and the requirement of athlete. Along with running, some exercises may also be included in this type of training .It is usually conducted over a hilly region. It may also be conducted in ploughed fields or sand beds. The trainer only fixes the duration of completion of running. The athlete has a freedom to run at an easy pace, change the pace while uphill and downhill running and sprinting in between. Squat jumps, hopping with one or both legs can also be included.
Define flexibility along with its types. Explain any two methods used to develop flexibility. (10.4) (SQP 2022-23)
Ans. Flexibility refers to the range of motion around a joint and the ability to perform movements with greater amplitude or range. It is influenced by genetic factors and physical activity programs. Flexibility is important for smooth and efficient movements, preventing injuries, improving posture, reducing back pain, maintaining healthy joints, and learning various skills quickly. There are two types of flexibility :
- Passive Flexibility : This is the ability to do movements with greater amplitude and with external help. It is primarily determined by the joint structure and stretchability of the muscles and ligaments. Examples include stretching with the help of a partner.
- Active Flexibility : This is the ability to perform a movement with greater amplitude without external help. It is always less than passive flexibility and indicates a lack of muscular strength or coordination. Examples include performing stretching exercises by oneself.
Two methods used to develop flexibility are :
- Slow Stretching : This method involves slowly stretching the muscles around the joint. It is important to perform the stretches slowly and without any jerky movements.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : After stretching, this method involves holding the stretch at the maximum stretching point for about 6-8 seconds. This is considered to be the most commonly used method in the field of games and sports.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Classification according to the nature of the activity :
Basic Endurance : This is the ability of a person to resist fatigue in which the load is of medium intensity and involves aerobic muscular metabolism. Therefore, it can be said that it is the ability to do movements that involve a large number of muscles at a slow pace for a prolonged period. For example, jogging, cycling, and swimming for more than 30 minutes. Basic endurance forms the base for all other types of endurance.
General Endurance : it is the ability to do such sporting movements for a prolonged duration that are general. This type is not specific to any sport and can be developed by performing general exercises. Unlike essential endurance, in which the intensity of the activity is medium, general endurance activities may incorporate high-intensity practices. But the duration for general endurance is much shorter than essential endurance.
Specific Endurance : This is the ability to perform movements of a particular sport to resist fatigue. Specific endurance varies from activity to activity as it depends on the nature of fatigue. For example, the specific endurance of a hockey player is different from that of a marathon runner or a cyclist as the need for the activity is different.
What ______
Ans. –
2. Classification according to the Duration of the Activity :
Speed Endurance : This is the ability to resist fatigue in cyclic activities that last up to 45 seconds. The classic example of this endurance type is a 400m sprint in track and field. This type of endurance is majorly dependent on the power and capacity to produce energy.
Short Term Endurance : This ability is needed for activities lasting 45 seconds to about 2 minutes. The most appropriate example for short-term endurance is an 800m run. This endurance depends majorly on speed endurance and strength endurance.
Medium Time Endurance : Medium time endurance is needed to resist fatigue in activities lasting from 2 minutes to about 11 minutes. The most common example of this type is 1500m and 3000m run and 100m rowing. As in short-time endurance, this type of endurance also depends on speed and strength endurance, but to a limited extent.
Long Time Endurance : This type of endurance is needed for activities that last for more than 11 minutes. This type of endurance is required in events like marathons, cross country, etc
What ______
Ans. –
3. Volume : Training volume is simply the amount of training you do. The primary training component includes duration or time of training, distance covered volume load (sets in weight training), number of repetitions, or performed work in a given time. It is a quantitative component of work.
Intensity : Training intensity refers to the effort by which a training session is completed. It is a qualitative component of work—more work or efforts done by the athlete per time. Assessment of intensity varies from sport to sport. Speed is assessed by metres per second, resistance in kilogram, team games, or distance races may be evaluated by heart rate, etc.
Density : Training density is simply the volume of training completed within a given time frame. As volume and intensity have an inverse relationship, density and intensity do. The less dense a session, the more intense it can be.
What ______
Ans. –
10.5 Speed
Multiple Choice Questions
Which is not a type of speed (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Reaction
(b) Sprinting
(c) Acceleration
(d) Speed endurance
What type of speed is defined as the ability to maintain maximal speed for maximal distance and maximum duration? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Acceleration ability
(b) Locomotor ability
(c) Movement ability
(d) Reaction ability
Acceleration run and pace run can be two methods of improving (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Flexibility
(b) Speed
(c) Endurance
(d) Strength
Very Short Answer Type Questions (1 Mark)
What do you understanding by reaction ability ? (10.5) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly and effectively to a stimulus or signal. It involves accurately and rapidly responding to visual, auditory, or tactile cues in different games and sports.
What are pace races ? (10.5) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Pace runs, also known as pace races, involve running a set distance at a consistent speed. These runs are typically used in middle and long-distance races, such as races of 800 meters and above.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What are acceleration runs ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Acceleration runs :
- Acceleration runs are a type of training exercise that focuses on developing speed and acceleration in athletes.
- In an acceleration run, the athlete starts from a static position and gradually increases their speed over a specific distance.
- The number of acceleration runs can be adjusted based on the athlete’s age, capacity, and fitness level.
- It is important to perform acceleration runs after a proper warm-up to prevent injuries.
Define speed. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Speed :
- Speed is defined as the ability of an individual to perform movements or actions in the minimum amount of time.
- It is a motor ability that depends on factors such as the central nervous system, explosive strength, correct technique, flexibility, and certain psychological factors.
- Speed can be categorized into different types, including reaction ability, acceleration ability, movement speed, locomotor ability, and speed endurance.
Define speed and mention the methods to improve it. (10.5) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Speed : Speed is defined as the ability of an individual to perform movements or actions in the minimum amount of time.
The methods to improve speed include :
- Acceleration Runs : These runs involve starting from a static position and trying to reach maximum speed over a specific distance.
- Interval Method : This method involves practicing the activity at a high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery.
- Repetition Method : This method is characterized by high intensity work with complete recovery intervals.
Acceleration run and pace run methods can be used to increase the speed of an athlete. Justify. (10.5) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
Ans. Acceleration runs and pace runs are both methods that can be used to increase the speed of an athlete.
- Acceleration runs involve starting from a static position and gradually increasing speed over a specific distance.
- By repeating acceleration runs with sufficient rest between runs, athletes can improve their ability to generate momentum and maintain their top speed for a longer distance.
- Pace runs, on the other hand, focus on maintaining a steady speed over a set distance.
- By running at a maximum steady speed for a distance slightly longer than the actual racing distance, athletes can improve their endurance and ability to maintain speed under fatigue.
Define speed and elaborate any one method to develop speed. (10.5) (CBSE 2020, Comptt.)
Ans. Speed is the ability of an individual to cover a distance or perform a movement in a minimum time.
Methods of developing speed :
(1) Acceleration runs : Acceleration is the rate of change of speed of an object. It is the ability to achieve maximum speed from a stationary position in the short time.
Acceleration takes place in the first 50-60 meters. Training to improve the acceleration such as repeated sprints of 50 meters with full rest period or recovery.
Accelerate quickly and powerfully is a technique required in most of the sports.
For example an athlete is required to run as fast as possible. This ability is very important in many sports such as sprints, swimming sprints, basketball, hockey, football etc.
Consider the following points to improve acceleration speed — Stride Length, Ground Contact Time, Velocity, Stride Frequency and Heel Recovery.
(2) Pace races : The pace is the speed at which an athlete runs. Developing a better sense of pace will help athlete conserve energy while running. Working on pace can help to achieve running goal. If an athlete starts running too fast and then slows down he won’t get the same training benefit.
The athlete tries to run or swim each repetition at the same pace to achieve maximum benefit. It is considered a good pacing technique. Pace race strategy refers to running in pace which help to achieve optimum level performance.
Example : 800 m race.
Break the race into sections, which makes it easier to determine your pace.
Pace strategy for 800 m running, keeps the 4-6 second difference in first and second 400 m to achieve optimum level of performance.
To develop the speed endurance we will have to work more on pace races because pace races means running the whole distance at a constant speed. (Explain any 1 method)
Write factors, determining ‘Speed’. Explain methods for improving speed. (10.5) (CBSE 2017, Comptt.)
Ans. Factors determining speed include :
- Mobility of the nervous system
- Explosive strength
- Correct technique
- Bio-chemical reserves and metabolic power
- Flexibility
- Psychic factors
Some methods for improving speed include :
- Acceleration Runs : These runs involve starting from a static position and trying to reach maximum speed over a specific distance. They are repeated with sufficient rest between runs.
- Interval Method : This method involves practicing an activity at a high intensity with intervals or breaks of incomplete recovery. The goal is to work at a speed and duration that raises the heart rate to 180 beats per minute, followed by a short interval when the heart rate drops to 120-130 beats per minute.
- Repetition Method : This method involves high-intensity work ranging from 90 to 100% with complete recovery intervals. It is particularly effective for developing speed endurance.
Short Answer Type-II Question (4 Marks)
Explain types of speed and methods to develop speed. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. The types of speed are as follows :
- Reaction Ability : This refers to the ability to react quickly to a stimulus or signal.
- Acceleration Ability : This is the ability to achieve a high speed from a stationary position.
- Movement Speed : This refers to the ability to perform a single movement in the shortest possible time.
- Locomotor Ability : Locomotor ability is the capacity to maintain maximum speed while in motion for the longest possible duration or distance.
- Speed Endurance : Speed endurance is the ability to sustain high-speed movements for a longer duration, even under fatigue.
Methods to develop speed include :
- Acceleration Runs : These involve running a specific distance from a stationary position and aiming to achieve maximum speed as quickly as possible.
- Interval Training : This method involves alternating periods of high-intensity sprinting with periods of active recovery.
- Plyometric Exercises : These exercises focus on explosive movements, such as jumping and bounding, to enhance power and speed.
- Resistance Training : Strength training exercises, particularly those targeting the lower body, can improve explosive strength and contribute to faster movements.
- Technique Training : Working with a coach or trainer to refine and optimize movement patterns can lead to improved speed.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
What is movement speed ? Explain the methods to develop speed endurance. (10.5) (CBSE 2015)
Ans. Movement speed refers to the ability to perform a single movement in the minimum possible time. It is a component of speed that is highly related to acyclic sports, but its importance in cyclic sports is limited to the initial phase.
Here are some of the commonly used methods :
- Interval Training : This method involves alternating between periods of high-intensity sprinting and periods of active recovery. For example, a sprinter may sprint at maximum speed for 200 meters, followed by a slower jog or walk for 200 meters.
- Fartlek Training : Fartlek, which means “speed play” in Swedish, is a method that combines continuous running with bursts of speed. During a fartlek run, a runner can vary their pace by sprinting for a certain distance or time, then slowing down to a comfortable pace.
- Tempo Runs : Tempo runs involve running at a steady pace that is slightly faster than the runner’s usual pace. The goal is to sustain this pace for a longer duration, gradually increasing the distance or time.
- Hill Training : Running uphill is an effective way to develop speed endurance. The incline increases the intensity of the workout, forcing the muscles to work harder.
- Circuit Training : Circuit training involves performing a series of exercises targeting different muscle groups with minimal rest in between. This method helps improve overall fitness, including speed endurance, by challenging the cardiovascular system and building muscular endurance.
What do you mean by specific sports programmes ? Explain any three. (10.5) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Specific sports programs refer to training programs that are designed specifically for a particular sport or athletic activity. Specific sports programs typically include a combination of strength training, endurance training, speed and agility training, flexibility training, and sport-specific skill development.
Here are three specific sports programs that focus on developing speed endurance :
- Sprint Training Program : This program is specifically designed for athletes participating in sprint events such as the 100m and 200m sprints. It includes a combination of short, intense sprints and longer distance runs to improve both speed and endurance. The program typically includes interval training, where athletes alternate between high-intensity sprints and periods of active recovery.
- Middle-Distance Running Program : This program is aimed at athletes participating in middle-distance events like the 800 m and 1500 m runs. It focuses on developing both speed and endurance to maintain a fast pace over a longer duration. The program includes a mix of interval training, tempo runs, and longer distance runs.
- Cycling Endurance Program : This program is designed for cyclists who participate in endurance events such as road races or time trials. It focuses on developing speed endurance by combining high-intensity intervals with longer duration rides. The program includes interval training on the bike, hill repeats, and long rides at a steady pace.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Types of Speed : From a general point of view, there are five different types of speed that are :
- Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly to a stimulus or signal. It depends entirely on the coordinative abilities of an individual. Different games and sports have other signs like visual, auditory and tactile, to name a few. And to respond to such signals accurately and as quickly as possible is known as reaction ability. It can be further classified into simple and complex reaction abilities.
- Acceleration Ability : Acceleration ability is the ability to achieve a high locomotion speed from a stationary position. It depends significantly on the explosive strength, technique, and movement frequency. This ability is essential in almost every game and sport but greatly influences sprinting events.
- Movement Speed : Movement speed can be defined as the ability to perform a single movement in the minimum possible time. It is highly related to acyclic sports, but its importance in cyclic sports is limited to the initial phase. It is dependent on the technique and explosive strength.
- Locomotor Ability : Locomotor ability is the ability to maintain maximum speed when in motion for the maximum possible duration or distance. It is essential in sports like 100m and 200m sprints, speed skating, and short sprints in cycling. Locomotor ability depends highly on the mobility of the nervous system. The chances of improving locomotor ability are relatively low.
- Speed Endurance : Speed endurance is a combination of two words, speed and endurance. It is the ability to do the movement with high speed for a longer duration, i.e., under fatigue. It depends highly on anaerobic capacity, technique, and psychic factors
What ______
Ans. –
2. Acceleration Runs are generally used to develop speed while attaining maximum speed from a static position. In an acceleration run, a sportsperson must run a specific distance. After starting, the athlete tries to gain total momentum at the earliest and finishes the specified distance. These runs are repeated with sufficient rest between the runs. It usually takes 50-60 meters for a sprinter to attain maximum speed after the start. According to the research, it is observed that even well-trained athletes can maintain their top speed for 20 meters only. The number of acceleration runs can be set according to an athlete’s age,
capacity, and fitness level. It may vary from 6-12 repetitions with intervals for complete recovery. The acceleration runs must be done after proper warmup.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Pace Runs : Unlike acceleration runs, pace runs incorporate the method of running the set distance at a uniform speed. It usually includes races of 800 meters and above. It is a fact that an athlete can run a distance of 300 meters at full speed, and in the case of longer races, he must conserve his energy by reducing speed.
Therefore, keeping the pace in mind in middle and long-distance races is
essential. At the beginning of such races, the speed should not be too high, and the pace should be maintained throughout the race. For this type of training, the athlete should run at a maximum steady speed for a distance 10-20% more than the actual racing distance. Repetition for pace run training can be fixed as per the athlete’s fitness level with complete recovery in between repetitions.
What ______
Ans. –
10.6 Flexibility
Multiple Choice Questions
Which is not a type of flexibility ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Active
(b) Passive
(c) Ballistic
(d) Stretch
In which method is stretching done rhythmically ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Slow stretch
(b) Slow stretch and hold
(c) Ballistic method
(d) PNF
Which of the following factors does not influence flexibility ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Structure of joints
(b) Proper warming-up
(c) Body temperature
(d) None of these
What are the necessary steps in improving flexibility ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Proper warm-up
(b) Proper stretching
(c) Repetition of exercise
(d) All of these
________ is the range of motion of joints. (10.6) (CBSE 2021, Comptt.)
(a) Endurance
(b) Strength
(c) Flexibility
(d) Speed
Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)
Suggest any two methods to improve flexibility ? (10.6) (CBSE 2019, Delhi)
Ans. Methods to improve flexibility :
- Stretch and hold method
- Dynamic stretching method
- Ballistic method (Yoga, Dance)
- Proprioceptive Neuro-muscular facilitation techniques (partner exercises or stretching on equipments) (Any two)
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
Define flexibility. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Flexibility :
- Flexibility is the range of motion around a joint, or the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range.
- It is the ability of muscles and joints to stretch, allowing for smooth and efficient movements.
- Flexibility is influenced by factors such as muscle strength, joint structure, and stretchability of muscles and ligaments.
What do you mean by passive flexibility ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Passive flexibility :
- Passive flexibility refers to the ability to perform movements with a greater range of motion with the help of external assistance, such as a partner or equipment.
- It is characterized by the ability to stretch muscles and ligaments beyond their normal range of motion.
- Passive flexibility is primarily determined by the joint structure and the stretchability of the muscles and ligaments.
What is active and passive flexibility ? (10.6) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Active flexibility : Active flexibility refers to the ability to perform a movement with a greater range of motion without any external help. For example, a sportsperson performing a stretching exercise on their own demonstrates active flexibility.
Passive flexibility : Passive flexibility is the ability to do movements with a greater range of motion with the help of external assistance, such as a partner or a prop. Passive flexibility is always greater than active flexibility and is primarily determined by the joint structure and the stretchability of the muscles and ligaments.
Define flexibility and its types. (10.6) (CBSE 2020)
Ans. The ability of an individual to move his or her joints through its complete range of motion. Or Flexibility refers to the range of movement in a joint.
Types of flexibility :
- Active flexibility : It is the ability to do movement with greater amplitude without any external support.
- Passive flexibility : It is the ability to do movement with external support.
Define flexibility. Explain any one method to develop it. (10.6) (CBSE 2022, Comptt.)
Ans. Flexibility : Flexibility is the range of motion around a joint, or the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range. It is the ability of muscles and joints to stretch, allowing for smooth and efficient movements.
One method to develop flexibility is slow stretching. This involves slowly stretching the muscles around a joint without any jerky movements. The key is to hold the stretch for about 6-8 seconds at the maximum stretching point. This method is commonly used in the field of games and sports. It is important to note that stretching should be done slowly and without any sudden movements to avoid injury.
Discuss in detail the methods of flexibility development. (10.6) (CBSE 2019, Comptt.)
Ans. The methods of flexibility development are :
- Slow Stretching : This involves slowly stretching the muscles around the joint without any jerky movements.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : After stretching, hold the stretch for about 6-8 seconds at the maximum stretching point. This is a commonly used method in sports and games.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Discuss methods to improve flexibility. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Some methods to improve flexibility include :
- Slow Stretching : Slowly stretching the muscles around the joint without any jerky movements.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : Holding the maximum stretching point for about 6-8 seconds after stretching.
- Proprioceptive Neuro-Muscular Facilitation (PNF) Technique : Contracting the muscle for 5-7 seconds and then gradually stretching it to its utmost limit and holding for about 8-10 seconds. This process is repeated 4-8 times for each muscle group.
- Dynamic Stretching : Performing controlled movements, usually of legs and hands, suitable for dynamic movement.
Define flexibility. Explain its types and any two methods to develop flexibility. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Flexibility : Flexibility is the range of motion around a joint, or the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range. It is the ability of muscles and joints to stretch, allowing for smooth and efficient movements.
Flexibility is classified into two types : (1) Passive flexibility and (2) Active flexibility. Active flexibility is further classified into two categories: (a) Static Flexibility and (b) Dynamic Flexibility
Two methods to develop flexibility are :
- Slow Stretching : The first and most common method to improve flexibility is to slowly stretch the muscles around the joint. It is important to perform the stretches slowly and without any jerky movements to avoid injury.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : After stretching, holding the stretch at the maximum point for about 6-8 seconds is another effective method. This method is widely used in the field of games and sports to improve flexibility.
Long Answer Type Question (5 Marks)
Define flexibility and explain the methods for its development. (10.6) (CBSE 2013, Comptt.)
Ans. Flexibility : Flexibility is the range of motion around a joint, or the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range. It is influenced by genetic factors and physical activity programs. Flexibility is not a conditional or coordinative ability, but it plays a crucial role in various aspects of physical performance. There are two types of flexibility: passive flexibility and active flexibility.
To develop flexibility, there are several methods that can be employed:
- Slow Stretching : This method involves slowly stretching the muscles around the joint. It is important to perform the stretches slowly and without any jerky movements.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : After stretching, holding the stretch for about 6-8 seconds at the maximum stretching point is recommended. This method is commonly used in the field of sports and games.
- Dynamic Stretching : This method involves performing controlled movements that mimic the activity or sport being performed. It helps to improve flexibility while also warming up the muscles.
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF) : PNF stretching involves a combination of stretching and contracting muscles. It is usually done with a partner and is highly effective in improving flexibility.
- Yoga and Pilates : These practices focus on stretching and strengthening the muscles, improving flexibility, and promoting overall body awareness.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Flexibility : Flexibility is also known as the range of motion around a joint. It is the ability to execute a movement with greater amplitude or range. Flexibility is related to genetic factors as well as physical activity programmes. Flexibility is a motor component that is not a conditional or a coordinative ability. In general, usage flexibility often corresponds with stretchability, elasticity, litheness, mobility, pliancy, etc. Flexibility is affected by muscle strength, the structure of the joints, tendons, ligaments, and other factors. A person possessing good flexibility can perform daily tasks with greater ease and comparatively more efficiency and effectiveness. Moreover, the personality and posture of such individuals is more attractive. Tight joints affect smooth and efficient movements, whereas flexibility ensures smooth and efficient workouts. Therefore, it can be said that flexibility is helpful in many ways, such as preventing injuries, improving posture, reducing back pain, maintaining healthy joints, improving balance during making movements, and learning various skills quickly, such as backstroke in swimming
What ______
Ans. –
2. Types of Flexibility : Flexibility is of the following two types :
(A) Passive Flexibility : the ability to do movements with greater amplitude and with external help is known as passive flexibility. Example, stretching with the help of a partner. Passive flexibility is always more than active flexibility and is primarily determined by the joint structure and stretchability of the muscles and ligaments. Passive flexibility is the base of operational flexibility.
(B) Active Flexibility : The ability to perform a movement with greater amplitude without external help is called active flexibility. For example, you are performing a stretching exercise by a sportsperson himself. Active flexibility is always less than passive flexibility, and the difference between the two indicates a lack of muscular strength or coordination. Active flexibility is further classified into the two categories: (a) Static Flexibility and (b) Dynamic Flexibility.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Methods to Improve Flexibility : The various methods that can help to improve flexibility are discussed below :
- Slow Stretching : The first and foremost way to improve flexibility is slowly stretching the muscles around the joint. The critical point to note here is that stretching should be slow and without any jerky movements.
- Slow Stretch and Hold : The next stage after stretching is to hold for about 6-8 seconds at the maximum stretching point. This method is considered to be the most commonly used method in the field of games and sports.
- Ballistic Method : This method performs the movement with a swing and rhythm. As the stretching is done rhythmically, it is called Ballistic Method. The ballistic method once experienced popularity but has come under the scanner by many physical therapists. This form of stretching uses the body’s momentum to extend the range of motion. However, many experts believe that ballistic stretching can lead to injury.
- Proprioceptive Neuro-Muscular Facilitation (PNF) Technique : It is also known as the post isometric stretch and is based on the principle of proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation. This principle states that if a muscle is contracted maximally for a few seconds, the muscle gains maximum relaxation after the contraction. In this method, the muscle is frst contracted for 5-7 seconds and then gradually stretched to its utmost limit and held for about 8-10 seconds. The process is repeated 4-8 times for each muscle group.
What ______
Ans. –
10.7 Coordinative Abilities
Multiple Choice Questions
The ability to coordinate body part movements with one another and about a definite goal-oriented body movement is known as : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Balance ability
(b) Adaptation ability
(c) Rhythm ability
(d) Coupling ability
The ability to attain a high level of fine-tuning of movement phases is known as : (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Differentiation ability
(b) Orientation ability
(c) Adaptation ability
(d) Coupling ability
What kind of coordinate abilities are defined as determining a body’s position and its part in time and space concerning gravity and moving objects ? (CBSE TBQ)
(a) Differentiation ability
(b) Orientation ability
(c) Adaptation ability
(d) Coupling ability
Fill in the Blanks :
Complete the following mind map about the factors that influence sports training. (CBSE TBQ)

Ans. ………………………………………..
Very Short Answer Type Question (1 Mark)
What is coordinative ability ? (10.7) (CBSE 2018)
Ans. Coordinative ability is the ability of the body to bring together different elements of a complex activity into an efficient relationship.
Or Coordinative ability is an ability that enables the sportsman to do a group of movements with better quality and effect.
Short Answer Type-I Questions (2/3 Marks)
What do you mean by the term coordinative abilities ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Coordinative abilities :
- Coordinative abilities refer to the abilities of an individual to perform various activities correctly and efficiently, relying on the central nervous system’s motor control and regulation processes.
- While coordinative abilities focus on the control and regulation of movements, flexibility primarily relates to the range of motion in the joints.
- Coordinative abilities involve the coordination and synchronization of body movements, while flexibility focuses on the mobility and elasticity of muscles and joints.
What is coupling ability ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Coupling ability :
- Coupling ability is the ability to coordinate body part movements with one another and about a definite goal-oriented body movement.
- It is essential in sports where activities with a high degree of difficulty have to be done, such as gymnastics and team games.
- Coupling ability depends on the functional capacity of kinaesthetic and visual sense organs.
Elucidate any two types of coordinative ability with suitable example. (10.7) (CBSE 2022)
Ans. Two types of coordinative abilities are :
- Orientation Ability: This ability refers to the individual’s capacity to determine and change their body’s position and movements in a specific field of action and in relation to moving objects. Example : In gymnastics, orientation ability is crucial.
- Coupling Ability : Coupling ability involves coordinating the movements of different body parts with each other to achieve a specific goal-oriented movement. Example : In football, coupling ability is essential for ball control and dribbling.
Explain differentiation and orientation ability. (10.7) (CBSE 2013)
Ans. Differentiation Ability :
- Differentiation Ability refers to the ability to achieve a high level of accuracy and fine-tuning in movement phases.
- It involves the ability to perform movements with precision and control.
- In sports, differentiation ability is crucial for sensing and implementing movements, such as in sports that require precise hand-eye coordination or intricate footwork.
Orientation Ability :
- Orientation Ability, refers to the ability to determine and change the position and movements of the body in a given time and space.
- It involves understanding one’s position in relation to the field of play, opponents, teammates, and moving objects like a ball.
- Orientation ability is essential in sports where spatial awareness and quick decision-making are required, such as volleyball, football, or skating.
Briefly explain different types of co-coordinative abilities. (10.7) (CBSE 2016, Outside)
Ans. There are seven types of coordinative abilities in sports :
- Orientation Ability : This ability involves determining and changing the position and movements of the body in a specific field of action and in relation to moving objects.
- Differentiation Ability : This ability refers to achieving a high level of accuracy and fine-tuning of movement phases.
- Coupling Ability : Coupling ability involves coordinating the movements of different body parts with each other and with a specific goal-oriented movement.
- Rhythm Ability : Rhythm ability is the ability to perceive and reproduce the rhythm of movements.
- Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly and effectively to stimuli.
- Adaptation Ability : Adaptation ability is the ability to adjust or change movement programs based on anticipated changes in the environment.
- Balance Ability : Balance ability is the ability to maintain equilibrium and regain balance quickly during movements.
Short Answer Type-II Questions (4 Marks)
Write about coordinative abilities in detail. (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Coordinative abilities :
- Coordinative abilities are a set of skills that enable individuals to perform various movements and actions accurately and efficiently.
- These abilities are primarily dependent on the central nervous system’s motor control and regulation processes.
- Coordinative abilities involve the integration of sensory information, motor skills, and cognitive processes to execute movements with precision and effectiveness.
- Overall, coordinative abilities play a vital role in sports performance.
- Athletes who possess strong coordinative abilities can execute movements with precision, efficiency, and effectiveness, giving them a competitive edge in their respective sports.
- Developing and improving these abilities through targeted training and practice can significantly enhance an athlete’s performance.
What are coordinative abilities, and explain different types of coordinative ability ? (CBSE TBQ)
Ans. Coordinative abilities are the abilities of an individual to perform various movements and actions accurately and efficiently. These abilities are dependent on the motor control and regulation processes of the central nervous system.
There are seven types of coordinative abilities in sports :
- Orientation Ability : This ability involves determining and changing the position and movements of the body in a specific field of action and in relation to moving objects.
- Differentiation Ability : This ability refers to achieving a high level of accuracy and fine-tuning of movement phases.
- Coupling Ability : Coupling ability involves coordinating the movements of different body parts with each other and with a specific goal-oriented movement.
- Rhythm Ability : Rhythm ability is the ability to perceive and reproduce the rhythm of movements.
- Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly and effectively to stimuli.
- Adaptation Ability : Adaptation ability is the ability to adjust or change movement programs based on anticipated changes in the environment.
- Balance Ability : Balance ability is the ability to maintain equilibrium and regain balance quickly during movements.
Long Answer Type Questions (5 Marks)
What do you understand by coordinative ability ? Discuss about different types of coordinative abilities. (10.7) (CBSE 2019)
Ans. Coordinative abilities are those abilities which enable an individual to do various related activities accurately and efficiently. Coordinative abilities mainly depend on the central Nervous System.
There are seven types of coordinative abilities in sports :
- Orientation Ability : This ability involves determining and changing the position and movements of the body in a specific field of action and in relation to moving objects. It is crucial for sports that require spatial awareness and quick decision-making, such as volleyball or football.
- Differentiation Ability : This ability refers to achieving a high level of accuracy and fine-tuning of movement phases. It requires precise control over motor actions and is used in sports that involve precise movements, such as gymnastics.
- Coupling Ability : Coupling ability involves coordinating the movements of different body parts with each other and with a specific goal-oriented movement. It is essential in sports that require complex movements, such as gymnastics or football.
- Rhythm Ability : Rhythm ability is the ability to perceive and reproduce the rhythm of movements. It is used in sports that involve synchronized movements with external rhythms, such as gymnastics or figure skating.
- Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly and effectively to stimuli. It involves responding to visual, auditory, or tactile signals in different sports.
- Adaptation Ability : Adaptation ability is the ability to adjust or change movement programs based on anticipated changes in the environment. It is crucial for sports that require quick decision-making and adaptability, such as basketball or tennis.
- Balance Ability : Balance ability is the ability to maintain equilibrium and regain balance quickly during movements. Balance ability can be further classified into maintaining balance during stationary positions or slow movements, and maintaining or regaining balance during rapidly changing positions.
Case Study Questions (4 Marks)
1. Coordinative Abilities : Coordinative abilities primarily depend on the central nervous system’s motor control and regulation process. For a coordinative ability, the control regulation processes must function in a particular manner. The coordinative abilities are those abilities of an individual that enable the individual to do various activities correctly and efficiently.
Zimmerman et al. stated that “Coordinative abilities are understood as relatively stabilized and generalized patterns of motor control and regulation processes. These enable the sportsman to do a group of movements with better quality and effect.”
What ______
Ans. –
2. Types of Coordinative Ability : In sports, the following seven types of coordinative abilities are essential.
- Orientation Ability : It is the ability to determine and change the position and movements of the body in the required time and available space in a definite field of action and a moving object.
- Differentiation Ability : It is the ability to attain a high fine-tuning of movement phases. It is the ability to achieve a high level of accuracy.
- Coupling Ability : It is the ability to coordinate body part movements with one another and about a definite goal-oriented body movement. Coupling ability is essential in sports where activities with a high degree of difficulty have to be done, such as gymnastics and team games.
- Rhythm Ability : Rhythm ability is the ability to perceive the rhythm of a movement and do the exercise with the required rhythm. It also denotes the ability to reproduce rhythm stored in motor memory, in motor action.
- Reaction Ability : Reaction ability is the ability to react quickly and effectively to a stimulus. Different games and sports have different types of signals like visual, auditory, and tactile, to name a few.
- Adaptation Ability : Adaptation Ability is the ability to adjust or completely change the movement programme based on changes and anticipated changes. The situational change may be expected or may take place suddenly.
- Balance Ability : Balance Ability is the ability to maintain equilibrium or balance throughout the movement and regain balance quickly after disturbing balance movements.
What ______
Ans. –
3. Training in sports (CBSE TBQ)
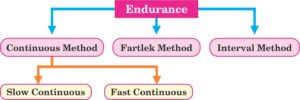
(a) The heart rate in continuous method of training should be about _________ beats per minute and duration for the activity should be __________.
Ans. –
(b) Interval Training Method is based on the principle of __________.
Ans. –
(c) Fartlek is a __________ term meaning speed play.
Ans. –
(d) Fartlek was developed by __________ in 1930.
Ans. –
4. (CBSE TBQ)
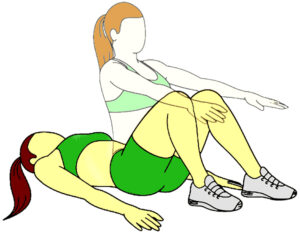
(a) Sit-ups are examples of which kind of strength ?
Ans. –
(b) Method was developed by J.J. Perrine in 1960.
Ans. –
(c) has no movement or change in size of muscles.
Ans. –